Difference between revisions of "Documentation/Nightly/Extensions/MABMIS"
XiaofengLiu (talk | contribs) |
XiaofengLiu (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
<!-- ---------------------------- --> | <!-- ---------------------------- --> | ||
{| | {| | ||
| − | |[[Image:MABMIS_algorithm.png|thumb| | + | |[[Image:MABMIS_algorithm.png|thumb|340px|Example: MABMIS segmentation results]] |
|} | |} | ||
The figure above shows an overview of the algorithm. MABMIS contains two modules: the training module, and the testing module. | The figure above shows an overview of the algorithm. MABMIS contains two modules: the training module, and the testing module. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| + | |||
In the training module, multiple atlas image pairs are required as the input. Each atlas image pair contains one pre-processed T1-weighted intensity image and one label image on which each interested structure on the T1 image is manually identified and assigned a unique label. The label image is generally generated by an expert. In the training module, the multiple atlas pairs are processed to construct an atlas tree, where each atlas is one node of the tree. The tree is constructed based on the similarity among the atlases and tree-based groupwise registration. | In the training module, multiple atlas image pairs are required as the input. Each atlas image pair contains one pre-processed T1-weighted intensity image and one label image on which each interested structure on the T1 image is manually identified and assigned a unique label. The label image is generally generated by an expert. In the training module, the multiple atlas pairs are processed to construct an atlas tree, where each atlas is one node of the tree. The tree is constructed based on the similarity among the atlases and tree-based groupwise registration. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
In the testing module, a group of target images are segmented based on the atlas tree. First, a novel tree-based groupwise registration method is employed to simultaneously register them to the atlas tree, the target images are segmented simultaneously using an iterative groupwise segmentation strategy, which provides improved accuracy and across-image consistency. | In the testing module, a group of target images are segmented based on the atlas tree. First, a novel tree-based groupwise registration method is employed to simultaneously register them to the atlas tree, the target images are segmented simultaneously using an iterative groupwise segmentation strategy, which provides improved accuracy and across-image consistency. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
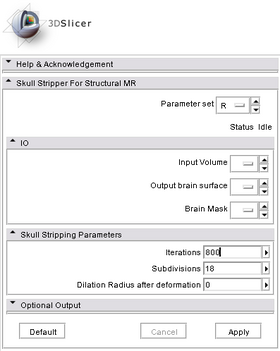
Before applying the modules, both atlas images and target images need to be pre-processed. The processing steps include bias correction ( e.g., N4), skull stripping (e.g., skullstripper in slicer), histogram matching. All images are then registered to a common space using affine registration. The pre-processing tools are not included in the module. | Before applying the modules, both atlas images and target images need to be pre-processed. The processing steps include bias correction ( e.g., N4), skull stripping (e.g., skullstripper in slicer), histogram matching. All images are then registered to a common space using affine registration. The pre-processing tools are not included in the module. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
Detailed description of the algorithm can be found in [1]. | Detailed description of the algorithm can be found in [1]. | ||
{{documentation/{{documentation/version}}/module-section|Use Cases}} | {{documentation/{{documentation/version}}/module-section|Use Cases}} | ||
{| | {| | ||
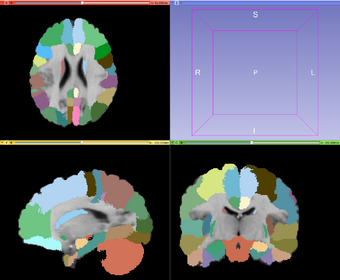
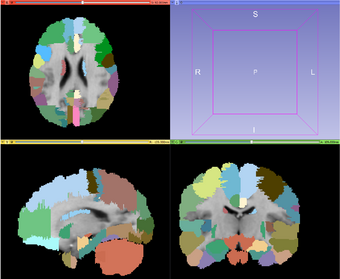
| − | |[[Image:MABMIS_results.png|thumb| | + | |[[Image:MABMIS_results.png|thumb|340px|Example: MABMIS segmentation results]] |
| − | |[[Image:MABMIS_groundtruth.png|thumb| | + | |[[Image:MABMIS_groundtruth.png|thumb|340px|Example: The ground truth]] |
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 21:53, 16 January 2014
Home < Documentation < Nightly < Extensions < MABMIS
|
For the latest Slicer documentation, visit the read-the-docs. |
Introduction and Acknowledgements
|
MABMIS is a Slicer extension that implements a multi-atlas based multi-image method for group-wise segmentation [1]. The method utilizes a novel tree-based groupwise registration method for concurrent alignment of both the atlases and the target images, and an iterative groupwise segmentation method for simultaneous consideration of segmentation information propagated from all available images, including the atlases and other newly segmented target images.
Contributor: Xiaofeng Liu, Minjeong Kim, Jim Miller, Dinggang Shen. | |||||
|
Module Description
The figure above shows an overview of the algorithm. MABMIS contains two modules: the training module, and the testing module.
In the training module, multiple atlas image pairs are required as the input. Each atlas image pair contains one pre-processed T1-weighted intensity image and one label image on which each interested structure on the T1 image is manually identified and assigned a unique label. The label image is generally generated by an expert. In the training module, the multiple atlas pairs are processed to construct an atlas tree, where each atlas is one node of the tree. The tree is constructed based on the similarity among the atlases and tree-based groupwise registration.
In the testing module, a group of target images are segmented based on the atlas tree. First, a novel tree-based groupwise registration method is employed to simultaneously register them to the atlas tree, the target images are segmented simultaneously using an iterative groupwise segmentation strategy, which provides improved accuracy and across-image consistency.
Before applying the modules, both atlas images and target images need to be pre-processed. The processing steps include bias correction ( e.g., N4), skull stripping (e.g., skullstripper in slicer), histogram matching. All images are then registered to a common space using affine registration. The pre-processing tools are not included in the module.
Detailed description of the algorithm can be found in [1].
Use Cases
Tutorials
Panels and their use
Similar Modules
References
- Hongjun Jia, Pew-Thian Yap, Dinggang Shen, "Iterative multi-atlas-based multi-image segmentation with tree-based registration", NeuroImage, 59:422-430, 2012.
Information for Developers
| Section under construction. |