Difference between revisions of "Modules:HammerRegistration"
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
Since Slicer3 takes into account the orientation of a volume, the re-oriented volume will not show any difference from the original volume. | Since Slicer3 takes into account the orientation of a volume, the re-oriented volume will not show any difference from the original volume. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Development == | == Development == | ||
Revision as of 12:50, 27 April 2010
Home < Modules:HammerRegistrationReturn to Slicer 3.6 Documentation
Module Name
Hammer Deformable Registration
|
|
General Information
Module Type & Category
Type: CLI
Category: Registration
Authors, Collaborators & Contact
- Author: Guorong Wu, Xiaodong Tao, Jim Miller, Dinggang Shen
- Contact: grwu at med.unc.edu, taox at research.ge.com
Module Description
HAMMER is an algorithm for elastic registration of medical images using geometric moment invariants as attributes and hierarchical attribute matching mechanism for finding deformation field. This module implements the algorithm described in 'HAMMER: Hierarchical Attribute Matching Mechanism for Elastic Registration', IEEE Trans. on Medical Imaging, 21(11):1421-1439, Nov 2002). Its inputs are skull stripped brain images with gray matter, white matter, and CSF segmentation.
Usage
Examples, Use Cases & Tutorials
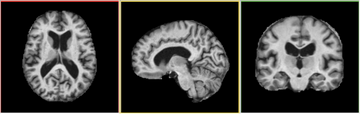
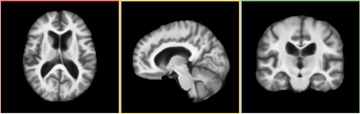
- This module, as an individual, takes as inputs two gray matter/white matter/ CSF segmented brain volumes and computes a deformation field based on attribute matching. The result deformation field can then be applied to the intensity volume corresponding to the moving image and generate a transformed intensity volume that matches the fixed image.
- A command line example of the module is
HammerRegistration -l 1,2,3 -i 50,50,50
FixedImageSegmentation.nrrd
MovingImageSegmentation.nrrd
MovingImageIntensity.nrrd
ResampledMovingImageSegmentation.nrrd
ResampledMovingImageIntensity.nrrd
Quick Tour of Features and Use
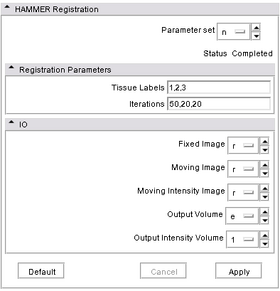
- Input/output panel:
In its current implementation, HammerRegistration takes three input volumes and generate two output volumes. Fixed Image is the tissue mask of the reference image. Moving Image is the tissue mask of the volume to be registered. Moving Intensity Image is the intensity volume corresponding to Moving Image. These volumes should not include extra-cranial tissue. The two output volumes -- Output Volume is the warped Moving Image and Output Intensity Image is the warped Moving Intensity Image. The output volumes are warped with the same deformation field.
- Parameters panel:
The two sets of parameters required are Tissue Labels, which are comma-separated CSF label (1 by default), gray matter label (2 by default), and white matter label (3 by default), and Iterations, which are number of iterations at three different resolutions. When using the default values of 50,20,20, it takes about 15 to 20 minutes for the module to register two volumes of size ~200x200x200.
- Viewing panel:
Since Slicer3 takes into account the orientation of a volume, the re-oriented volume will not show any difference from the original volume.
Development
Dependencies
- Depending on SkullStripper Module to remove extra-cranial tissue.
- Depending on FuzzyTissueClassification Module to segment the brain tissue into gray matter, white matter, CSF.
Known bugs
None.
Usability issues
None.
Source code & documentation
Source Code:
XML Description:
Usage:
USAGE:
/Users/taox/dev/Slicer3-ext/HammerRegistration-build/lib/Slicer3/Plugins
/HammerRegistration
[--returnparameterfile
<std::string>]
[--processinformationaddress
<std::string>] [--xml] [--echo] [-i
<std::vector<int>>] [-l
<std::vector<int>>] [--]
[--version] [-h] <std::string>
<std::string> <std::string>
<std::string> <std::string>
Where:
--returnparameterfile <std::string>
Filename in which to write simple return parameters (int, float,
int-vector, etc.) as opposed to bulk return parameters (image,
geometry, transform, measurement, table).
--processinformationaddress <std::string>
Address of a structure to store process information (progress, abort,
etc.). (default: 0)
--xml
Produce xml description of command line arguments (default: 0)
--echo
Echo the command line arguments (default: 0)
-i <std::vector<int>>, --iterations <std::vector<int>>
Comma separated list of iterations, for low resolution, middle
resolution, and high resolution. (default: 50,20,20)
-l <std::vector<int>>, --tissuelabel <std::vector<int>>
Tissue label for csf, gm, and wm (in this order) in the input images.
(default: 10,150,250)
--, --ignore_rest
Ignores the rest of the labeled arguments following this flag.
--version
Displays version information and exits.
-h, --help
Displays usage information and exits.
<std::string>
(required) Fixed image to which to register
<std::string>
(required) Moving image
<std::string>
(required) Moving intensity image, (optional).
<std::string>
(required) Resampled moving image to the fixed image coordinate
frame.
<std::string>
(required) Resampled moving intensity image to the fixed image
coordinate frame (optional).
Description: HAMMER is an algorithm for elastic registration of
medical images using geometric moment invariants as attributes and
hierarchical attribute matching mechanism for finding deformation
field. This module implements the algorithm described in 'HAMMER:
Hierarchical Attribute Matching Mechanism for Elastic Registration',
IEEE Trans. on Medical Imaging, 21(11):1421-1439, Nov 2002). Its
inputs are skull stripped brain images with gray matter, white matter,
and CSF segmentation.
Author(s): Guorong Wu, Dinggang Shen, Xiaodong Tao, Jim
Miller
Acknowledgements: This work is part of the National Alliance for Medical
Image Computing (NAMIC), funded by the National Institutes of Health
through the NIH Roadmap for Medical Research, Grant U54 EB005149. This
work is also partly supported by NIH Grant EB006733.
More Information
Acknowledgment
This work is part of the National Alliance for Medical Image Computing (NAMIC), funded by the National Institutes of Health through the NIH Roadmap for Medical Research, Grant U54 EB005149. This work is also partly supported by NIH Grant EB006733.