Difference between revisions of "Documentation/Nightly/Modules/SurfaceToolbox"
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
|[[Image:SurfaceToolbox.png|thumb|380px|SurfaceToolbox User Interface]] | |[[Image:SurfaceToolbox.png|thumb|380px|SurfaceToolbox User Interface]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The module is appropriate when a surface has been extracted (e.g. with the Modelmaker module) but its appearance has to be improved. | ||
This module supports various cleanup and optimization processes on surface models. For example, a noisy image data set can lead to models that have bumpy surfaces which do not accurately depict the actual anatomy of interest. In this case, the model can be smoothed to better approximate the actual surface. Another application is to reduce the geometric complexity of surface models to reduce the file size or rendering time of the models. | This module supports various cleanup and optimization processes on surface models. For example, a noisy image data set can lead to models that have bumpy surfaces which do not accurately depict the actual anatomy of interest. In this case, the model can be smoothed to better approximate the actual surface. Another application is to reduce the geometric complexity of surface models to reduce the file size or rendering time of the models. | ||
| Line 35: | Line 38: | ||
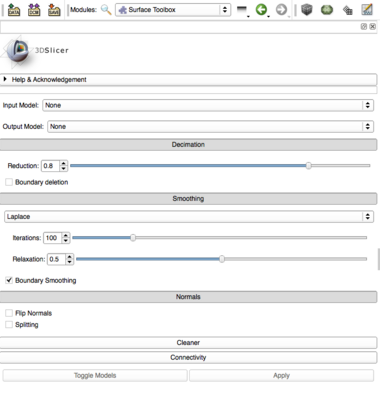
Select the input and output models, and then enable the stages of the pipeline by selecting the buttons. Stages that include parameters will open up when they are enabled. Click apply to activate the pipeline and then click the Toggle button to compare the model before and after the operation. | Select the input and output models, and then enable the stages of the pipeline by selecting the buttons. Stages that include parameters will open up when they are enabled. Click apply to activate the pipeline and then click the Toggle button to compare the model before and after the operation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | * '''Surface Decimation:''' | ||
| + | ** ''Enabled'': enable topology-preserving surface decimation. | ||
| + | ** ''Target reduction'': target percentage reduction in number of triangles (this target reduction may not be achieved depending on the constraints on the topology). | ||
| + | ** ''Boundary vertex deletion'': allow deletion of points located on the boundary of the surface. | ||
| + | * '''Surface Smoothing:''' | ||
| + | ** ''Enabled'': enable surface smoothing. | ||
| + | ** ''Smoothing method'': choose between Laplace or Taubin surface smoothing algorithms (while Taubin is a non-shrinking filter, Laplace will tend to shrink the surface under the effect of curvature). | ||
| + | ** ''Boundary smoothing'': allow smoothing of points located on the boundary of the surface. | ||
| + | ** ''Laplace number of iterations'': number of iterations set when the Laplace algorithm is selected. | ||
| + | ** ''Laplace relaxation factor'': the factor by which a point moves towards the barycenter of its neighbors in the Laplace algorithm. | ||
| + | ** ''Taubin number of iterations'': number of iterations set when the Taubin algorithm is selected. | ||
| + | ** ''Taubin passband'': spatial frequency cutoff for the Taubin algorithm. | ||
| + | * '''Surface Normals:''' | ||
| + | ** ''Enabled'': enable computation of consistently-oriented surface normals (advised after smoothing - smoothing algorithms only move points and do not update normals accordingly, so the surface might still look non-smooth after smoothing when Gouraud shading is used). | ||
| + | ** ''Flip normals'': toggle direction of normals - the algorithm will do its best to orient the normals consistently "outwards" a surface, if the surface is orientable. This switch will make normals point "inwards" | ||
| + | ** ''Splitting'': toggle splitting of surface when angle between the normals of two neighboring triangles is above the Feature angle. This improves the shading appearance of sharp edges but produces topological holes in the surface. | ||
| + | ** ''Feature angle'': angle (in degrees) between two neighboring triangles beyond which the edge between the triangles is split. | ||
| + | * '''Surface Cleaner:''' | ||
| + | ** ''Enabled'': enable cleaning (merging of coincident points, elimination of unused points, treatment of degenerate cells) of the surface. | ||
| + | * '''IO:''' | ||
| + | ** ''Input Surface'': the input surface | ||
| + | ** ''Output Surface'': the output surface, i.e. the input surface filtered through all the "Enabled" filters. | ||
<!-- ---------------------------- --> | <!-- ---------------------------- --> | ||
| Line 44: | Line 71: | ||
{{documentation/{{documentation/version}}/module-developerinfo}} | {{documentation/{{documentation/version}}/module-developerinfo}} | ||
This is a scripted module. | This is a scripted module. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The module internally uses the following VTK filters: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.vtk.org/doc/nightly/html/classvtkDecimatePro.html vtkDecimatePro] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.vtk.org/doc/nightly/html/classvtkSmoothPolyDataFilter.html vtkSmoothPolyDataFilter] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.vtk.org/doc/nightly/html/classvtkWindowedSincPolyDataFilter.html vtkWindowedSincPolyDataFilter] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.vtk.org/doc/nightly/html/classvtkPolyDataNormals.html vtkPolyDataNormals] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.vtk.org/doc/nightly/html/classvtkCleanPolyData.html vtkCleanPolyData] | ||
<!-- ---------------------------- --> | <!-- ---------------------------- --> | ||
{{documentation/{{documentation/version}}/module-footer}} | {{documentation/{{documentation/version}}/module-footer}} | ||
<!-- ---------------------------- --> | <!-- ---------------------------- --> | ||
Revision as of 10:39, 22 August 2013
Home < Documentation < Nightly < Modules < SurfaceToolbox
|
For the latest Slicer documentation, visit the read-the-docs. |
Introduction and Acknowledgements
|
Module Description
Use Cases
The module is appropriate when a surface has been extracted (e.g. with the Modelmaker module) but its appearance has to be improved.
This module supports various cleanup and optimization processes on surface models. For example, a noisy image data set can lead to models that have bumpy surfaces which do not accurately depict the actual anatomy of interest. In this case, the model can be smoothed to better approximate the actual surface. Another application is to reduce the geometric complexity of surface models to reduce the file size or rendering time of the models.
Tutorials
N/A
Panels
Select the input and output models, and then enable the stages of the pipeline by selecting the buttons. Stages that include parameters will open up when they are enabled. Click apply to activate the pipeline and then click the Toggle button to compare the model before and after the operation.
- Surface Decimation:
- Enabled: enable topology-preserving surface decimation.
- Target reduction: target percentage reduction in number of triangles (this target reduction may not be achieved depending on the constraints on the topology).
- Boundary vertex deletion: allow deletion of points located on the boundary of the surface.
- Surface Smoothing:
- Enabled: enable surface smoothing.
- Smoothing method: choose between Laplace or Taubin surface smoothing algorithms (while Taubin is a non-shrinking filter, Laplace will tend to shrink the surface under the effect of curvature).
- Boundary smoothing: allow smoothing of points located on the boundary of the surface.
- Laplace number of iterations: number of iterations set when the Laplace algorithm is selected.
- Laplace relaxation factor: the factor by which a point moves towards the barycenter of its neighbors in the Laplace algorithm.
- Taubin number of iterations: number of iterations set when the Taubin algorithm is selected.
- Taubin passband: spatial frequency cutoff for the Taubin algorithm.
- Surface Normals:
- Enabled: enable computation of consistently-oriented surface normals (advised after smoothing - smoothing algorithms only move points and do not update normals accordingly, so the surface might still look non-smooth after smoothing when Gouraud shading is used).
- Flip normals: toggle direction of normals - the algorithm will do its best to orient the normals consistently "outwards" a surface, if the surface is orientable. This switch will make normals point "inwards"
- Splitting: toggle splitting of surface when angle between the normals of two neighboring triangles is above the Feature angle. This improves the shading appearance of sharp edges but produces topological holes in the surface.
- Feature angle: angle (in degrees) between two neighboring triangles beyond which the edge between the triangles is split.
- Surface Cleaner:
- Enabled: enable cleaning (merging of coincident points, elimination of unused points, treatment of degenerate cells) of the surface.
- IO:
- Input Surface: the input surface
- Output Surface: the output surface, i.e. the input surface filtered through all the "Enabled" filters.
References
N/A
Information for Developers
| Section under construction. |
This is a scripted module.
The module internally uses the following VTK filters: