Documentation/4.3/Developers/Python scripting
|
For the latest Slicer documentation, visit the read-the-docs. |
Contents
- 1 Background
- 2 Start Here for Scripted Module and Extension Development
- 3 Usage options
- 4 Resources
- 5 Issues
- 6 Developer FAQ: Python Scripting
- 6.1 How to systematically execute custom python code at startup ?
- 6.2 How to save an image/volume using python ?
- 6.3 How to assign a volume to a Slice view ?
- 6.4 How to access vtkRenderer in Slicer 3D view ?
- 6.5 Should I used 'old style' or 'new style' python classes in my scripted module
- 6.6 How to harden a transform ?
- 6.7 Where can I find example scripts?
Background
This is an evolution of the python implementation in slicer3. Slicer's APIs are now natively wrapped in python.
Topics like plotting are still experimental in slicer4.
See this 2012 presentation on the state of python in slicer4.
See the python slicer4 tutorial for more examples.
Slicer Self Tests can be written in python, and provide a good source of examples for manipulating the data, logic, and gui of slicer.
Start Here for Scripted Module and Extension Development
An extensive tutorial and reference page was created for the Slicer/Python breakout session at the NA-MIC 2014 Summer Project Week.
Usage options
Python Interactor
Use the Window->Python Interactor (Control-3 on window/linux, Command-3 on mac) to bring up the Qt-based console with access to the vtk, Qt, and Slicer wrapped APIs.
Most python code can be installed and run from this window, but because it exists in the event driven Qt GUI environment, some operations like, like parallel processing or headless operation, are not easily supported.
Examples
Start slicer4 and bring up python console. Load a volume like this:
>>> slicer.util.loadVolume(slicer.app.slicerHome + "/share/MRML/Testing/TestData/fixed.nrrd")
Get the volume node for that volume:
>>> n = getNode('fixed')
You can use Tab to see lists of methods for a class instance.
Accessing Volume data as numpy array
You can easily inspect and manipulate volume data using numpy and related code. In slicer you can do this:
>>> a = array('fixed')
and a will be a pointer to the appropriate data (no data copying). Scalar volumes become three-dimensional arrays, while vector volumes become 4D, and tensor volumes are 5D. All arrays can be manipulated directly.
Running a CLI from Python
Here's an example to create a model from a volume using the Grayscale Model Maker
def grayModel(volumeNode):
parameters = {}
parameters["InputVolume"] = volumeNode.GetID()
outModel = slicer.vtkMRMLModelNode()
slicer.mrmlScene.AddNode( outModel )
parameters["OutputGeometry"] = outModel.GetID()
grayMaker = slicer.modules.grayscalemodelmaker
return (slicer.cli.run(grayMaker, None, parameters))
To try this, download the MRHead dataset from the Sample Data and paste the code into the python console and then run this:
v = getNode('MRHead')
cliNode = grayModel(v)
Note that the CLI module runs in a background thread, so the call to grayModel will return right away. But the slicer.cli.run call returns a cliNode (an instance of vtkMRMLCommandLineModuleNode) which can be used to monitor the progress of the module.
Passing Fiducials to CLIs via a Python Script
import SampleData
sampleDataLogic = SampleData.SampleDataLogic()
head = sampleDataLogic.downloadMRHead()
volumesLogic = slicer.modules.volumes.logic()
headLabel = volumesLogic.CreateLabelVolume(slicer.mrmlScene, head, 'head-label')
fiducialNode = slicer.vtkMRMLAnnotationFiducialNode()
fiducialNode.SetFiducialWorldCoordinates((1,0,5))
fiducialNode.SetName('Seed Point')
fiducialNode.Initialize(slicer.mrmlScene)
fiducialsList = getNode('Fiducials List')
params = {'inputVolume': head.GetID(), 'outputVolume': headLabel.GetID(), 'seed' : fiducialsList.GetID(), 'iterations' : 2}
cliNode = slicer.cli.run(slicer.modules.simpleregiongrowingsegmentation, None, params , wait_for_completion=True)
Checking Status
In this example we create a simple callback that will be called whenever the cliNode is modified. The status will tell you if the nodes is Pending, Running, or Completed.
def printStatus(caller, event):
print("Got a %s from a %s" % (event, caller.GetClassName()))
if caller.IsA('vtkMRMLCommandLineModuleNode'):
print("Status is %s" % caller.GetStatusString())
cliNode.AddObserver('ModifiedEvent', printStatus)
Accessing slice vtkRenderWindows from slice views
The example below shows how to get the rendered slice window.
lm = slicer.app.layoutManager()
redWidget = lm.sliceWidget('Red')
redView = redWidget.sliceView()
wti = vtk.vtkWindowToImageFilter()
wti.SetInput(redView.renderWindow())
wti.Update()
v = vtk.vtkImageViewer()
v.SetColorWindow(255)
v.SetColorLevel(128)
v.SetInputConnection(wti.GetOutputPort())
v.Render()
TODO: some more samples of the Qt console
In iPython
Important: The example below was developed for an early beta version of slicer4 and is not supported in Slicer 4.0 or 4.1
See this thread for information on adapting this approach to Slicer 4.1.
iPython is a powerful shell and can also be used to access the vtk and slicer APIs (but not Qt at the moment).
As of Slicer4 beta in February 2011, it is possible to use these steps for installation. This has only been tested on a ubuntu linux system so far.
These instructions assume you have a Slicer4-superbuild directory created according to the Slicer4 Build Instructions.
See the [1] website for more example plot types.
Prerequisites
- Get readline - it will make iPython more useful.
# do this before building slicer4 - or do "cd Slicer4-superbuild/; rm -rf python* ; make" sudo apt-get install libreadline6-dev
cd to your Slicer4-superbuild directory for the rest of these steps
- Install the vtk package in the python tree
# TODO: this should be done in superbuild script (cd ./VTK-build/Wrapping/Python; ../../../Slicer-build/Slicer4 --launch ../../../python-build/bin/python setup.py install)
- Install ipython:
git clone git://github.com/ipython/ipython.git (cd ./ipython; git checkout 0.10.2) (cd ./ipython; ../Slicer-build/Slicer4 --launch ../python-build/bin/python setup.py install)
- Install matplotlib (remove the source after installing so python import will not get confused by it.)
git clone git://github.com/pieper/matplotlib.git (cd ./matplotlib; ../Slicer-build/Slicer4 --launch ../python-build/bin/python setup.py install) rm -rf matplotlib
Now try it!
Launch an xterm with all the paths set correctly to find the slicer python packages
./Slicer-build/Slicer4 --launch xterm &
Now, inside the xterm launch ipython
./python-build/bin/ipython
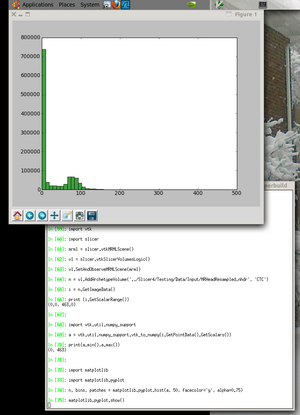
Inside ipython you can past the following script that does:
- create a mrml scene and add a volume
- make a numpy aray from the image data
- do calculations in numpy and vtk for comparision
- make a histogram plot of the data
import vtk
import slicer
mrml = slicer.vtkMRMLScene()
vl = slicer.vtkSlicerVolumesLogic()
vl.SetAndObserveMRMLScene(mrml)
n = vl.AddArchetypeVolume('../Slicer4/Testing/Data/Input/MRHeadResampled.nhdr', 'CTC')
i = n.GetImageData()
print (i.GetScalarRange())
import vtk.util.numpy_support
a = vtk.util.numpy_support.vtk_to_numpy(i.GetPointData().GetScalars())
print(a.min(),a.max())
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot
n, bins, patches = matplotlib.pyplot.hist(a, 50, facecolor='g', alpha=0.75)
matplotlib.pyplot.show()
If all goes well, you should see an image like the one shown here.
Parallel Processing
In the shell, run this to install joblib
wget http://pypi.python.org/packages/source/j/joblib/joblib-0.4.6.dev.tar.gz tar xvfz joblib-0.4.6.dev.tar.gz (cd ./joblib-0.4.6.dev; ../Slicer-build/Slicer4 --launch ../python-build/bin/python setup.py install)
Then in ipython you can run this example:
from joblib import * from math import * for jobs in xrange(1,8): print (jobs, Parallel(n_jobs=jobs)(delayed(sqrt)(i**2) for i in range(10000))[-1])
Packaging/Saving Scenes
A basic example. The following packages all of the scene's referenced files into one specified folder. All images, csvs, volumes, etc. (everything except the scene .mrml) are copied into the folder "<package dir>/data." The scene .mrml is in the "<package dir>" directory.
import os # Library for OS specific routines tempDir = os.path.join(slicer.app.slicerHome, ‘testScene’) # Put our temp scene directory into the slicer directory. os.path.join takes care of slash issues that you may encounter with UNIX-Windows compatibility. os.mkdir(tempDir)
l = slicer.app.applicationLogic() l.SaveSceneToSlicerDataBundleDirectory(tempDir, None)
Loading DICOM Sets
The approach is to point Slicer's DICOM database to the directory of the new files. The command appends the existing database with the files found in the inputted directory.
i = ctk.ctkDICOMIndexer() i.addDirectory(slicer.dicomDatabase, '/yourDICOMdir/')
One approach to begin the load process is to call on the DICOM module, which will automatically open the "DICOM Details" popup. However, if the popup has been used already in the current Slicer session, a refresh may not occur and a restart may be required.
m = slicer.util.mainWindow()
m.moduleSelector().selectModule('DICOM')
Resources
Installing Pip
In a nutshell, both distribute and pip will have to be installed.
1. Download distribute: http://python-distribute.org/distribute_setup.py
2. Install distribute:
$ Slicer distribute_setup.py
Number of registered modules: 1 Number of instantiated modules: 1 Number of loaded modules: 1 Loading Slicer RC file [/home/jchris/.slicerrc.py] Slicer RC file loaded [09/01/2013 20:23:41] Downloading http://pypi.python.org/packages/source/d/distribute/distribute-0.6.34.tar.gz Extracting in /tmp/tmpW05FBr Now working in /tmp/tmpW05FBr/distribute-0.6.34 Installing Distribute File "/tmp/tmpW05FBr/distribute-0.6.34/qSlicerBaseQTCore_fr.qm" doesn't exist. Number of registered modules: 1 Number of instantiated modules: 1 Number of loaded modules: 1 Loading Slicer RC file [/home/jchris/.slicerrc.py] Slicer RC file loaded [09/01/2013 20:24:29] Before install bootstrap. Scanning installed packages No setuptools distribution found running install running bdist_egg running egg_info writing distribute.egg-info/PKG-INFO writing top-level names to distribute.egg-info/top_level.txt [...] Installed /home/jchris/Projects/Slicer-AHM-Superbuild-Debug/python-build/lib/python2.6/site-packages/distribute-0.6.34-py2.6.egg Processing dependencies for distribute==0.6.34 Finished processing dependencies for distribute==0.6.34 After install bootstrap. Creating /home/jchris/Projects/Slicer-AHM-Superbuild-Debug/python-build/lib/python2.6/site-packages/setuptools-0.6c11-py2.6.egg-info Creating /home/jchris/Projects/Slicer-AHM-Superbuild-Debug/python-build/lib/python2.6/site-packages/setuptools.pth
3. Download pip: https://raw.github.com/pypa/pip/master/contrib/get-pip.py
4. Install pip:
$ Slicer get-pip.py
Number of registered modules: 1
Number of instantiated modules: 1
Number of loaded modules: 1
Loading Slicer RC file [/home/jchris/.slicerrc.py]
Slicer RC file loaded [09/01/2013 20:41:29]
Downloading/unpacking pip
Running setup.py egg_info for package pip
Number of registered modules: 1
Number of instantiated modules: 1
Number of loaded modules: 1
Loading Slicer RC file [/home/jchris/.slicerrc.py]
Slicer RC file loaded [09/01/2013 20:41:38]
warning: manifest_maker: standard file '' not found
warning: no files found matching '*.html' under directory 'docs'
warning: no previously-included files matching '*.txt' found under directory 'docs/_build'
no previously-included directories found matching 'docs/_build/_sources'
Installing collected packages: pip
Running setup.py install for pip
Number of registered modules: 1
Number of instantiated modules: 1
Number of loaded modules: 1
Loading Slicer RC file [/home/jchris/.slicerrc.py]
Slicer RC file loaded [09/01/2013 20:41:41]
warning: manifest_maker: standard file '' not found
warning: no files found matching '*.html' under directory 'docs'
warning: no previously-included files matching '*.txt' found under directory 'docs/_build'
no previously-included directories found matching 'docs/_build/_sources'
Installing pip script to /home/jchris/Projects/Slicer-AHM-Superbuild-Debug/python-build/bin
Installing pip-2.6 script to /home/jchris/Projects/Slicer-AHM-Superbuild-Debug/python-build/bin
Successfully installed pip
Cleaning up...
For additional information regarding installation of pip. See http://www.pip-installer.org/en/latest/installing.html
Using Pip
1. Within the Slicer python interactor:
./Slicer --no-main-window --disable-cli-modules --disable-loadable-modules --disable-scripted-loadable-modules --show-python-interactor
2. Define the function install_distributions
def install_distributions(distributions): """ Copied from http://threebean.org/blog/2011/06/06/installing-from-pip-inside-python-or-a-simple-pip-api/ """ import pip.commands.install command = pip.commands.install.InstallCommand() opts, args = command.parser.parse_args() # TBD, why do we have to run the next part here twice before actual install requirement_set = command.run(opts, distributions) requirement_set = command.run(opts, distributions) requirement_set.install(opts)
3. Try to install a package
install_distributions(["Markdown"])
Issues
- matplotlib currently uses Tk to show the window on Linux and it does not handle pan/zoom events correctly. Ideally there would be a PythonQt wrapper for the plots and this is probably required for use on windows (and maybe mac).
- the matplotlib window is in the same thread with the ipython window so you cannot keep the plot open while working on the next one. However you can save the plot to a file (png, pdf, etc...) and look at it with another program while working in ipython.
- in slicer4 the PythonQt package is loaded as 'qt', however matplotlib tries running 'import qt' as a way to determine if it is running in PyQt version 3. Because of this a patched version of matplotlib is required (see this diff)
- Tested in Windows 7: Python 2.6.6 (used in Slicer 4.1) has errors in referencing its XML DOM parsers, such as ElementTree. This is a Windows-specific issue -- the same code works in Linux Ubuntu. Solution thus far is to write your own XML parser.
Developer FAQ: Python Scripting
How to systematically execute custom python code at startup ?
Each time Slicer starts, it will look up for a file named .slicerrc.py into your HOME folder.
How to save an image/volume using python ?
The module slicer.util provides methods allowing to save either a node or an entire scene:
- saveNode
- saveScene
For more details see:
- https://github.com/Slicer/Slicer/blob/master/Base/Python/slicer/util.py#L229-267
- https://github.com/Slicer/Slicer/blob/master/Base/Python/slicer/tests/test_slicer_util_save.py
How to assign a volume to a Slice view ?
Assuming the MRHead sample data has been loaded, you could do the following:
red_logic = slicer.app.layoutManager().sliceWidget("Red").sliceLogic()
red_cn = red_logic.GetSliceCompositeNode()
red_logic.GetSliceCompositeNode().SetBackgroundVolumeID(slicer.util.getNode('MRHead').GetID())
Discussion: http://slicer-devel.65872.n3.nabble.com/Assign-volumes-to-views-tt4028694.html
How to access vtkRenderer in Slicer 3D view ?
renderer = slicer.app.layoutManager().threeDWidget(0).threeDView().renderWindow().GetRenderers().GetFirstRenderer()
Should I used 'old style' or 'new style' python classes in my scripted module
When python classes have no superclass specified they are 'old style' as described here [2].
In general it doesn't matter for the classes in a scripted module, since they won't be subclassed either old or new style should be the same.
For other python code in slicer where you might be subclassing, it's better to use new style classes. See the class hierarchies in the EditorLib and the DICOMLib for examples.
How to harden a transform ?
>>> n = getNode('Bone')
>>> logic = slicer.vtkSlicerTransformLogic()
>>> logic.hardenTransform(n)
Discussion: http://slicer-devel.65872.n3.nabble.com/Scripting-hardened-transforms-tt4029456.html
Where can I find example scripts?
Have a look at Documentation/4.3/ScriptRepository.