Difference between revisions of "Modules:SubtractImages-Documentation-3.6"
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
Load the input volumes. The default setting of the interpolation order should work fine. Its best to use the input volumes of the same size as the module does pixel-wise additions. | Load the input volumes. The default setting of the interpolation order should work fine. Its best to use the input volumes of the same size as the module does pixel-wise additions. | ||
===Examples, Use Cases & Tutorials=== | ===Examples, Use Cases & Tutorials=== | ||
| − | This module can be used for | + | This module can be used for the following: |
| + | * Producing intermediate results that can then be plugged as inputs to other filters and modules. | ||
| + | * Compare the results produced by two different algorithms. The example depicted on this page shows the subtraction performed on two different segmentation masks. The segmentation masks were produced by two different algorithms. | ||
| + | * Additionally, this module can also be used to directly visualize the results of segmentation compared with a ground truth mask. | ||
===Quick Tour of Features and Use=== | ===Quick Tour of Features and Use=== | ||
Revision as of 17:26, 15 April 2010
Home < Modules:SubtractImages-Documentation-3.6Return to Slicer 3.6 Documentation
Module Name
Filtering:Subtract
General Information
Module Type & Category
Type: CLI
Category: Base or (Filtering, Registration, etc.)
Authors, Collaborators & Contact
- Author: Bill Lorensen
- Contact: bill.lorensen at gmail.com
Module Description
The module performs pixel-wise subtraction. The module provides support for rescaling the images such that their sizes match, but does not register the images with respect to one another. Hence, for accurate results, its best to make sure that the input images have the same size. The module supports operations on inputs of any type. However, it produces only signed output types.
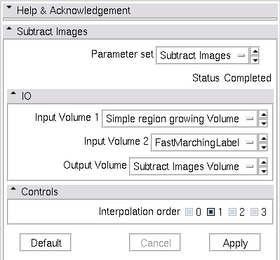
Usage
Load the input volumes. The default setting of the interpolation order should work fine. Its best to use the input volumes of the same size as the module does pixel-wise additions.
Examples, Use Cases & Tutorials
This module can be used for the following:
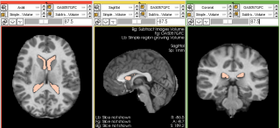
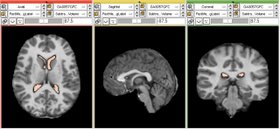
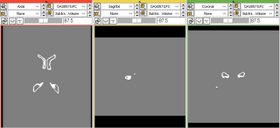
- Producing intermediate results that can then be plugged as inputs to other filters and modules.
- Compare the results produced by two different algorithms. The example depicted on this page shows the subtraction performed on two different segmentation masks. The segmentation masks were produced by two different algorithms.
- Additionally, this module can also be used to directly visualize the results of segmentation compared with a ground truth mask.
Quick Tour of Features and Use
- "Inputs/Outputs:" This module requires two input volumes, and the specification of an output volume. The module produces the output volume of the same size as the first input volume.
- "Parameters:" The module uses one parameter Interpolation Order. The interpolation order sets the degree of B-spline interpolation to be performed on the second input image for resampling it to the same size as the first input image. The default setting is 1. In general, if the input and output images are of the same size, this parameter can be left at the default setting.
Development
Dependencies
Other modules or packages that are required for this module's use.
Known bugs
Follow this link to the Slicer3 bug tracker.
Usability issues
Follow this link to the Slicer3 bug tracker. Please select the usability issue category when browsing or contributing.
Source code & documentation
Source Code: [1]
Documentation:
More Information
Acknowledgment
This work is part of the National Alliance for Medical Image Computing (NAMIC), funded by the National Institutes of Health through the NIH Roadmap for Medical Research, Grant U54 EB005149. Information on the National Centers for Biomedical Computing can be obtained from National Centers for Biomedical Computing.