Difference between revisions of "Modules:FourDImage-Documentation-3.5"
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
==Tutorials== | ==Tutorials== | ||
This document will demonstrates: | This document will demonstrates: | ||
| − | *Basic | + | *Basic operations (loading, viewing and editing) |
*Importing 4D data from external software using [[Modules:OpenIGTLinkIF-Documentation-3.4| OpenIGTLink]] | *Importing 4D data from external software using [[Modules:OpenIGTLinkIF-Documentation-3.4| OpenIGTLink]] | ||
| − | ===Basic | + | ===Basic operations (loading, viewing and editing)=== |
====Step 1: Open the module==== | ====Step 1: Open the module==== | ||
====Step 2: Load image==== | ====Step 2: Load image==== | ||
Revision as of 21:10, 30 June 2009
Home < Modules:FourDImage-Documentation-3.5Return to Slicer 3.5 Documentation
Module Name
4D Image Module
General Information
Module Type & Category
Type: Interactive
Category: 4D
Authors, Collaborators & Contact
- Junichi Tokuda, BWH
- Hiroto Hatabu, BWH
- Contact: Junichi Tokuda, tokuda at bwh.harvard.edu
Module Description
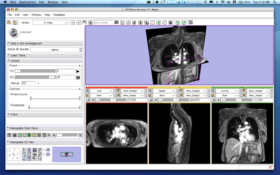
The 4D Image module is designed to handle a time-series of 3D volume images (4D image), e.g. fMRI, cardiac images, dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) images in 3D Slicer. You can do:
- Load and save a series of 3D volume images from a directory, which contains multiple volume images.
- Scroll through a time-series.
- Edit (add, delete and insert) frames in a time series.
The core component of 4D Image module is time series bundle node, which is defined as a vtkMRMLScalarVolumeNode class. This special MRML node is designed to hold pointers to scalar volume nodes in the time series, and in addition, two scalar volume nodes for visualization. The two visualization scalar nodes contains byte arrays that are displayed in the 2D and 3D viewers; whenever the user scrolls the time-series, the module copies byte arrays from the scalar volume node at the current time point in the series to the nodes for visualization. This approach gives a flexibility to use the existing frame works of image processing for each scalar volume nodes in the time-series data. The reason why it holds two visualization scalar nodes is that one is used for background and the other is used for foreground for comparing two volumes at different time points.
Usage
Quick Tour of Features and Use
- Active 4D Bundle panel: This panel allows choosing the active time series bundle node from MRML scene. If you choose "Create New TimeSeriesBundle", the module creates a time series bundle node with no volumes. You can add volumes in the Editor panel.
- Load / Save panel: This panel is used to load and save time-series of volume images. To load a time-series of volume images, first specify the directory that contains the volumes from "Brows Input Directory" dialog box, and then press "Load Series" button.
- Control panel: This panel provides slider user interfaces to scroll the images in time-dimension. The panel allows scrolling foreground and background images independently. The module can also automatically scroll the images with interval specified in the entry in the panel.
- Editor panel: The panel allows editing the volume images in the time series. The users can move, insert and delete volume images.
Tutorials
This document will demonstrates:
- Basic operations (loading, viewing and editing)
- Importing 4D data from external software using OpenIGTLink
Basic operations (loading, viewing and editing)
Step 1: Open the module
Step 2: Load image
Step 3: Scroll image
Step 4: Edit time-series
Importing 4D data from external software using OpenIGTLink
Step 1: Setup example data and simulator to send the 4D data
Step 2: Configure OpenIGTLink IF
Step 3: Run the simulator to transfer the 4D data
Step 4: Create and edit time-series bundle
Development
Dependencies
This module does not require any other module. To import 4D image through network as demonstrated in the tutorial, you need to have OpenIGTLink IF module.
Known bugs
Follow this link to the Slicer3 bug tracker.
Usability issues
Follow this link to the Slicer3 bug tracker. Please select the usability issue category when browsing or contributing.
Source code & documentation
Customize following links for your module.
Links to documentation generated by doxygen.
More Information
Acknowledgment
This work is partly supported by NIH R21CA116271-02 (PI: Hiroto Hatabu), P01CA067165 (PI: Ferenc Jolesz), U41RR019703 (PI: Ferenc Jolesz), U54EB005149 (PI: Ron Kikinis) and P41RR013218-12 (PI: Ron Kikinis).