Difference between revisions of "Documentation/Nightly/Modules/ShapeVariationAnalyzer"
| Line 171: | Line 171: | ||
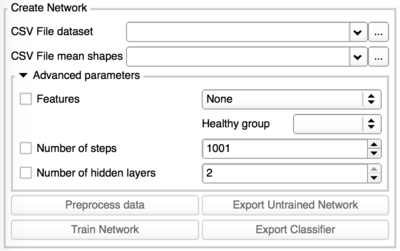
TODO: Choice of more advanced network parameters | TODO: Choice of more advanced network parameters | ||
| − | |[[Image:MorphologicalClassification-CreateNetwork.png| | + | |[[Image:MorphologicalClassification-CreateNetwork.png|400px]] |
|} | |} | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 179: | Line 179: | ||
|[[Image:MorphologicalClassification-Classify.png|300px]] | |[[Image:MorphologicalClassification-Classify.png|300px]] | ||
| | | | ||
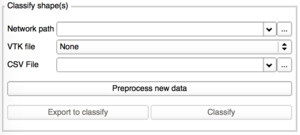
| − | + | To classify one or more shapes, you would need: | |
| − | + | * The network previously trained (zipfile) | |
| + | * The VTK file of the shape you would like to classify OR a CSV file containing all the paths to the VTK you want to classify. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | Please note that classifying too many shapes at the same time (via CSV file), can stop Slicer. | ||
|} | |} | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 16:30, 5 May 2017
Home < Documentation < Nightly < Modules < ShapeVariationAnalyzer
|
For the latest Slicer documentation, visit the read-the-docs. |
Introduction and Acknowledgements
|
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Dental and Craniofacial Research and Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering of the National Institutes of Health under Award Number R01DE024450. Author: Priscille de Dumast (University of Michigan) License: Apache License, Version 2.0 |
|
|
Module Description
Shape Variation Analyzer allows the classification of 3D models, according to their morphological variation.
This tool is based on a deep learning neural network.
The module is composed of multiple panels to perform the different steps of the process: create the classification groups, compute their average shapes, train the classifier and classify shapes.
What is an artificial neural network?
A neural network is a computing system, inspired by our own human brain. It learns from a large dataset (training dataset) containing both the input and the expected output (in our case, the 3D model and its morphology classification). During the training, the network’s settings are adjusted until we achieve automatic classification that matches the expert classification.
The network can then be tested with any input, preferably not from the training dataset. This allows to evaluate the performance of the network.
Use Cases
Tutorials
Prerequisities
The classification can be performed with as many groups as desired.
Please note that the amount of data is very important. The more data you have, the more accurate the classification will be. Moreover, it is better to have a dataset equally divided into the classes.
Both the 3D models into the training dataset and those to classify must have the same number of points. The most correspondent the shapes are, the best it is for the computation.
Those 2 steps can be performed thanks to ShapeAnalysisModule and RigidAlignment/Groups.
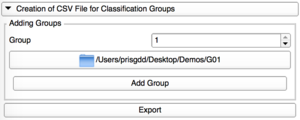
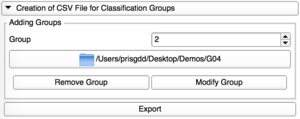
Creation of CSV File
|
Add Group
Add one by one the directories containing the VTK files for each group. |
Modify Group
Each group can be edited, with a modification of its corresponding repository. |
Remove Group
Only the last group added can be removed. |
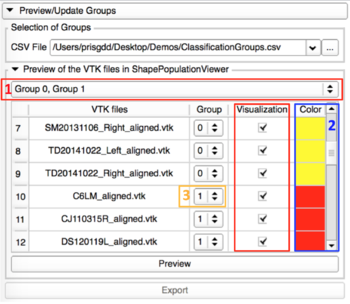
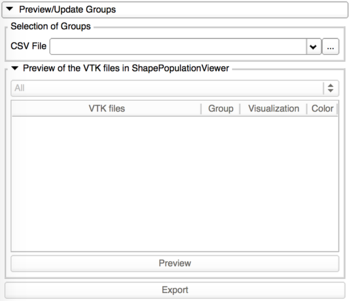
Preview/Update of the classification groups
|
This tab allows the visualization of the 3D models in ShapePopulationViewer, and update the group assigned to the shapes if needed. |
- Preview with ShapePopulationViewer
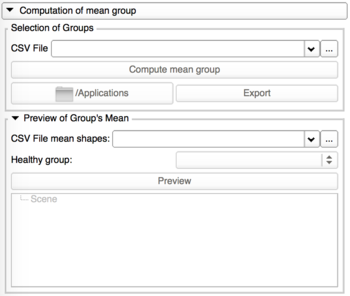
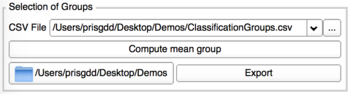
Computation of mean groups
- Perform the computation
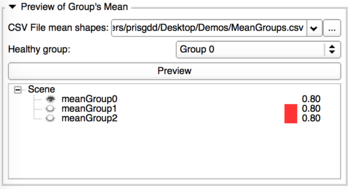
- Preview of Group's mean
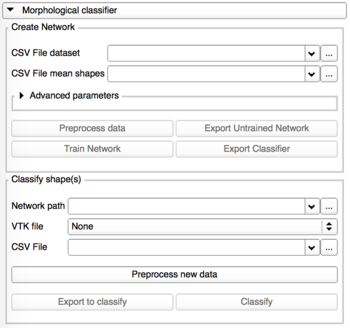
Morphological classification
|
This tab is divided into 2 panels:
|
- Create Network
- Classify shape(s)
Results/Analysis
|
|
Similar Modules
N/A
References
N/A
Information for Developers
This extension has been designed to work with this website and should not work with other architectures.
If you want to use this plugin on another server, you need to make sure your documents are stored by CouchDB and your documents contains a field "type" set to "morphologicalData".
Your user would need to connect using JWT and have a "scope" field.
For more information, you can take a look at the website source code here.
The source code is available on github