Return to Slicer 3.6 Documentation
Gallery of New Features
Module Name
BRAINSFit
General Information
Module Type & Category
Type: CLI
Category: Registration
Authors, Collaborators & Contact
Author: Hans J. Johnson, hans-johnson -at- uiowa.edu, http://wwww.psychiatry.uiowa.edu
Contributors: Hans Johnson(1,3,4); Kent Williams(1); Gregory Harris(1), Vincent Magnotta(1,2,3); Andriy Fedorov(5), fedorov -at- bwh.harvard.edu (Slicer integration); (1=University of Iowa Department of Psychiatry, 2=University of Iowa Department of Radiology, 3=University of Iowa Department of Biomedical Engineering, 4=University of Iowa Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, 5=Surgical Planning Lab, Harvard)
Module Description
Insight/Examples/Registration/ImageRegistration8.cxx
This program is the most functional example of multi-modal 3D rigid image registration provided with ITK. ImageRegistration8 is in the Examples directory, and also sec. 8.5.3 in the ITK manual. We have modified and extended this example in several ways:
- defined a new ITK Transform class, based on itkScaleSkewVersor3DTransform which has 3 dimensions of scale but no skew aspect.
- implemented a set of functions to convert between Versor Transforms and the general itk::AffineTransform and deferred converting from specific to more general representations to preserve transform information specificity as long as possible. Our Rigid transform is the narrowest, a Versor rotation plus separate translation.
- Added a template class itkMultiModal3DMutualRegistrationHelper which is templated over the type of ITK transform generated, and the optimizer used.
- Added image masks as an optional input to the Registration algorithm, limiting the volume considered during registration to voxels within the brain.
- Added image mask generation as an optional input to the Registration algorithm when meaningful masks such as for whole brain are not available, allowing the fit to at least be focused on whole head tissue.
- Added the ability to use one transform result, such as the Rigid transform, to initialize a more adaptive transform
- Defined the command line parameters using tools from the Slicer [ 3] program, in order to conform to the Slicer3 Execution model.
Added the ability to write output images in any ITK-supported scalar image format.
Usage
The BRAINSFit distribution contains a directory named TestData, which contains two example images. The first, test.nii.gz is a NIfTI format image volume, which is used the input for the CTest-managed regression test program. The program makexfrmedImage.cxx, included in the BRAINSFit distribution was used to generate test2.nii.gz, by scaling, rotating and translating test.nii.gz. You can see representative Sagittal slices of test.nii.gz (in this case, the fixed image, test2.nii.gz (the moving image), and the two images ’checkerboarded’ together to the right. To register test2.nii.gz to test.nii.gz, you can use the following command:
BRAINSFit --fixedVolume test.nii.gz \
--movingVolume test2.nii.gz \
--outputVolume registered.nii.gz \
--transformType Affine
A representative slice of the registered results image registered.nii.gz is to the right. You can see from the Checkerboard of the Fixed and Registered images that the fit is quite good with Affine transform-based registration. The blurring of the registered images is a consequence of the initial scaling used in generating the moving image from the fixed image, compounded by the interpolation necessitated by the transform operation.
You can see the differences in results if you re-run BRAINSFit using Rigid, ScaleVersor3D, or ScaleSkewVersor3D as the ----transformType parameter. In this case, the authors judged Affine the best method for registering these particular two images; in the BRAINS2 automated processing pipeline, Rigid usually works well for registering research scans.
Quick Tour of Features and Use
A list panels in the interface, their features, what they mean, and how to use them. For instance:
- Input Parameters
- Fixed Image Volume [--fixedVolume]: The fixed image for registration by mutual information optimization.
- Moving Image Volume [--movingVolume]: The moving image for registration by mutual information optimization.
- Class of Registration [--registrationClass]: Specifies one of the five supported transform types. The valid types are, (R)Rigid, (R+S)ScaleVersor3D, (R+S+S)ScaleSkewVersor3D, (A)Affine, (BS)BSpline, (O)ther. Note that registration proceeds from the lowest parameter dimension upto the parameter type choosen. Selecting BS for registrationClass has the same effect as setting transformType to "Rigid,ScaleVersor3D,ScaleSkewVersor3D,Affine,BSpline". Set to (O)ther when using the more flexible Transform Type flag under Registration Parameters settings.
- Output Settings (At least one output must be specified.)
- Slicer BSpline Transform [--bsplineTransform]: (optional) Filename to which save the estimated transform. NOTE: You must set at least one output object (either a deformed image or a transform. NOTE: USE THIS ONLY IF THE FINAL TRANSFORM IS BSpline
- Slicer Linear Transform [--linearTransform]: (optional) Filename to which save the estimated transform. NOTE: You must set at least one output object (either a deformed image or a transform. NOTE: USE THIS ONLY IF THE FINAL TRANSFORM IS ---NOT--- BSpline
- Output Transform [--outputTransform]: (optional) Filename to which save the (optional) estimated transform. NOTE: You must select either the outputTransform or the outputVolume option.
- Output Image Volume [--outputVolume]: (optional) Output image for registration. NOTE: You must select either the outputTransform or the outputVolume option.
- Output Image Pixel Type [--outputVolumePixelType]: The output image Pixel Type is the scalar datatype for representation of the Output Volume.
- Transform Initialization Parameters
- Intitialze Transform Mode [--initializeTransformMode]: Determine how to initialize the transform center. GeometryOn on assumes that the center of the voxel lattice of the images represent similar structures. MomentsOn assumes that the center of mass of the images represent similar structures. CenterOfHead attempts to use the top of head and shape of neck to drive a center of mass estimate. Off assumes that the physical space of the images are close, and that centering in terms of the image Origins is a good starting point. This flag is mutually exclusive with the initialTransform flag.
- Initial Transform [--initialTransform]: Filename of transform used to initialize the registration.
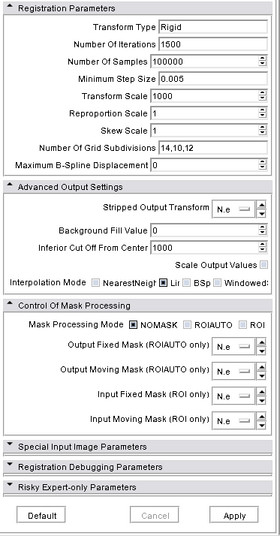
- Registration Parameters
- Transform Type [--transformType]: Specifies a list of registration types to be used. The valid types are, Rigid, ScaleVersor3D, ScaleSkewVersor3D, Affine, and BSpline. Specifiying more than one in a comma separated list will initialize the next stage with the previous results. If registrationClass flag is used, it overrides this parameter setting.
- Number Of Iterations [--numberOfIterations]: The maximum number of iterations to try before failing to converge. Use an explicit limit like 500 or 1000 to manage risk of divergence
- Number Of Samples [--numberOfSamples]: The number of voxels sampled for mutual information computation. Increase this for a slower, more careful fit. You can also limit the sampling focus with ROI masks and ROIAUTO mask generation.
- Minimum Step Size [--minimumStepSize]: Each step in the optimization takes steps at least this big. When none are possible, registration is complete.
- Transform Scale [--translationScale]: How much to scale up changes in position compared to unit rotational changes in radians -- decrease this to put more rotation in the search pattern.
- Reproportion Scale [--reproportionScale]: ScaleVersor3D 'Scale' compensation factor. Increase this to put more rescaling in a ScaleVersor3D or ScaleSkewVersor3D search pattern. 1.0 works well with a translationScale of 1000.0
- Skew Scale [--skewScale]: ScaleSkewVersor3D Skew compensation factor. Increase this to put more skew in a ScaleSkewVersor3D search pattern. 1.0 works well with a translationScale of 1000.0
- Number Of Grid Subdivisions [--splineGridSize]: The number of subdivisions of the BSpline Grid to be centered on the image space. Each dimension must have at least 3 subdivisions for the BSpline to be correctly computed.
- Maximum B-Spline Displacement [--maxBSplineDisplacement]: Sets the maximum allowed displacements in image physical coordinates for BSpline control grid along each axis. A value of 0.0 indicates that the problem should be unbounded. NOTE: This only constrains the BSpline portion, and does not limit the displacement from the associated bulk transform. This can lead to a substantial reduction in computation time in the BSpline optimizer.
- Advanced Output Settings
- Stripped Output Transform [--strippedOutputTransform]: File name for the rigid component of the estimated affine transform. Can be used to rigidly register the moving image to the fixed image. NOTE: This value is overwritten if either bsplineTransform or linearTransform is set.
- Background Fill Value [--backgroundFillValue]: Background fill value for output image.
- Inferior Cut Off From Center [--maskInferiorCutOffFromCenter]: For use with --initializeTransformMode CenterOfHead (and --maskProcessingMode ROIAUTO): the cut-off below the image centers, in millimeters,
- Scale Output Values [--scaleOutputValues]: If true, and the voxel values do not fit within the minimum and maximum values of the desired outputVolumePixelType, then linearly scale the min/max output image voxel values to fit within the min/max range of the outputVolumePixelType.
- Interpolation Mode [--interpolationMode]: Type of interpolation to be used when applying transform to moving volume. Options are Linear, NearestNeighbor, BSpline, or WindowedSinc
- Control of Mask Processing
- Mask Processing Mode [--maskProcessingMode]: What mode to use for using the masks. If ROIAUTO is choosen, then the mask is implicitly defined using a otsu forground and hole filling algorithm. The Region Of Interest mode (choose ROI) uses the masks to define what parts of the image should be used for computing the transform.
- Output Fixed Mask (ROIAUTO only) [--outputFixedVolumeROI]: The ROI automatically found in fixed image.
- Output Moving Mask (ROIAUTO only) [--outputMovingVolumeROI]: The ROI automatically found in moving image.
- Input Fixed Mask (ROI only) [--fixedBinaryVolume]: Fixed Image binary mask volume.
- Input Moving Mask (ROI only) [--movingBinaryVolume]: Moving Image binary mask volume.
- Special Input Image Parameters
- Fixed Image Time Index [--fixedVolumeTimeIndex]: The index in the time series for the 3D fixed image to fit, if 4-dimensional.
- Moving Image Time Index [--movingVolumeTimeIndex]: The index in the time series for the 3D moving image to fit, if 4-dimensional.
- Median Filter Size [--medianFilterSize]: The radius for the optional MedianImageFilter preprocessing in all 3 directions.
- Histogram Match [--histogramMatch][-e]: Histogram Match the input images. This is suitable for images of the same modality that may have different absolute scales, but the same overall intensity profile.
- Number of Histogram Bins [--numberOfHistogramBins]: the number of histogram levels
- Number of Match Points [--numberOfMatchPoints]: the number of match points
- Registration Debugging Parameters
- Caching BSpline Weights Mode [--useCachingOfBSplineWeightsMode]: This is a 5x speed advantage at the expense of requiring much more memory. Only relevant when transformType is BSpline.
- Explicit PDF Derivatives Mode [--useExplicitPDFDerivativesMode]: Using mode AUTO means OFF for BSplineDeformableTransforms and ON for the linear transforms. The ON alternative uses more memory to sometimes do a better job.
- ROIAuto Dilate Size [--ROIAutoDilateSize]: This flag is only relavent when using ROIAUTO mode for initializing masks. It defines the final dilation size to capture a bit of background outside the tissue region. At setting of 10mm has been shown to help regularize a BSpline registration type so that there is some background constraints to match the edges of the head better.
- Relaxation Factor [--relaxationFactor]: Internal debugging parameter, and should probably never be used from the command line. This will be removed in the future.
- Maximum Step Size [--maximumStepSize]: Internal debugging parameter, and should probably never be used from the command line. This will be removed in the future.
- Failure Exit Code [--failureExitCode]: If the fit fails, exit with this status code. (It can be used to force a successfult exit status of (0) if the registration fails due to reaching the maximum number of iterations.
- Write Transform On Failure [--writeTransformOnFailure]: Flag to save the final transform even if the numberOfIterations are reached without convergence. (Intended for use when --failureExitCode 0 )
- debugNumberOfThreads [--debugNumberOfThreads]: Explicitly specify the maximum number of threads to use.
- Debug option [--debugLevel]: Display debug messages, and produce debug intermediate results. 0=OFF, 1=Minimal, 10=Maximum debugging.
- Risky Expert-only Parameters
- Selective Permission for Transform Parameters to Vary [--permitParameterVariation]: A bit vector to permit linear transform parameters to vary under optimization. The vector order corresponds with transform parameters, and beyond the end ones fill in as a default. For instance, you can choose to rotate only in x (pitch) with 1,0,0; this is mostly for expert use in turning on and off individual degrees of freedom in rotation, translation or scaling without multiplying the number of transform representations; this trick is probably meaningless when tried with the general affine transform.
- Fixed Image Origin [--fixedVolumeOrigin]: The coordinates of the origin of the fixed image. This will over-ride the information read from disk and is VERY DANGEROUS.
- Moving Image Origin [--movingVolumeOrigin]: The coordinates of the origin of the moving image. This will over-ride the information read from disk and is VERY DANGEROUS.
|
|
Development
Notes from the Developer(s)
This is a thin wrapper program around the BRAINSFitHelper class in BRAINSCommonLib. The BRAINSFitHelper class
is intended to allow all the functionality of BRAINSFit to be easily incorporated into another program by including a single header file, linking against the BRAINSCommonLib library, and adding code similar to the following to your application:
typedef itk::BRAINSFitHelper HelperType;
HelperType::Pointer myHelper=HelperType::New();
myHelper->SetTransformType(localTransformType);
myHelper->SetFixedVolume(extractFixedVolume);
myHelper->SetMovingVolume(extractMovingVolume);
myHelper->StartRegistration();
currentGenericTransform=myHelper->GetCurrentGenericTransform();
MovingVolumeType::ConstPointer preprocessedMovingVolume = myHelper->GetPreprocessedMovingVolume();
/* Optional member functions that can also be set
myHelper->SetHistogramMatch(histogramMatch);
myHelper->SetNumberOfMatchPoints(numberOfMatchPoints);
myHelper->SetFixedBinaryVolume(fixedMask);
myHelper->SetMovingBinaryVolume(movingMask);
myHelper->SetPermitParameterVariation(permitParameterVariation);
myHelper->SetNumberOfSamples(numberOfSamples);
myHelper->SetNumberOfHistogramBins(numberOfHistogramBins);
myHelper->SetNumberOfIterations(numberOfIterations);
myHelper->SetMaximumStepLength(maximumStepSize);
myHelper->SetMinimumStepLength(minimumStepSize);
myHelper->SetRelaxationFactor(relaxationFactor);
myHelper->SetTranslationScale(translationScale);
myHelper->SetReproportionScale(reproportionScale);
myHelper->SetSkewScale(skewScale);
myHelper->SetUseExplicitPDFDerivativesMode(useExplicitPDFDerivativesMode);
myHelper->SetUseCachingOfBSplineWeightsMode(useCachingOfBSplineWeightsMode);
myHelper->SetBackgroundFillValue(backgroundFillValue);
myHelper->SetInitializeTransformMode(localInitializeTransformMode);
myHelper->SetMaskInferiorCutOffFromCenter(maskInferiorCutOffFromCenter);
myHelper->SetCurrentGenericTransform(currentGenericTransform);
myHelper->SetSplineGridSize(splineGridSize);
myHelper->SetCostFunctionConvergenceFactor(costFunctionConvergenceFactor);
myHelper->SetProjectedGradientTolerance(projectedGradientTolerance);
myHelper->SetMaxBSplineDisplacement(maxBSplineDisplacement);
myHelper->SetDisplayDeformedImage(UseDebugImageViewer);
myHelper->SetPromptUserAfterDisplay(PromptAfterImageSend);
myHelper->SetDebugLevel(debugLevel);
if(debugLevel > 7 )
{
myHelper->PrintCommandLine(true,"BF");
}
*/
Dependencies
BRAINSFit depends on Slicer3 (for the SlicerExecutionModel support) and ITK.
BRAINSFit depends on the BRAINSCommonLib library
Tests
Nightly testing of the development head can be found at: http://testing.psychiatry.uiowa.edu/CDash
Known bugs
Links to known bugs and feature requests are listed at:
Usability issues
Follow this link to the Slicer3 bug tracker. Please select the usability issue category when browsing or contributing.
Source code & documentation
Links to the module's source code:
Source code:
More Information
Acknowledgment
Include funding and other support here.
References
Publications related to this module go here. Links to pdfs would be useful.