Difference between revisions of "Documentation/Nightly/ScriptRepository"
Tag: 2017 source edit |
Tag: 2017 source edit |
||
| Line 2,031: | Line 2,031: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
# Disable slice annotations immediately | # Disable slice annotations immediately | ||
| − | slicer.modules.DataProbeInstance.infoWidget.sliceAnnotations.sliceViewAnnotationsEnabled=False | + | sliceAnnotations = slicer.modules.DataProbeInstance.infoWidget.sliceAnnotations |
| − | + | sliceAnnotations.sliceViewAnnotationsEnabled=False | |
| + | sliceAnnotations.updateSliceViewFromGUI() | ||
# Disable slice annotations persistently (after Slicer restarts) | # Disable slice annotations persistently (after Slicer restarts) | ||
settings = qt.QSettings() | settings = qt.QSettings() | ||
settings.setValue('DataProbe/sliceViewAnnotations.enabled', 0) | settings.setValue('DataProbe/sliceViewAnnotations.enabled', 0) | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Show scalar bar (DataProbe)== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Display color bar for background volume in slice views: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | sliceAnnotations = slicer.modules.DataProbeInstance.infoWidget.sliceAnnotations | ||
| + | sliceAnnotations.sliceViewAnnotationsEnabled = True | ||
| + | sliceAnnotations.scalarBarEnabled = 1 | ||
| + | sliceAnnotations.scalarBarSelectedLayer = 'background' # alternative is 'foreground' | ||
| + | sliceAnnotations.rangeLabelFormat = 'test %G' | ||
| + | sliceAnnotations.updateSliceViewFromGUI() | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
Revision as of 06:17, 13 April 2021
Home < Documentation < Nightly < ScriptRepository
|
For the latest Slicer documentation, visit the read-the-docs. |
Contents
- 1 Community-contributed modules
- 2 Community-contributed examples
- 2.1 Get node object from the scene from node name or ID
- 2.2 Capture
- 2.3 Launching Slicer
- 2.4 Load volume from file
- 2.5 Load volume from URL
- 2.6 Show volume rendering automatically when a volume is loaded
- 2.7 Automatically load volumes that are copied into a folder
- 2.8 DICOM
- 2.8.1 How to load DICOM files into the scene from a folder
- 2.8.2 How to import DICOM files into the application's DICOM database
- 2.8.3 How to import DICOM files using DICOMweb
- 2.8.4 How to access top level tags of DICOM images imported into Slicer?
- 2.8.5 How to access DICOM tags nested in a sequence
- 2.8.6 How to access tag of a volume loaded from DICOM? For example, get the patient position stored in a volume:
- 2.8.7 How to access tag of an item in the Subject Hierachy tree? For example, get the content time tag of a structure set:
- 2.8.8 How to get path and filename of a loaded DICOM volume?
- 2.8.9 How can I convert DICOM to NRRD on the command line?
- 2.8.10 Export a volume to DICOM file format
- 2.8.11 Export a segmentation to DICOM segmentation object
- 2.8.12 Customize table columns in DICOM browser
- 2.8.13 Query and retrieve data from a PACS using classic DIMSE DICOM networking
- 2.9 Toolbar functions
- 2.10 Switch to a different module
- 2.11 Set a new default module at startup
- 2.12 Manipulating objects in the slice viewer
- 2.13 Measure angle between two slice planes
- 2.14 Measure angle between two markup planes
- 2.15 Measure angle between two markup lines
- 2.16 Set slice position and orientation from 3 markup fiducials
- 2.17 Set slice position and orientation from a normal vector and position
- 2.18 Extract randomly oriented slabs of given shape from a volume
- 2.19 Switching to markup fiducial placement mode
- 2.20 Change markup fiducial display properties
- 2.21 Get a notification if a markup point position is modified
- 2.22 Get a notification if a transform is modified
- 2.23 Rotate a node around a specified point
- 2.24 Rotate a node around a specified line
- 2.25 Show a context menu when a markup point is clicked in a slice or 3D view
- 2.26 Write markup positions to JSON file
- 2.27 Write annotation ROI to JSON file
- 2.28 Show a simple surface mesh as a model node
- 2.29 Measure distance of points from surface
- 2.30 Add a texture mapped plane to the scene as a model
- 2.31 Get scalar values at surface of a model
- 2.32 Apply VTK filter on a model node
- 2.33 Select cells of a model using markups fiducial points
- 2.34 Load volume from .vti file
- 2.35 Export entire scene as VRML
- 2.36 Export model to Blender, including color by scalar
- 2.37 Export a tract (FiberBundle) to Blender, including color
- 2.38 Iterate over tract (FiberBundle) streamline points
- 2.39 Clone a node
- 2.40 Clone a volume
- 2.41 Create a new volume
- 2.42 Get value of a volume at specific voxel coordinates
- 2.43 Modify voxels in a volume
- 2.44 Get volume voxel coordinates from markup fiducial RAS coordinates
- 2.45 Get markup fiducial RAS coordinates from volume voxel coordinates
- 2.46 Get the values of all voxels for a label value
- 2.47 Access values in a DTI tensor volume
- 2.48 Change window/level (brightness/contrast) or colormap of a volume
- 2.49 Make mouse left-click and drag on the image adjust window/level
- 2.50 Create custom color table
- 2.51 Manipulate a Slice View
- 2.52 Show a volume in slice views
- 2.53 Show comparison view of all model files a folder
- 2.54 Change opacity of foreground volume in slice views
- 2.55 Fit slice plane to markup fiducials
- 2.56 Save a series of images from a Slice View
- 2.57 Rasterize a model and save it to a series of image files
- 2.58 Save the scene into a new directory
- 2.59 Save the scene into a single MRB file
- 2.60 Save a node to file
- 2.61 Override default scene save dialog
- 2.62 Override application close behavior
- 2.63 Center the 3D View on the Scene
- 2.64 Rotate the 3D View
- 2.65 Display text in a 3D view or slice view
- 2.66 Hide slice view annotations (DataProbe)
- 2.67 Show scalar bar (DataProbe)
- 2.68 Turning off interpolation
- 2.69 Customize viewer layout
- 2.70 Customize keyboard shortcuts
- 2.71 Customize keyboard/mouse gestures in viewers
- 2.72 Disable certain user interactions in slice views
- 2.73 Change default slice view orientation
- 2.74 Set all slice views linked by default
- 2.75 Set crosshair jump mode to centered by default
- 2.76 Add keyboard shortcut to jump to center or world coordinate system
- 2.77 Display mouse pointer coordinates in alternative coordinate system
- 2.78 Set up custom units in slice view ruler
- 2.79 Show orientation marker in all views
- 2.80 Show a slice view outside the view layout
- 2.81 Show a 3D view outside the view layout
- 2.82 Get displayable manager of a certain type for a certain view
- 2.83 Running an ITK filter in Python using SimpleITK
- 2.84 Get current mouse coordinates in a slice view
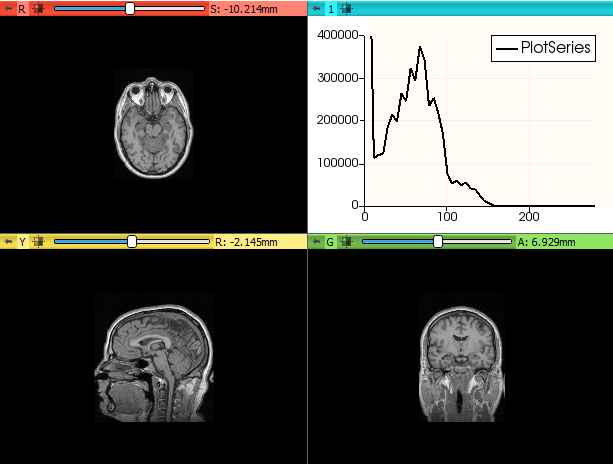
- 2.85 Get DataProbe text
- 2.86 Get axial slice as numpy array
- 2.87 Get reformatted image from a slice viewer as numpy array
- 2.88 Combine multiple volumes into one
- 2.89 Add noise to image
- 2.90 Mask volume using segmentation
- 2.91 Apply random deformations to image
- 2.92 Thick slab reconstruction and maximum/minimum intensity volume projections
- 2.93 Change default file type for nodes (that have never been saved yet)
- 2.94 Change file type for saving for all volumes (with already existing storage nodes)
- 2.95 Sequences
- 2.96 Segmentations
- 2.96.1 Create a segmentation from a labelmap volume and display in 3D
- 2.96.2 Export labelmap node from segmentation node
- 2.96.3 Export model nodes from segmentation node
- 2.96.4 Create a hollow model from boundary of solid segment
- 2.96.5 Show a segmentation in 3D
- 2.96.6 Get a representation of a segment
- 2.96.7 Convert all segments using default path and conversion parameters
- 2.96.8 Convert all segments using custom path or conversion parameters
- 2.96.9 Re-convert using a modified conversion parameter
- 2.96.10 Create keyboard shortcut for toggling sphere brush for paint and erase effects
- 2.96.11 Customize list of displayed Segment editor effects
- 2.96.12 Get centroid of a segment in world (RAS) coordinates
- 2.96.13 Get histogram of a segmented region
- 2.96.14 Get segments visible at a selected position
- 2.96.15 Set default segmentation options
- 2.96.16 How to run segment editor effects from a script
- 2.96.17 Process segment using a VTK filter
- 2.96.18 Get information from segmentation nrrd file header
- 2.97 Quantifying segments
- 2.98 Markups
- 2.99 Accessing views, renderers, and cameras
- 2.100 Access VTK actor properties
- 2.101 Hide view controller bars
- 2.102 Customize widgets in view controller bars
- 2.103 Change 3D view background color
- 2.104 Change view axis labels
- 2.105 Hide Slicer logo from main window (to increase space)
- 2.106 Subject hierarchy
- 2.106.1 Get the pseudo-singleton subject hierarchy node
- 2.106.2 Create subject hierarchy item
- 2.106.3 Get subject hierarchy item
- 2.106.4 Traverse children of a subject hierarchy item
- 2.106.5 Manipulate subject hierarchy item
- 2.106.6 Filter items in TreeView or ComboBox
- 2.106.7 Listen to subject hierarchy item events
- 2.106.8 Subject hierarchy plugin offering view context menu action
- 2.106.9 Use whitelist to customize view menu
- 2.107 Plotting
- 2.108 Execute external applications
- 2.109 Manage extensions
Community-contributed modules
The examples in this section are Scripted Modules that provide a user interface in the module panel along with specialized implementation logic.
Usage: save the .py file to a directory, add the directory to the additional module paths in the Slicer application settings (choose in the menu: Edit / Application settings, click Modules, click >> next to Additional module paths, click Add, and choose the .py file's location).
More information about python scripted modules and more usage examples can be found in the Python scripting wiki page.
Filters
- VolumeMasker.py: Update a target volume with the results of setting all input volume voxels to 0 except for those that correspond to a selected label value in an input label map (Used for example in the volume rendering in [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dfu2gugHLHs this video).
DICOM
- dicom header browser to easily scroll through dicom files using dcmdump.
- SlicerRT batch processing to batch convert RT structure sets to labelmap NRRD files.
Informatics
- MarkupsInfo.py: Compute the total length between all the points of a markup list.
- LineProfile.py: Compute intensity profile in a volume along a line.
Community-contributed examples
Usage: Copy-paste the shown code lines or linked .py file contents into Python console in Slicer. Or save them to a file and run them using execfile.
Get node object from the scene from node name or ID
Examples in the script repository commonly use slicer.util.getNode() function for getting a node object from the scene. This method is only recommended for testing and interactive debugging.
slicer.util.getNode()is recommended **only for interactive debugging** in the Python console/Jupyter notebook- its input is intentionally defined vaguely (it can be either node ID or name and you can use wildcards such as
*), which is good because it make it simpler to use, but the uncertain behavior is not good for general-purpose use in a module - throws an exception so that the developer knows immediately that there was a typo or other unexpected error
- its input is intentionally defined vaguely (it can be either node ID or name and you can use wildcards such as
slicer.mrmlScene.GetNodeByID()is optimized for usage in modules:- its behavior is more predictable: it only accepts node ID as input.
slicer.mrmlScene.GetFirstNodeByName()can be used to get a node by its name, but since multiple nodes in the scene can have the same name, it is not recommended to keep reference to a node by its name. - if node is not found it returns
None(instead of throwing an exception), because this is often not considered an error in module code (it is just used to check existence of a node) and using return value for not-found nodes allows simpler syntax
- its behavior is more predictable: it only accepts node ID as input.
Capture
- Capture the full Slicer screen and save it into a file
img = qt.QPixmap.grabWidget(slicer.util.mainWindow()).toImage()
img.save('c:/tmp/test.png')
- Capture all the views save it into a file:
import ScreenCapture cap = ScreenCapture.ScreenCaptureLogic() cap.showViewControllers(False) cap.captureImageFromView(None,'c:/tmp/test.png') cap.showViewControllers(True)
- Capture a single view:
viewNodeID = 'vtkMRMLViewNode1' import ScreenCapture cap = ScreenCapture.ScreenCaptureLogic() view = cap.viewFromNode(slicer.mrmlScene.GetNodeByID(viewNodeID)) cap.captureImageFromView(view,'c:/tmp/test.png')
Common values for viewNodeID: vtkMRMLSliceNodeRed, vtkMRMLSliceNodeYellow, vtkMRMLSliceNodeGreen, vtkMRMLViewNode1, vtkMRMLViewNode2. The ScreenCapture module can also create video animations of rotating views, slice sweeps, etc.
- Capture a slice view sweep into a series of PNG files - for example, Red slice view, 30 images, from position -125.0 to 75.0, into c:/tmp folder, with name image_00001.png, image_00002.png, ...
import ScreenCapture
ScreenCapture.ScreenCaptureLogic().captureSliceSweep(getNode('vtkMRMLSliceNodeRed'), -125.0, 75.0, 30, "c:/tmp", "image_%05d.png")
- Capture 3D view into PNG file with transparent background
renderWindow = slicer.app.layoutManager().threeDWidget(0).threeDView().renderWindow()
renderWindow.SetAlphaBitPlanes(1)
wti = vtk.vtkWindowToImageFilter()
wti.SetInputBufferTypeToRGBA()
wti.SetInput(renderWindow)
writer = vtk.vtkPNGWriter()
writer.SetFileName("c:/tmp/screenshot.png")
writer.SetInputConnection(wti.GetOutputPort())
writer.Write()
Launching Slicer
- How to open an .mrb file with Slicer at the command line?
Slicer.exe --python-code "slicer.util.loadScene( 'f:/2013-08-23-Scene.mrb' )"
- How to run a script in the Slicer environment in batch mode (without showing any graphical user interface)?
Slicer.exe --python-code "doSomething; doSomethingElse; etc." --testing --no-splash --no-main-window
Load volume from file
loadedVolumeNode = slicer.util.loadVolume('c:/Users/abc/Documents/MRHead.nrrd')
Additional options may be specified in properties argument. For example, load an image stack by disabling singleFile option:
loadedVolumeNode = slicer.util.loadVolume('c:/Users/abc/Documents/SomeImage/file001.png', {'singleFile': False})
Get a MRML node in the scene based on the node name and call methods of that object. For the MRHead sample data:
vol=slicer.util.getNode('MR*')
vol.GetImageData().GetDimensions()
Load volume from URL
Download a volume from a URL and load it into the scene using the code snippet below. Downloaded data is temporarily preserved in the application's cache folder and if the checksum of the already downloaded data matches the specified checksum (<algo>:<digest>) then the file is retrieved from the cache instead of being downloaded again. To compute digest with algo SHA256, you can run slicer.util.computeChecksum("SHA256", "path/to/file").
import SampleData
sampleDataLogic = SampleData.SampleDataLogic()
loadedNodes = sampleDataLogic.downloadFromURL(
nodeNames='MRHead',
fileNames='MR-head25.nrrd',
uris='https://github.com/Slicer/SlicerTestingData/releases/download/SHA256/cc211f0dfd9a05ca3841ce1141b292898b2dd2d3f08286affadf823a7e58df93',
checksums='SHA256:cc211f0dfd9a05ca3841ce1141b292898b2dd2d3f08286affadf823a7e58df93')[0]
With interruptible progress reporting using a progress bar:
import SampleData
def reportProgress(msg, level=None):
# Print progress in the console
print("Loading... {0}%".format(sampleDataLogic.downloadPercent))
# Abort download if cancel is clicked in progress bar
if slicer.progressWindow.wasCanceled:
raise Exception('download aborted')
# Update progress window
slicer.progressWindow.show()
slicer.progressWindow.activateWindow()
slicer.progressWindow.setValue(int(sampleDataLogic.downloadPercent))
slicer.progressWindow.setLabelText("Downloading...")
# Process events to allow screen to refresh
slicer.app.processEvents()
try:
volumeNode = None
slicer.progressWindow = slicer.util.createProgressDialog()
sampleDataLogic = SampleData.SampleDataLogic()
sampleDataLogic.logMessage = reportProgress
loadedNodes = sampleDataLogic.downloadFromURL(
nodeNames='MRHead',
fileNames='MR-head25.nrrd',
uris='https://github.com/Slicer/SlicerTestingData/releases/download/SHA256/cc211f0dfd9a05ca3841ce1141b292898b2dd2d3f08286affadf823a7e58df93',
checksums='SHA256:cc211f0dfd9a05ca3841ce1141b292898b2dd2d3f08286affadf823a7e58df93')
volumeNode = loadedNodes[0]
finally:
slicer.progressWindow.close()
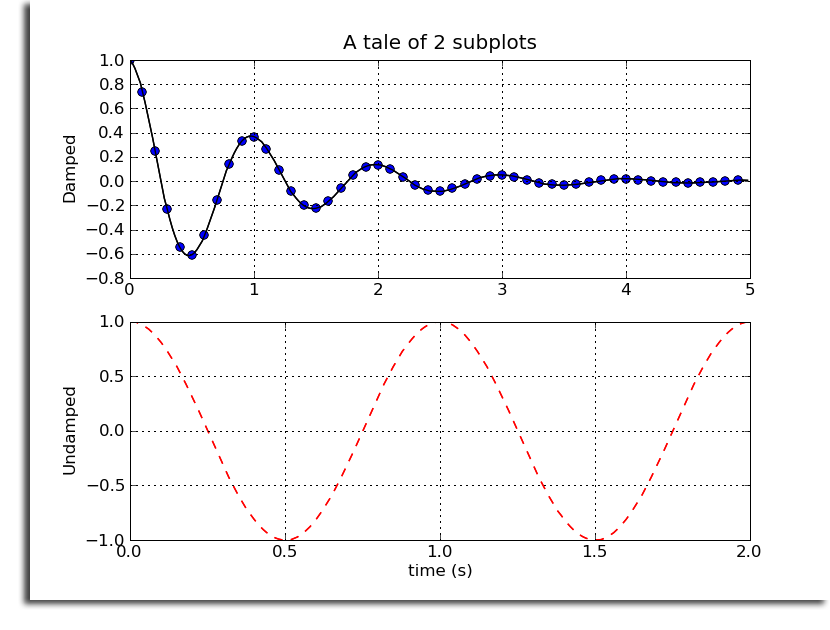
Show volume rendering automatically when a volume is loaded
To show volume rendering of a volume automatically when it is loaded, add the lines below to your .slicerrc file.
@vtk.calldata_type(vtk.VTK_OBJECT)
def onNodeAdded(caller, event, calldata):
node = calldata
if isinstance(node, slicer.vtkMRMLVolumeNode):
# Call showVolumeRendering using a timer instead of calling it directly
# to allow the volume loading to fully complete.
qt.QTimer.singleShot(0, lambda: showVolumeRendering(node))
def showVolumeRendering(volumeNode):
print("Show volume rendering of node "+volumeNode.GetName())
volRenLogic = slicer.modules.volumerendering.logic()
displayNode = volRenLogic.CreateDefaultVolumeRenderingNodes(volumeNode)
displayNode.SetVisibility(True)
scalarRange = volumeNode.GetImageData().GetScalarRange()
if scalarRange[1]-scalarRange[0] < 1500:
# small dynamic range, probably MRI
displayNode.GetVolumePropertyNode().Copy(volRenLogic.GetPresetByName('MR-Default'))
else:
# larger dynamic range, probably CT
displayNode.GetVolumePropertyNode().Copy(volRenLogic.GetPresetByName('CT-Chest-Contrast-Enhanced'))
slicer.mrmlScene.AddObserver(slicer.vtkMRMLScene.NodeAddedEvent, onNodeAdded)
Automatically load volumes that are copied into a folder
This example shows how to implement a simple background task by using a timer. The background task is to check for any new volume files in folder and if there is any then automatically load it.
There are more efficient methods for file system monitoring or exchanging image data in real-time (for example, using OpenIGTLink), the example below is just for demonstration purposes.
incomingVolumeFolder = "c:/tmp/incoming"
incomingVolumesProcessed = []
def checkForNewVolumes():
# Check if there is a new file in the
from os import listdir
from os.path import isfile, join
for f in listdir(incomingVolumeFolder):
if f in incomingVolumesProcessed:
# this is an incoming file, it was already there
continue
filePath = join(incomingVolumeFolder, f)
if not isfile(filePath):
# ignore directories
continue
logging.info("Loading new file: "+f)
incomingVolumesProcessed.append(f)
slicer.util.loadVolume(filePath)
# Check again in 3000ms
qt.QTimer.singleShot(3000, checkForNewVolumes)
# Start monitoring
checkForNewVolumes()
DICOM
How to load DICOM files into the scene from a folder
This code loads all DICOM objects into the scene from a file folder. All the registered plugins are evaluated and the one with the highest confidence will be used to load the data. Files are imported into a temporary DICOM database, so the current Slicer DICOM database is not impacted.
dicomDataDir = "c:/my/folder/with/dicom-files" # input folder with DICOM files
loadedNodeIDs = [] # this list will contain the list of all loaded node IDs
from DICOMLib import DICOMUtils
with DICOMUtils.TemporaryDICOMDatabase() as db:
DICOMUtils.importDicom(dicomDataDir, db)
patientUIDs = db.patients()
for patientUID in patientUIDs:
loadedNodeIDs.extend(DICOMUtils.loadPatientByUID(patientUID))
How to import DICOM files into the application's DICOM database
This code snippet uses Slicer DICOM browser built-in indexer to import DICOM files into the database. Images are not loaded into the scene, but they show up in the DICOM browser. After import, data sets can be loaded using DICOMUtils functions (e.g., loadPatientByUID) - see above for an example.
# instantiate a new DICOM browser
slicer.util.selectModule("DICOM")
dicomBrowser = slicer.modules.DICOMWidget.browserWidget.dicomBrowser
# use dicomBrowser.ImportDirectoryCopy to make a copy of the files (useful for importing data from removable storage)
dicomBrowser.importDirectory(dicomFilesDirectory, dicomBrowser.ImportDirectoryAddLink)
# wait for import to finish before proceeding (optional, if removed then import runs in the background)
dicomBrowser.waitForImportFinished()
How to import DICOM files using DICOMweb
Download and import DICOM data set using DICOMweb from Kheops, Google Health API, etc.
How to obtain accessToken:
- Google Cloud: Execute
gcloud auth print-access-tokenonce you have logged in - Kheops: create an album, create a sharing link (somethin like
https://demo.kheops.online/view/TfYXwbKAW7JYbAgZ7MyISf), the token is the string after the last slash
slicer.util.selectModule("DICOM") # ensure DICOM database is initialized and
slicer.app.processEvents()
from DICOMLib import DICOMUtils
DICOMUtils.importFromDICOMWeb(
dicomWebEndpoint="http://demo.kheops.online/api",
studyInstanceUID="1.3.6.1.4.1.14519.5.2.1.8421.4009.985792766370191766692237040819",
accessToken="TfYXwbKAW7JYbAgZ7MyISf")
How to access top level tags of DICOM images imported into Slicer?
For example, to print the first patient's first study's first series' "0020,0032" field:
db=slicer.dicomDatabase
patientList=db.patients()
studyList=db.studiesForPatient(patientList[0])
seriesList=db.seriesForStudy(studyList[0])
fileList=db.filesForSeries(seriesList[0])
# Note, fileValue accesses the database of cached top level tags
# (nested tags are not included)
print(db.fileValue(fileList[0],'0020,0032'))
# Get tag group,number from dicom dictionary
import pydicom as dicom
tagName = "StudyDate"
tagStr = str(dicom.tag.Tag(tagName))[1:-1].replace(' ','')
print(db.fileValue(fileList[0],tagStr))
How to access DICOM tags nested in a sequence
db=slicer.dicomDatabase patientList=db.patients() studyList=db.studiesForPatient(patientList[0]) seriesList=db.seriesForStudy(studyList[0]) fileList=db.filesForSeries(seriesList[0]) # use pydicom to access the full header, which requires # re-reading the dataset instead of using the database cache import pydicom pydicom.dcmread(fileList[0]) ds.CTExposureSequence[0].ExposureModulationType
How to access tag of a volume loaded from DICOM? For example, get the patient position stored in a volume:
volumeName='2: ENT IMRT'
n=slicer.util.getNode(volumeName)
instUids=n.GetAttribute('DICOM.instanceUIDs').split()
filename=slicer.dicomDatabase.fileForInstance(instUids[0])
print(slicer.dicomDatabase.fileValue(filename,'0018,5100'))
How to access tag of an item in the Subject Hierachy tree? For example, get the content time tag of a structure set:
rtStructName = '3: RTSTRUCT: PROS' rtStructNode = slicer.util.getNode(rtStructName) shNode = slicer.vtkMRMLSubjectHierarchyNode.GetSubjectHierarchyNode(slicer.mrmlScene) rtStructShItemID = shNode.GetItemByDataNode(rtStructNode) ctSliceInstanceUids = shNode.GetItemAttribute(rtStructShItemID, 'DICOM.ReferencedInstanceUIDs').split() filename = slicer.dicomDatabase.fileForInstance(ctSliceInstanceUids[0]) print(slicer.dicomDatabase.fileValue(filename,'0008,0033'))
How to get path and filename of a loaded DICOM volume?
def pathFromNode(node):
storageNode=node.GetStorageNode()
if storageNode is not None: # loaded via drag-drop
filepath=storageNode.GetFullNameFromFileName()
else: # loaded via DICOM browser
instanceUIDs=node.GetAttribute('DICOM.instanceUIDs').split()
filepath=slicer.dicomDatabase.fileForInstance(instUids[0])
return filepath
# example:
node=slicer.util.getNode('volume1')
path=self.pathFromNode(node)
print("DICOM path=%s" % path)
How can I convert DICOM to NRRD on the command line?
/Applications/Slicer-4.6.2.app/Contents/MacOS/Slicer --no-main-window --python-code "node=slicer.util.loadVolume('/tmp/series/im0.dcm'); slicer.util.saveNode(node, '/tmp/output.nrrd'); exit()"
The same can be done on windows by using the top level Slicer.exe. Be sure to use forward slashes in the pathnames within quotes on the command line.
Export a volume to DICOM file format
volumeNode = getNode('CTChest')
outputFolder = "c:/tmp/dicom-output"
# Create patient and study and put the volume under the study
shNode = slicer.vtkMRMLSubjectHierarchyNode.GetSubjectHierarchyNode(slicer.mrmlScene)
patientItemID = shNode.CreateSubjectItem(shNode.GetSceneItemID(), "test patient")
studyItemID = shNode.CreateStudyItem(patientItemID, "test study")
volumeShItemID = shNode.GetItemByDataNode(volumeNode)
shNode.SetItemParent(volumeShItemID, studyItemID)
import DICOMScalarVolumePlugin
exporter = DICOMScalarVolumePlugin.DICOMScalarVolumePluginClass()
exportables = exporter.examineForExport(volumeShItemID)
for exp in exportables:
exp.directory = outputFolder
exporter.export(exportables)
Export a segmentation to DICOM segmentation object
segmentationNode = ...
referenceVolumeNode = ...
outputFolder = "c:/tmp/dicom-output"
# Associate segmentation node with a reference volume node
shNode = slicer.vtkMRMLSubjectHierarchyNode.GetSubjectHierarchyNode(slicer.mrmlScene)
referenceVolumeShItem = shNode.GetItemByDataNode(referenceVolumeNode)
studyShItem = shNode.GetItemParent(referenceVolumeShItem)
segmentationShItem = shNode.GetItemByDataNode(segmentationNode)
shNode.SetItemParent(segmentationShItem, studyShItem)
# Export to DICOM
import DICOMSegmentationPlugin
exporter = DICOMSegmentationPlugin.DICOMSegmentationPluginClass()
exportables = exporter.examineForExport(segmentationShItem)
for exp in exportables:
exp.directory = outputFolder
exporter.export(exportables)
Customize table columns in DICOM browser
Documentation of methods for changing DICOM browser columns: https://github.com/commontk/CTK/blob/master/Libs/DICOM/Core/ctkDICOMDatabase.h#L354-L375
# Get browser and database
dicomBrowser = slicer.modules.dicom.widgetRepresentation().self().browserWidget.dicomBrowser
dicomDatabase = dicomBrowser.database()
# Print list of available columns
print(dicomDatabase.patientFieldNames)
print(dicomDatabase.studyFieldNames)
print(dicomDatabase.seriesFieldNames)
# Change column order
dicomDatabase.setWeightForField('Series', 'SeriesDescription', 7)
dicomDatabase.setWeightForField('Studies', 'StudyDescription', 6)
# Change column visibility
dicomDatabase.setVisibilityForField('Patients', 'PatientsBirthDate', False)
dicomDatabase.setVisibilityForField('Patients', 'PatientsComments', True)
dicomDatabase.setWeightForField('Patients', 'PatientsComments', 8)
# Change column name
dicomDatabase.setDisplayedNameForField('Series', 'DisplayedCount', 'Number of images')
# Change column width to manual
dicomDatabase.setFormatForField('Series', 'SeriesDescription', '{"resizeMode":"interactive"}')
# Customize table manager in DICOM browser
dicomTableManager = dicomBrowser.dicomTableManager()
dicomTableManager.selectionMode = qt.QAbstractItemView.SingleSelection
dicomTableManager.autoSelectSeries = False
# Force database views update
dicomDatabase.closeDatabase()
dicomDatabase.openDatabase(dicomBrowser.database().databaseFilename)
Query and retrieve data from a PACS using classic DIMSE DICOM networking
# Query
dicomQuery = ctk.ctkDICOMQuery()
dicomQuery.callingAETitle = "SLICER"
dicomQuery.calledAETitle = "ANYAE"
dicomQuery.host = "dicomserver.co.uk"
dicomQuery.port = 11112
dicomQuery.preferCGET = True
dicomQuery.filters = {'Name':'Anon', 'Modalities':'MR'}
# temporary in-memory database for storing query results
tempDb = ctk.ctkDICOMDatabase()
tempDb.openDatabase('')
dicomQuery.query(tempDb)
# Retrieve
dicomRetrieve = ctk.ctkDICOMRetrieve()
dicomRetrieve.callingAETitle = dicomQuery.callingAETitle
dicomRetrieve.calledAETitle = dicomQuery.calledAETitle
dicomRetrieve.host = dicomQuery.host
dicomRetrieve.port = dicomQuery.port
dicomRetrieve.setMoveDestinationAETitle("SLICER");
dicomRetrieve.setDatabase(slicer.dicomDatabase)
for study in dicomQuery.studyInstanceUIDQueried:
print(f"ctkDICOMRetrieveTest2: Retrieving {study}")
slicer.app.processEvents()
if dicomQuery.preferCGET:
success = dicomRetrieve.getStudy(study)
else:
success = dicomRetrieve.moveStudy(study)
print(f" - {'success' if success else 'failed'}")
slicer.dicomDatabase.updateDisplayedFields()
Toolbar functions
- How to turn on slice intersections in the crosshair menu on the toolbar:
viewNodes = slicer.util.getNodesByClass('vtkMRMLSliceCompositeNode')
for viewNode in viewNodes:
viewNode.SetSliceIntersectionVisibility(1)
How to find similar functions? For this one I searched for "slice intersections" text in the whole slicer source code, found that the function is implemented in Base\QTGUI\qSlicerViewersToolBar.cxx, then translated the qSlicerViewersToolBarPrivate::setSliceIntersectionVisible(bool visible) method to Python.
Switch to a different module
This utility function can be used to open a different module:
slicer.util.selectModule('DICOM')
Set a new default module at startup
Instead of the default Welcome module:
qt.QSettings().setValue("Modules/HomeModule", "Data")
Manipulating objects in the slice viewer
How to define/edit a circular region of interest in a slice viewer?
Drop two markup points on a slice view and copy-paste the code below into the Python console. After this, as you move the markups you’ll see a circle following the markups.
# Update the sphere from the fiducial points
def UpdateSphere(param1, param2):
import math
centerPointCoord = [0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
markups.GetNthFiducialPosition(0,centerPointCoord)
circumferencePointCoord = [0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
markups.GetNthFiducialPosition(1,circumferencePointCoord)
sphere.SetCenter(centerPointCoord)
radius=math.sqrt((centerPointCoord[0]-circumferencePointCoord[0])**2+(centerPointCoord[1]-circumferencePointCoord[1])**2+(centerPointCoord[2]-circumferencePointCoord[2])**2)
sphere.SetRadius(radius)
sphere.SetPhiResolution(30)
sphere.SetThetaResolution(30)
sphere.Update()
# Get markup node from scene
markups=slicer.util.getNode('F')
sphere = vtk.vtkSphereSource()
UpdateSphere(0,0)
# Create model node and add to scene
modelsLogic = slicer.modules.models.logic()
model = modelsLogic.AddModel(sphere.GetOutput())
model.GetDisplayNode().SetSliceIntersectionVisibility(True)
model.GetDisplayNode().SetSliceIntersectionThickness(3)
model.GetDisplayNode().SetColor(1,1,0)
# Call UpdateSphere whenever the fiducials are changed
markups.AddObserver(slicer.vtkMRMLMarkupsNode.PointModifiedEvent, UpdateSphere, 2)
Specify a sphere by multiple of markups points
Drop multiple markup points at the boundary of the spherical object and and copy-paste the code below into the Python console to get best-fit sphere. Minimum 4 points are required, it is recommended to place the points far from each other for most accurate fit.
# Get markup node from scene
markups = slicer.util.getNode('F')
from scipy.optimize import least_squares
import numpy
def fit_sphere_least_squares(x_values, y_values, z_values, initial_parameters, bounds=((-numpy.inf, -numpy.inf, -numpy.inf, -numpy.inf),(numpy.inf, numpy.inf, numpy.inf, numpy.inf))):
"""
Source: https://github.com/thompson318/scikit-surgery-sphere-fitting/blob/master/sksurgeryspherefitting/algorithms/sphere_fitting.py
Uses scipy's least squares optimisor to fit a sphere to a set
of 3D Points
:return: x: an array containing the four fitted parameters
:return: ier: int An integer flag. If it is equal to 1, 2, 3 or 4, the
solution was found.
:param: (x,y,z) three arrays of equal length containing the x, y, and z
coordinates.
:param: an array containing four initial values (centre, and radius)
"""
return least_squares(_calculate_residual_sphere, initial_parameters, bounds=bounds, method='trf', jac='3-point', args=(x_values, y_values, z_values))
def _calculate_residual_sphere(parameters, x_values, y_values, z_values):
"""
Source: https://github.com/thompson318/scikit-surgery-sphere-fitting/blob/master/sksurgeryspherefitting/algorithms/sphere_fitting.py
Calculates the residual error for an x,y,z coordinates, fitted
to a sphere with centre and radius defined by the parameters tuple
:return: The residual error
:param: A tuple of the parameters to be optimised, should contain [x_centre, y_centre, z_centre, radius]
:param: arrays containing the x,y, and z coordinates.
"""
#extract the parameters
x_centre, y_centre, z_centre, radius = parameters
#use numpy's sqrt function here, which works by element on arrays
distance_from_centre = numpy.sqrt((x_values - x_centre)**2 + (y_values - y_centre)**2 + (z_values - z_centre)**2)
return distance_from_centre - radius
# Fit a sphere to the markups fidicual points
markupsPositions = slicer.util.arrayFromMarkupsControlPoints(markups)
import numpy as np
# initial guess
center0 = np.mean(markupsPositions, 0)
radius0 = np.linalg.norm(np.amin(markupsPositions,0)-np.amax(markupsPositions,0))/2.0
fittingResult = fit_sphere_least_squares(markupsPositions[:,0], markupsPositions[:,1], markupsPositions[:,2], [center0[0], center0[1], center0[2], radius0])
[centerX, centerY, centerZ, radius] = fittingResult['x']
# Create a sphere using the fitted parameters
sphere = vtk.vtkSphereSource()
sphere.SetPhiResolution(30)
sphere.SetThetaResolution(30)
sphere.SetCenter(centerX, centerY, centerZ)
sphere.SetRadius(radius)
sphere.Update()
# Add the sphere to the scene
modelsLogic = slicer.modules.models.logic()
model = modelsLogic.AddModel(sphere.GetOutput())
model.GetDisplayNode().SetSliceIntersectionVisibility(True)
model.GetDisplayNode().SetSliceIntersectionThickness(3)
model.GetDisplayNode().SetColor(1,1,0)
Measure angle between two slice planes
Measure angle between red and yellow slice nodes. Whenever any of the slice nodes are moved, the updated angle is printed on the console.
sliceNodeIds = ['vtkMRMLSliceNodeRed', 'vtkMRMLSliceNodeYellow']
# Print angles between slice nodes
def ShowAngle(unused1=None, unused2=None):
sliceNormalVector = []
for sliceNodeId in sliceNodeIds:
sliceToRAS = slicer.mrmlScene.GetNodeByID(sliceNodeId).GetSliceToRAS()
sliceNormalVector.append([sliceToRAS.GetElement(0,2), sliceToRAS.GetElement(1,2), sliceToRAS.GetElement(2,2)])
angleRad = vtk.vtkMath.AngleBetweenVectors(sliceNormalVector[0], sliceNormalVector[1])
angleDeg = vtk.vtkMath.DegreesFromRadians(angleRad)
print('Angle between slice planes = {0:0.3f}'.format(angleDeg))
# Observe slice node changes
for sliceNodeId in sliceNodeIds:
slicer.mrmlScene.GetNodeByID(sliceNodeId).AddObserver(vtk.vtkCommand.ModifiedEvent, ShowAngle)
# Print current angle
ShowAngle()
Measure angle between two markup planes
Measure angle between two markup plane nodes. Whenever any of the plane nodes are moved, the updated angle is printed on the console.
planeNodeNames = ['P', 'P_1']
# Print angles between slice nodes
def ShowAngle(unused1=None, unused2=None):
planeNormalVectors = []
for planeNodeName in planeNodeNames:
planeNode = slicer.util.getFirstNodeByClassByName('vtkMRMLMarkupsPlaneNode', planeNodeName)
planeNormalVector = [0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
planeNode.GetNormalWorld(planeNormalVector)
planeNormalVectors.append(planeNormalVector)
angleRad = vtk.vtkMath.AngleBetweenVectors(planeNormalVectors[0], planeNormalVectors[1])
angleDeg = vtk.vtkMath.DegreesFromRadians(angleRad)
print('Angle between planes {0} and {1} = {2:0.3f}'.format(planeNodeNames[0], planeNodeNames[1], angleDeg))
# Observe plane node changes
for planeNodeName in planeNodeNames:
planeNode = slicer.util.getFirstNodeByClassByName('vtkMRMLMarkupsPlaneNode', planeNodeName)
planeNode.AddObserver(slicer.vtkMRMLMarkupsPlaneNode.PointModifiedEvent, ShowAngle)
# Print current angle
ShowAngle()
Measure angle between two markup lines
Measure angle between two markup line nodes. Whenever either line is moved, the updated angle is printed on the console.
lineNodeNames = ['L', 'L_1']
# Print angles between slice nodes
def ShowAngle(unused1=None, unused2=None):
import numpy as np
lineDirectionVectors = []
for lineNodeName in lineNodeNames:
lineNode = slicer.util.getFirstNodeByClassByName('vtkMRMLMarkupsLineNode', lineNodeName)
lineStartPos = np.zeros(3)
lineEndPos = np.zeros(3)
lineNode.GetNthControlPointPositionWorld(0, lineStartPos)
lineNode.GetNthControlPointPositionWorld(1, lineEndPos)
lineDirectionVector = (lineEndPos-lineStartPos)/np.linalg.norm(lineEndPos-lineStartPos)
lineDirectionVectors.append(lineDirectionVector)
angleRad = vtk.vtkMath.AngleBetweenVectors(lineDirectionVectors[0], lineDirectionVectors[1])
angleDeg = vtk.vtkMath.DegreesFromRadians(angleRad)
print('Angle between lines {0} and {1} = {2:0.3f}'.format(lineNodeNames[0], lineNodeNames[1], angleDeg))
# Observe line node changes
for lineNodeName in lineNodeNames:
lineNode = slicer.util.getFirstNodeByClassByName('vtkMRMLMarkupsLineNode', lineNodeName)
lineNode.AddObserver(slicer.vtkMRMLMarkupsLineNode.PointModifiedEvent, ShowAngle)
# Print current angle
ShowAngle()
Set slice position and orientation from 3 markup fiducials
Drop 3 markup points in the scene and copy-paste the code below into the Python console. After this, as you move the markups you’ll see the red slice view position and orientation will be set to make it fit to the 3 points.
# Update plane from fiducial points
def UpdateSlicePlane(param1=None, param2=None):
# Get point positions as numpy array
import numpy as np
nOfFiduciallPoints = markups.GetNumberOfFiducials()
if nOfFiduciallPoints < 3:
return # not enough points
points = np.zeros([3,nOfFiduciallPoints])
for i in range(0, nOfFiduciallPoints):
markups.GetNthFiducialPosition(i, points[:,i])
# Compute plane position and normal
planePosition = points.mean(axis=1)
planeNormal = np.cross(points[:,1] - points[:,0], points[:,2] - points[:,0])
planeX = points[:,1] - points[:,0]
sliceNode.SetSliceToRASByNTP(planeNormal[0], planeNormal[1], planeNormal[2],
planeX[0], planeX[1], planeX[2],
planePosition[0], planePosition[1], planePosition[2], 0)
# Get markup node from scene
sliceNode = slicer.app.layoutManager().sliceWidget('Red').mrmlSliceNode()
markups = slicer.util.getNode('F')
# Update slice plane manually
UpdateSlicePlane()
# Update slice plane automatically whenever points are changed
markupObservation = [markups, markups.AddObserver(slicer.vtkMRMLMarkupsNode.PointModifiedEvent, UpdateSlicePlane, 2)]
To stop automatic updates, run this:
markupObservation[0].RemoveObserver(markupObservation[1])
Set slice position and orientation from a normal vector and position
This code snippet shows how to display a slice view defined by a normal vector and position in an anatomically sensible way: rotating slice view so that "up" direction (or "right" direction) is towards an anatomical axis.
def setSlicePoseFromSliceNormalAndPosition(sliceNode, sliceNormal, slicePosition, defaultViewUpDirection=None, backupViewRightDirection=None):
"""
Set slice pose from the provided plane normal and position. View up direction is determined automatically,
to make view up point towards defaultViewUpDirection.
:param defaultViewUpDirection Slice view will be spinned in-plane to match point approximately this up direction. Default: patient superior.
:param backupViewRightDirection Slice view will be spinned in-plane to match point approximately this right direction
if defaultViewUpDirection is too similar to sliceNormal. Default: patient left.
"""
# Fix up input directions
if defaultViewUpDirection is None:
defaultViewUpDirection = [0,0,1]
if backupViewRightDirection is None:
backupViewRightDirection = [-1,0,0]
if sliceNormal[1]>=0:
sliceNormalStandardized = sliceNormal
else:
sliceNormalStandardized = [-sliceNormal[0], -sliceNormal[1], -sliceNormal[2]]
# Compute slice axes
sliceNormalViewUpAngle = vtk.vtkMath.AngleBetweenVectors(sliceNormalStandardized, defaultViewUpDirection)
angleTooSmallThresholdRad = 0.25 # about 15 degrees
if sliceNormalViewUpAngle > angleTooSmallThresholdRad and sliceNormalViewUpAngle < vtk.vtkMath.Pi() - angleTooSmallThresholdRad:
viewUpDirection = defaultViewUpDirection
sliceAxisY = viewUpDirection
sliceAxisX = [0, 0, 0]
vtk.vtkMath.Cross(sliceAxisY, sliceNormalStandardized, sliceAxisX)
else:
sliceAxisX = backupViewRightDirection
# Set slice axes
sliceNode.SetSliceToRASByNTP(sliceNormalStandardized[0], sliceNormalStandardized[1], sliceNormalStandardized[2],
sliceAxisX[0], sliceAxisX[1], sliceAxisX[2],
slicePosition[0], slicePosition[1], slicePosition[2], 0)
# Example usage:
sliceNode = getNode('vtkMRMLSliceNodeRed')
transformNode = getNode('Transform_3')
transformMatrix = vtk.vtkMatrix4x4()
transformNode.GetMatrixTransformToParent(transformMatrix)
sliceNormal = [transformMatrix.GetElement(0,2), transformMatrix.GetElement(1,2), transformMatrix.GetElement(2,2)]
slicePosition = [transformMatrix.GetElement(0,3), transformMatrix.GetElement(1,3), transformMatrix.GetElement(2,3)]
setSlicePoseFromSliceNormalAndPosition(sliceNode, sliceNormal, slicePosition)
Extract randomly oriented slabs of given shape from a volume
Returns a numpy array of sliceCount random tiles.
def randomSlices(volume, sliceCount, sliceShape):
layoutManager = slicer.app.layoutManager()
redWidget = layoutManager.sliceWidget('Red')
sliceNode = redWidget.mrmlSliceNode()
sliceNode.SetDimensions(*sliceShape, 1)
sliceNode.SetFieldOfView(*sliceShape, 1)
bounds = [0]*6
volume.GetRASBounds(bounds)
imageReslice = redWidget.sliceLogic().GetBackgroundLayer().GetReslice()
sliceSize = sliceShape[0] * sliceShape[1]
X = numpy.zeros([sliceCount, sliceSize])
for sliceIndex in range(sliceCount):
position = numpy.random.rand(3) * 2 - 1
position = [bounds[0] + bounds[1]-bounds[0] * position[0],
bounds[2] + bounds[3]-bounds[2] * position[1],
bounds[4] + bounds[5]-bounds[4] * position[2]]
normal = numpy.random.rand(3) * 2 - 1
normal = normal / numpy.linalg.norm(normal)
transverse = numpy.cross(normal, [0,0,1])
orientation = 0
sliceNode.SetSliceToRASByNTP( normal[0], normal[1], normal[2],
transverse[0], transverse[1], transverse[2],
position[0], position[1], position[2],
orientation)
if sliceIndex % 100 == 0:
slicer.app.processEvents()
imageReslice.Update()
imageData = imageReslice.GetOutputDataObject(0)
array = vtk.util.numpy_support.vtk_to_numpy(imageData.GetPointData().GetScalars())
X[sliceIndex] = array
return X
Switching to markup fiducial placement mode
To activate a fiducial placement mode, both interaction mode has to be set and a fiducial node has to be selected:
interactionNode = slicer.app.applicationLogic().GetInteractionNode()
selectionNode = slicer.app.applicationLogic().GetSelectionNode()
selectionNode.SetReferenceActivePlaceNodeClassName("vtkMRMLMarkupsFiducialNode")
fiducialNode = slicer.vtkMRMLMarkupsFiducialNode()
slicer.mrmlScene.AddNode(fiducialNode)
fiducialNode.CreateDefaultDisplayNodes()
selectionNode.SetActivePlaceNodeID(fiducialNode.GetID())
interactionNode.SetCurrentInteractionMode(interactionNode.Place)
Alternatively, qSlicerMarkupsPlaceWidget widget can be used to initiate markup placement:
# Temporary markups node
markupsNode = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass("vtkMRMLMarkupsFiducialNode")
def placementModeChanged(active):
print("Placement: " +("active" if active else "inactive"))
# You can inspect what is in the markups node here, delete the temporary markup node, etc.
# Create and set up widget that contains a single "place markup" button. The widget can be placed in the module GUI.
placeWidget = slicer.qSlicerMarkupsPlaceWidget()
placeWidget.setMRMLScene(slicer.mrmlScene)
placeWidget.setCurrentNode(markupsNode)
placeWidget.buttonsVisible=False
placeWidget.placeButton().show()
placeWidget.connect('activeMarkupsFiducialPlaceModeChanged(bool)', placementModeChanged)
placeWidget.show()
Change markup fiducial display properties
Display properties are stored in display node(s) associated with the fiducial node.
fiducialNode = getNode('F')
fiducialDisplayNode = fiducialNode.GetDisplayNode()
fiducialDisplayNode.SetVisibility(False) # Hide all points
fiducialDisplayNode.SetVisibility(True) # Show all points
fiducialDisplayNode.SetSelectedColor(1,1,0) # Set color to yellow
fiducialDisplayNode.SetViewNodeIDs(["vtkMRMLSliceNodeRed", "vtkMRMLViewNode1"]) # Only show in red slice view and first 3D view
Get a notification if a markup point position is modified
Event management of Slicer-4.11 version is still subject to change. The example below shows how point manipulation can be observed now.
def onMarkupChanged(caller,event):
markupsNode = caller
sliceView = markupsNode.GetAttribute('Markups.MovingInSliceView')
movingMarkupIndex = markupsNode.GetDisplayNode().GetActiveControlPoint()
if movingMarkupIndex >= 0:
pos = [0,0,0]
markupsNode.GetNthFiducialPosition(movingMarkupIndex, pos)
isPreview = markupsNode.GetNthControlPointPositionStatus(movingMarkupIndex) == slicer.vtkMRMLMarkupsNode.PositionPreview
if isPreview:
logging.info("Point {0} is previewed at {1} in slice view {2}".format(movingMarkupIndex, pos, sliceView))
else:
logging.info("Point {0} was moved {1} in slice view {2}".format(movingMarkupIndex, pos, sliceView))
else:
logging.info("Points modified: slice view = {0}".format(sliceView))
def onMarkupStartInteraction(caller, event):
markupsNode = caller
sliceView = markupsNode.GetAttribute('Markups.MovingInSliceView')
movingMarkupIndex = markupsNode.GetDisplayNode().GetActiveControlPoint()
logging.info("Start interaction: point ID = {0}, slice view = {1}".format(movingMarkupIndex, sliceView))
def onMarkupEndInteraction(caller, event):
markupsNode = caller
sliceView = markupsNode.GetAttribute('Markups.MovingInSliceView')
movingMarkupIndex = markupsNode.GetDisplayNode().GetActiveControlPoint()
logging.info("End interaction: point ID = {0}, slice view = {1}".format(movingMarkupIndex, sliceView))
markupsNode = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass("vtkMRMLMarkupsFiducialNode")
markupsNode.CreateDefaultDisplayNodes()
markupsNode.AddFiducial(0,0,0)
markupsNode.AddObserver(slicer.vtkMRMLMarkupsNode.PointModifiedEvent, onMarkupChanged)
markupsNode.AddObserver(slicer.vtkMRMLMarkupsNode.PointStartInteractionEvent, onMarkupStartInteraction)
markupsNode.AddObserver(slicer.vtkMRMLMarkupsNode.PointEndInteractionEvent, onMarkupEndInteraction)
Get a notification if a transform is modified
def onTransformNodeModified(transformNode, unusedArg2=None, unusedArg3=None):
transformMatrix = vtk.vtkMatrix4x4()
transformNode.GetMatrixTransformToWorld(transformMatrix)
print("Position: [{0}, {1}, {2}]".format(transformMatrix.GetElement(0,3), transformMatrix.GetElement(1,3), transformMatrix.GetElement(2,3)))
transformNode = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass("vtkMRMLTransformNode")
transformNode.AddObserver(slicer.vtkMRMLTransformNode.TransformModifiedEvent, onTransformNodeModified)
Rotate a node around a specified point
Set up the scene:
- Add a markup fiducial node (centerOfRotationMarkupsNode) with a single point to specify center of rotation.
- Add a rotation transform (rotationTransformNode) that will be edited in Transforms module to specify rotation angles.
- Add a transform (finalTransformNode) and apply it (not harden) to those nodes (images, models, etc.) that you want to rotate around the center of rotation point.
Then run the script below, go to Transforms module, select rotationTransformNode, and move rotation sliders.
# This markups fiducial node specifies the center of rotation
centerOfRotationMarkupsNode = getNode('F')
# This transform can be edited in Transforms module
rotationTransformNode = getNode('LinearTransform_3')
# This transform has to be applied to the image, model, etc.
finalTransformNode = getNode('LinearTransform_4')
def updateFinalTransform(unusedArg1=None, unusedArg2=None, unusedArg3=None):
rotationMatrix = vtk.vtkMatrix4x4()
rotationTransformNode.GetMatrixTransformToParent(rotationMatrix)
rotationCenterPointCoord = [0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
centerOfRotationMarkupsNode.GetNthControlPointPositionWorld(0, rotationCenterPointCoord)
finalTransform = vtk.vtkTransform()
finalTransform.Translate(rotationCenterPointCoord)
finalTransform.Concatenate(rotationMatrix)
finalTransform.Translate(-rotationCenterPointCoord[0], -rotationCenterPointCoord[1], -rotationCenterPointCoord[2])
finalTransformNode.SetAndObserveMatrixTransformToParent(finalTransform.GetMatrix())
# Manual initial update
updateFinalTransform()
# Automatic update when point is moved or transform is modified
rotationTransformNodeObserver = rotationTransformNode.AddObserver(slicer.vtkMRMLTransformNode.TransformModifiedEvent, updateFinalTransform)
centerOfRotationMarkupsNodeObserver = centerOfRotationMarkupsNode.AddObserver(slicer.vtkMRMLMarkupsNode.PointModifiedEvent, updateFinalTransform)
# Execute these lines to stop automatic updates:
# rotationTransformNode.RemoveObserver(rotationTransformNodeObserver)
# centerOfRotationMarkupsNode.RemoveObserver(centerOfRotationMarkupsNodeObserver)
Rotate a node around a specified line
Set up the scene:
- Add a markup line node (rotationAxisMarkupsNode) with 2 points to specify rotation axis.
- Add a rotation transform (rotationTransformNode) that will be edited in Transforms module to specify rotation angle.
- Add a transform (finalTransformNode) and apply it (not harden) to those nodes (images, models, etc.) that you want to rotate around the line.
Then run the script below, go to Transforms module, select rotationTransformNode, and move Edit / Rotation / IS slider.
# This markups fiducial node specifies the center of rotation
rotationAxisMarkupsNode = getNode('L')
# This transform can be edited in Transforms module (Edit / Rotation / IS slider)
rotationTransformNode = getNode('LinearTransform_3')
# This transform has to be applied to the image, model, etc.
finalTransformNode = getNode('LinearTransform_4')
def updateFinalTransform(unusedArg1=None, unusedArg2=None, unusedArg3=None):
import numpy as np
rotationAxisPoint1_World = np.zeros(3)
rotationAxisMarkupsNode.GetNthControlPointPositionWorld(0, rotationAxisPoint1_World)
rotationAxisPoint2_World = np.zeros(3)
rotationAxisMarkupsNode.GetNthControlPointPositionWorld(1, rotationAxisPoint2_World)
axisDirectionZ_World = rotationAxisPoint2_World-rotationAxisPoint1_World
axisDirectionZ_World = axisDirectionZ_World/np.linalg.norm(axisDirectionZ_World)
# Get transformation between world coordinate system and rotation axis aligned coordinate system
worldToRotationAxisTransform = vtk.vtkMatrix4x4()
p=vtk.vtkPlaneSource()
p.SetNormal(axisDirectionZ_World)
axisOrigin = np.array(p.GetOrigin())
axisDirectionX_World = np.array(p.GetPoint1())-axisOrigin
axisDirectionY_World = np.array(p.GetPoint2())-axisOrigin
rotationAxisToWorldTransform = np.row_stack((np.column_stack((axisDirectionX_World, axisDirectionY_World, axisDirectionZ_World, rotationAxisPoint1_World)), (0, 0, 0, 1)))
rotationAxisToWorldTransformMatrix = slicer.util.vtkMatrixFromArray(rotationAxisToWorldTransform)
worldToRotationAxisTransformMatrix = slicer.util.vtkMatrixFromArray(np.linalg.inv(rotationAxisToWorldTransform))
# Compute transformation chain
rotationMatrix = vtk.vtkMatrix4x4()
rotationTransformNode.GetMatrixTransformToParent(rotationMatrix)
finalTransform = vtk.vtkTransform()
finalTransform.Concatenate(rotationAxisToWorldTransformMatrix)
finalTransform.Concatenate(rotationMatrix)
finalTransform.Concatenate(worldToRotationAxisTransformMatrix)
finalTransformNode.SetAndObserveMatrixTransformToParent(finalTransform.GetMatrix())
# Manual initial update
updateFinalTransform()
# Automatic update when point is moved or transform is modified
rotationTransformNodeObserver = rotationTransformNode.AddObserver(slicer.vtkMRMLTransformNode.TransformModifiedEvent, updateFinalTransform)
rotationAxisMarkupsNodeObserver = rotationAxisMarkupsNode.AddObserver(slicer.vtkMRMLMarkupsNode.PointModifiedEvent, updateFinalTransform)
# Execute these lines to stop automatic updates:
# rotationTransformNode.RemoveObserver(rotationTransformNodeObserver)
# rotationAxisMarkupsNode.RemoveObserver(rotationAxisMarkupsNodeObserver)
Subject hierarchy plugins can offer actions in the view context menu when right-clicking objects that support such picking (such as Markups fiducials). A comprehensive subject hierarchy plugin example is for the Annotations module.
def viewContextMenuActions(self):
return [self.doSomething]
def showViewContextMenuActionsForItem(self, itemID, eventData):
if not itemID:
logging.error('Invalid item for view context menu ' + str(itemID))
return
pluginHandlerSingleton = slicer.qSlicerSubjectHierarchyPluginHandler.instance()
shNode = pluginHandlerSingleton.subjectHierarchyNode()
if shNode is None:
logging.error('Failed to access subject hierarchy node')
return
associatedNode = shNode.GetItemDataNode(itemID)
if not associatedNode or not associatedNode.IsA("vtkMRMLMarkupsNode"):
return
self.viewMenuEventData = eventData
self.viewMenuEventData['NodeID'] = associatedNode.GetID()
def onDoSomething(self):
nodeID = self.viewMenuEventData['NodeID']
markupsNode = slicer.mrmlScene.GetNodeByID(nodeID)
if markupsNode is None or not markupsNode.IsA("vtkMRMLMarkupsNode"):
logging.error('Failed to get fiducial markups node by ID ' + str(nodeID))
return
componentIndex = self.viewMenuEventData['ComponentIndex']
markupID = markupsNode.GetNthMarkupID(componentIndex)
# Do something with the clicked fiducial
Write markup positions to JSON file
markupNode = getNode('F')
outputFileName = 'c:/tmp/test.json'
# Get markup positions
data = []
for fidIndex in range(markupNode.GetNumberOfFiducials()):
coords=[0,0,0]
markupNode.GetNthFiducialPosition(fidIndex,coords)
data.append({'label': markupNode.GetNthFiducialLabel(), 'position': coords})
import json
with open(outputFileName, 'w') as outfile:
json.dump(data, outfile)
Write annotation ROI to JSON file
roiNode = getNode('R')
outputFileName = "c:/tmp/test.json"
# Get annotation ROI data
center = [0,0,0]
radius = [0,0,0]
roiNode.GetControlPointWorldCoordinates(0, center)
roiNode.GetControlPointWorldCoordinates(1, radius)
data = {'center': radius, 'radius': radius}
# Write to json file
import json
with open(outputFileName, 'w') as outfile:
json.dump(data, outfile)
Show a simple surface mesh as a model node
This example shows how to display a simple surface mesh (a box, created by a VTK source filter) as a model node.
# Create and set up polydata source box = vtk.vtkCubeSource() box.SetXLength(30) box.SetYLength(20) box.SetZLength(15) box.SetCenter(10,20,5) # Create a model node that displays output of the source boxNode = slicer.modules.models.logic().AddModel(box.GetOutputPort()) # Adjust display properties boxNode.GetDisplayNode().SetColor(1,0,0) boxNode.GetDisplayNode().SetOpacity(0.8)
Measure distance of points from surface
This example computes closest distance of points (markups fiducial 'F') from a surface (model node 'mymodel') and writes results into a table.
markupsNode = getNode('F')
modelNode = getNode('mymodel')
# Transform model polydata to world coordinate system
if modelNode.GetParentTransformNode():
transformModelToWorld = vtk.vtkGeneralTransform()
slicer.vtkMRMLTransformNode.GetTransformBetweenNodes(modelNode.GetParentTransformNode(), None, transformModelToWorld)
polyTransformToWorld = vtk.vtkTransformPolyDataFilter()
polyTransformToWorld.SetTransform(transformModelToWorld)
polyTransformToWorld.SetInputData(modelNode.GetPolyData())
polyTransformToWorld.Update()
surface_World = polyTransformToWorld.GetOutput()
else:
surface_World = modelNode.GetPolyData()
# Create arrays to store results
indexCol = vtk.vtkIntArray()
indexCol.SetName("Index")
labelCol = vtk.vtkStringArray()
labelCol.SetName("Name")
distanceCol = vtk.vtkDoubleArray()
distanceCol.SetName("Distance")
distanceFilter = vtk.vtkImplicitPolyDataDistance()
distanceFilter.SetInput(surface_World);
nOfFiduciallPoints = markupsNode.GetNumberOfFiducials()
for i in range(0, nOfFiduciallPoints):
point_World = [0,0,0]
markupsNode.GetNthControlPointPositionWorld(i, point_World)
closestPointOnSurface_World = [0,0,0]
closestPointDistance = distanceFilter.EvaluateFunctionAndGetClosestPoint(point_World, closestPointOnSurface_World)
indexCol.InsertNextValue(i)
labelCol.InsertNextValue(markupsNode.GetNthControlPointLabel(i))
distanceCol.InsertNextValue(closestPointDistance)
# Create a table from result arrays
resultTableNode = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass("vtkMRMLTableNode", "Points from surface distance")
resultTableNode.AddColumn(indexCol)
resultTableNode.AddColumn(labelCol)
resultTableNode.AddColumn(distanceCol)
# Show table in view layout
slicer.app.layoutManager().setLayout(slicer.vtkMRMLLayoutNode.SlicerLayoutFourUpTableView)
slicer.app.applicationLogic().GetSelectionNode().SetReferenceActiveTableID(resultTableNode.GetID())
slicer.app.applicationLogic().PropagateTableSelection()
Add a texture mapped plane to the scene as a model
Note that model textures are not exposed in the GUI and are not saved in the scene
# Create model node planeSource = vtk.vtkPlaneSource() planeSource.SetOrigin(-50.0, -50.0, 0.0) planeSource.SetPoint1(50.0, -50.0, 0.0) planeSource.SetPoint2(-50.0, 50.0, 0.0) model = slicer.modules.models.logic().AddModel(planeSource.GetOutputPort()) # Tune display properties modelDisplay = model.GetDisplayNode() modelDisplay.SetColor(1,1,0) # yellow modelDisplay.SetBackfaceCulling(0) # Add texture (just use image of an ellipsoid) e = vtk.vtkImageEllipsoidSource() modelDisplay.SetTextureImageDataConnection(e.GetOutputPort())
Get scalar values at surface of a model
The following script allows getting selected scalar value at a selected position of a model. Position can be selected by moving the mouse while holding down Shift key.
modelNode = getNode('sphere')
modelPointValues = modelNode.GetPolyData().GetPointData().GetArray("Normals")
markupsNode = slicer.mrmlScene.GetFirstNodeByName('F')
if not markupsNode:
markupsNode = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass("vtkMRMLMarkupsFiducialNode","F")
pointsLocator = vtk.vtkPointLocator() # could try using vtk.vtkStaticPointLocator() if need to optimize
pointsLocator.SetDataSet(modelNode.GetPolyData())
pointsLocator.BuildLocator()
def onMouseMoved(observer,eventid):
ras=[0,0,0]
crosshairNode.GetCursorPositionRAS(ras)
if markupsNode.GetNumberOfFiducials() == 0:
markupsNode.AddFiducial(*ras)
else:
markupsNode.SetNthFiducialPosition(0,*ras)
closestPointId = pointsLocator.FindClosestPoint(ras)
closestPointValue = modelPointValues.GetTuple(closestPointId)
print("RAS = " + repr(ras) + " value = " + repr(closestPointValue))
crosshairNode=slicer.util.getNode('Crosshair')
observationId = crosshairNode.AddObserver(slicer.vtkMRMLCrosshairNode.CursorPositionModifiedEvent, onMouseMoved)
# To stop printing of values run this:
# crosshairNode.RemoveObserver(observationId)
Apply VTK filter on a model node
modelNode = getNode('tip')
# Compute curvature
curv = vtk.vtkCurvatures()
curv.SetInputData(modelNode.GetPolyData())
modelNode.SetPolyDataConnection(curv.GetOutputPort())
# Set up coloring by Curvature
modelNode.GetDisplayNode().SetActiveScalar("Gauss_Curvature", vtk.vtkAssignAttribute.POINT_DATA)
modelNode.GetDisplayNode().SetAndObserveColorNodeID("Viridis")
modelNode.GetDisplayNode().SetScalarVisibility(True)
Select cells of a model using markups fiducial points
The following script selects cells of a model node that are closest to positions of markups fiducial points.
# Get input nodes
modelNode = slicer.util.getNode('Segment_1') # select cells in this model
markupsNode = slicer.util.getNode('F') # points will be selected at positions specified by this markups fiducial node
# Create scalar array that will store selection state
cellScalars = modelNode.GetMesh().GetCellData()
selectionArray = cellScalars.GetArray('selection')
if not selectionArray:
selectionArray = vtk.vtkIntArray()
selectionArray.SetName('selection')
selectionArray.SetNumberOfValues(modelNode.GetMesh().GetNumberOfCells())
selectionArray.Fill(0)
cellScalars.AddArray(selectionArray)
# Set up coloring by selection array
modelNode.GetDisplayNode().SetActiveScalar("selection", vtk.vtkAssignAttribute.CELL_DATA)
modelNode.GetDisplayNode().SetAndObserveColorNodeID("vtkMRMLColorTableNodeWarm1")
modelNode.GetDisplayNode().SetScalarVisibility(True)
# Initialize cell locator
cell = vtk.vtkCellLocator()
cell.SetDataSet(modelNode.GetMesh())
cell.BuildLocator()
def onPointsModified(observer=None, eventid=None):
global markupsNode, selectionArray
selectionArray.Fill(0) # set all cells to non-selected by default
markupPoints = slicer.util.arrayFromMarkupsControlPoints(markupsNode)
closestPoint = [0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
cellObj = vtk.vtkGenericCell()
cellId = vtk.mutable(0)
subId = vtk.mutable(0)
dist2 = vtk.mutable(0.0)
for markupPoint in markupPoints:
cell.FindClosestPoint(markupPoint, closestPoint, cellObj, cellId, subId, dist2)
closestCell = cellId.get()
if closestCell >=0:
selectionArray.SetValue(closestCell, 100) # set selected cell's scalar value to non-zero
selectionArray.Modified()
# Initial update
onPointsModified()
# Automatic update each time when a markup point is modified
markupsNodeObserverTag = markupsNode.AddObserver(slicer.vtkMRMLMarkupsFiducialNode.PointModifiedEvent, onPointsModified)
# To stop updating selection, run this:
# markupsNode.RemoveObserver(markupsNodeObserverTag)
Load volume from .vti file
Slicer does not provide reader for VTK XML image data file format (as they are not commonly used for storing medical images and they cannot store image axis directions) but such files can be read by using this script:
reader=vtk.vtkXMLImageDataReader()
reader.SetFileName("/path/to/file.vti")
reader.Update()
imageData = reader.GetOutput()
spacing = imageData.GetSpacing()
origin = imageData.GetOrigin()
imageData.SetOrigin(0,0,0)
imageData.SetSpacing(1,1,1)
volumeNode=slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass("vtkMRMLScalarVolumeNode")
volumeNode.SetAndObserveImageData(imageData)
volumeNode.SetSpacing(spacing)
volumeNode.SetOrigin(origin)
slicer.util.setSliceViewerLayers(volumeNode, fit=True)
Export entire scene as VRML
Save all surface meshes displayed in the scene (models, markups, etc). Solid colors and coloring by scalar is preserved. Textures are not supported.
exporter = vtk.vtkVRMLExporter()
exporter.SetRenderWindow(slicer.app.layoutManager().threeDWidget(0).threeDView().renderWindow())
exporter.SetFileName('C:/tmp/something.wrl')
exporter.Write()
Export model to Blender, including color by scalar
modelNode = getNode("Model")
plyFilePath = "c:/tmp/model.ply"
modelDisplayNode = modelNode.GetDisplayNode()
triangles = vtk.vtkTriangleFilter()
triangles.SetInputConnection(modelDisplayNode.GetOutputPolyDataConnection())
plyWriter = vtk.vtkPLYWriter()
plyWriter.SetInputConnection(triangles.GetOutputPort())
lut = vtk.vtkLookupTable()
lut.DeepCopy(modelDisplayNode.GetColorNode().GetLookupTable())
lut.SetRange(modelDisplayNode.GetScalarRange())
plyWriter.SetLookupTable(lut)
plyWriter.SetArrayName(modelDisplayNode.GetActiveScalarName())
plyWriter.SetFileName(plyFilePath)
plyWriter.Write()
Export a tract (FiberBundle) to Blender, including color
Note: an interactive version of this script is now included in the SlicerDMRI extension (module code). After installing SlicerDMRI, go to Modules -> Diffusion -> Import and Export -> Export tractography to PLY (mesh).
The example below shows how to export a tractography "FiberBundleNode" to a PLY file:
lineDisplayNode = getNode("*LineDisplay*")
plyFilePath = "/tmp/fibers.ply"
tuber = vtk.vtkTubeFilter()
tuber.SetInputData(lineDisplayNode.GetOutputPolyData())
tuber.Update()
tubes = tuber.GetOutputDataObject(0)
scalars = tubes.GetPointData().GetArray(0)
scalars.SetName("scalars")
triangles = vtk.vtkTriangleFilter()
triangles.SetInputData(tubes)
triangles.Update()
colorNode = lineDisplayNode.GetColorNode()
lookupTable = vtk.vtkLookupTable()
lookupTable.DeepCopy(colorNode.GetLookupTable())
lookupTable.SetTableRange(0,1)
plyWriter = vtk.vtkPLYWriter()
plyWriter.SetInputData(triangles.GetOutput())
plyWriter.SetLookupTable(lookupTable)
plyWriter.SetArrayName("scalars")
plyWriter.SetFileName(plyFilePath)
plyWriter.Write()
Iterate over tract (FiberBundle) streamline points
This example shows how to access the points in each line of a FiberBundle as a numpy array (view).
from vtk.util.numpy_support import vtk_to_numpy
fb = getNode("FiberBundle_F") # <- fill in node ID here
# get point data as 1d array
points = slicer.util.arrayFromModelPoints(fb)
# get line cell ids as 1d array
line_ids = vtk_to_numpy(fb.GetPolyData().GetLines().GetData())
# VTK cell ids are stored as
# [ N0 c0_id0 ... c0_id0
# N1 c1_id0 ... c1_idN1 ]
# so we need to
# - read point count for each line (cell)
# - grab the ids in that range from `line_ids` array defined above
# - index the `points` array by those ids
cur_idx = 1
for _ in range(pd.GetLines().GetNumberOfCells()):
# - read point count for this line (cell)
count = lines[cur_idx - 1]
# - grab the ids in that range from `lines`
index_array = line_ids[ cur_idx : cur_idx + count]
# update to the next range
cur_idx += count + 1
# - index the point array by those ids
line_points = points[index_array]
# do work here
Clone a node
This example shows how to make a copy of any node that appears in Subject Hierarchy (in Data module).
# Get a node from SampleData that we will clone import SampleData nodeToClone = SampleData.SampleDataLogic().downloadMRHead() # Clone the node shNode = slicer.vtkMRMLSubjectHierarchyNode.GetSubjectHierarchyNode(slicer.mrmlScene) itemIDToClone = shNode.GetItemByDataNode(nodeToClone) clonedItemID = slicer.modules.subjecthierarchy.logic().CloneSubjectHierarchyItem(shNode, itemIDToClone) clonedNode = shNode.GetItemDataNode(clonedItemID)
Clone a volume
This example shows how to clone the MRHead sample volume, including its pixel data and display settings.
sourceVolumeNode = slicer.util.getNode('MRHead')
volumesLogic = slicer.modules.volumes.logic()
clonedVolumeNode = volumesLogic.CloneVolume(slicer.mrmlScene, sourceVolumeNode, 'Cloned volume')
Create a new volume
This example shows how to create a new empty volume.
nodeName = "MyNewVolume"
imageSize = [512, 512, 512]
voxelType=vtk.VTK_UNSIGNED_CHAR
imageOrigin = [0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
imageSpacing = [1.0, 1.0, 1.0]
imageDirections = [[1,0,0], [0,1,0], [0,0,1]]
fillVoxelValue = 0
# Create an empty image volume, filled with fillVoxelValue
imageData = vtk.vtkImageData()
imageData.SetDimensions(imageSize)
imageData.AllocateScalars(voxelType, 1)
imageData.GetPointData().GetScalars().Fill(fillVoxelValue)
# Create volume node
volumeNode = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass("vtkMRMLScalarVolumeNode", nodeName)
volumeNode.SetOrigin(imageOrigin)
volumeNode.SetSpacing(imageSpacing)
volumeNode.SetIJKToRASDirections(imageDirections)
volumeNode.SetAndObserveImageData(imageData)
volumeNode.CreateDefaultDisplayNodes()
volumeNode.CreateDefaultStorageNode()
Get value of a volume at specific voxel coordinates
This example shows how to get voxel value of "volumeNode" at "ijk" volume voxel coordinates.
volumeNode = slicer.util.getNode('MRHead')
ijk = [20,40,30] # volume voxel coordinates
voxels = slicer.util.arrayFromVolume(volumeNode) # get voxels as a numpy array
voxelValue = voxels[ijk[2], ijk[1], ijk[0]] # note that numpy array index order is kji (not ijk)
Modify voxels in a volume
Typically the fastest and simplest way of modifying voxels is by using numpy operators. Voxels can be retrieved in a numpy array using the `array` method and modified using standard numpy methods. For example, threshold a volume:
nodeName = 'MRHead' thresholdValue = 100 voxelArray = array(nodeName) # get voxels as numpy array voxelArray[voxelArray < thresholdValue] = 0 # modify voxel values getNode(nodeName).Modified() # at the end of all processing, notify Slicer that the image modification is completed
This example shows how to change voxels values of the MRHead sample volume. The values will be computed by function f(r,a,s,) = (r-10)*(r-10)+(a+15)*(a+15)+s*s.
volumeNode=slicer.util.getNode('MRHead')
ijkToRas = vtk.vtkMatrix4x4()
volumeNode.GetIJKToRASMatrix(ijkToRas)
imageData=volumeNode.GetImageData()
extent = imageData.GetExtent()
for k in range(extent[4], extent[5]+1):
for j in range(extent[2], extent[3]+1):
for i in range(extent[0], extent[1]+1):
position_Ijk=[i, j, k, 1]
position_Ras=ijkToRas.MultiplyPoint(position_Ijk)
r=position_Ras[0]
a=position_Ras[1]
s=position_Ras[2]
functionValue=(r-10)*(r-10)+(a+15)*(a+15)+s*s
imageData.SetScalarComponentFromDouble(i,j,k,0,functionValue)
imageData.Modified()
Get volume voxel coordinates from markup fiducial RAS coordinates
This example shows how to get voxel coordinate of a volume corresponding to a markup fiducial point position.
# Inputs
volumeNode = getNode('MRHead')
markupsNode = getNode('F')
markupsIndex = 0
# Get point coordinate in RAS
point_Ras = [0, 0, 0, 1]
markupsNode.GetNthFiducialWorldCoordinates(markupsIndex, point_Ras)
# If volume node is transformed, apply that transform to get volume's RAS coordinates
transformRasToVolumeRas = vtk.vtkGeneralTransform()
slicer.vtkMRMLTransformNode.GetTransformBetweenNodes(None, volumeNode.GetParentTransformNode(), transformRasToVolumeRas)
point_VolumeRas = transformRasToVolumeRas.TransformPoint(point_Ras[0:3])
# Get voxel coordinates from physical coordinates
volumeRasToIjk = vtk.vtkMatrix4x4()
volumeNode.GetRASToIJKMatrix(volumeRasToIjk)
point_Ijk = [0, 0, 0, 1]
volumeRasToIjk.MultiplyPoint(np.append(point_VolumeRas,1.0), point_Ijk)
point_Ijk = [ int(round(c)) for c in point_Ijk[0:3] ]
# Print output
print(point_Ijk)
Get markup fiducial RAS coordinates from volume voxel coordinates
This example shows how to get position of maximum intensity voxel of a volume (determined by numpy, in IJK coordinates) in RAS coordinates so that it can be marked with a markup fiducial.
# Inputs
volumeNode = getNode('MRHead')
markupsNode = getNode('F')
# Get voxel position in IJK coordinate system
import numpy as np
volumeArray = slicer.util.arrayFromVolume(volumeNode)
# Get position of highest voxel value
point_Kji = np.where(volumeArray == volumeArray.max())
point_Ijk = [point_Kji[2][0], point_Kji[1][0], point_Kji[0][0]]
# Get physical coordinates from voxel coordinates
volumeIjkToRas = vtk.vtkMatrix4x4()
volumeNode.GetIJKToRASMatrix(volumeIjkToRas)
point_VolumeRas = [0, 0, 0, 1]
volumeIjkToRas.MultiplyPoint(np.append(point_Ijk,1.0), point_VolumeRas)
# If volume node is transformed, apply that transform to get volume's RAS coordinates
transformVolumeRasToRas = vtk.vtkGeneralTransform()
slicer.vtkMRMLTransformNode.GetTransformBetweenNodes(volumeNode.GetParentTransformNode(), None, transformVolumeRasToRas)
point_Ras = transformVolumeRasToRas.TransformPoint(point_VolumeRas[0:3])
# Add a markup at the computed position and print its coordinates
markupsNode.AddFiducial(point_Ras[0], point_Ras[1], point_Ras[2], "max")
print(point_Ras)
Get the values of all voxels for a label value
If you have a background image called ‘Volume’ and a mask called ‘Volume-label’ created with the Editor you could do something like this:
import numpy
volume = array('Volume')
label = array('Volume-label')
points = numpy.where( label == 1 ) # or use another label number depending on what you segmented
values = volume[points] # this will be a list of the label values
values.mean() # should match the mean value of LabelStatistics calculation as a double-check
numpy.savetxt('values.txt', values)
Access values in a DTI tensor volume
This example shows how to access individual tensors at the voxel level.
First load your DWI volume and estimate tensors to produce a DTI volume called ‘Output DTI Volume’
Then open the python window: View->Python interactor
Use this command to access tensors through numpy:
tensors = array('Output DTI Volume')
Type the following code into the Python window to access all tensor components using vtk commands:
volumeNode=slicer.util.getNode('Output DTI Volume')
imageData=volumeNode.GetImageData()
tensors = imageData.GetPointData().GetTensors()
extent = imageData.GetExtent()
idx = 0
for k in range(extent[4], extent[5]+1):
for j in range(extent[2], extent[3]+1):
for i in range(extent[0], extent[1]+1):
tensors.GetTuple9(idx)
idx += 1
Change window/level (brightness/contrast) or colormap of a volume
This example shows how to change window/level of the MRHead sample volume.
volumeNode = getNode('MRHead')
displayNode = volumeNode.GetDisplayNode()
displayNode.AutoWindowLevelOff()
displayNode.SetWindow(50)
displayNode.SetLevel(100)
Change color mapping from grayscale to rainbow:
displayNode.SetAndObserveColorNodeID('vtkMRMLColorTableNodeRainbow')
Make mouse left-click and drag on the image adjust window/level
In older Slicer versions, by default, left-click and drag in a slice view adjusted window/level of the displayed image. Window/level adjustment is now a new mouse mode that can be activated by clicking on its toolbar button or running this code:
slicer.app.applicationLogic().GetInteractionNode().SetCurrentInteractionMode(slicer.vtkMRMLInteractionNode.AdjustWindowLevel)
Create custom color table
This example shows how to create a new color table, for example with inverted color range from the default Ocean color table.
invertedocean = slicer.vtkMRMLColorTableNode()
invertedocean.SetTypeToUser()
invertedocean.SetNumberOfColors(256)
invertedocean.SetName("InvertedOcean")
for i in range(0,255):
invertedocean.SetColor(i, 0.0, 1 - (i+1e-16)/255.0, 1.0, 1.0)
slicer.mrmlScene.AddNode(invertedocean)
Manipulate a Slice View
Change slice offset
Equivalent to moving the slider in slice view controller.
layoutManager = slicer.app.layoutManager()
red = layoutManager.sliceWidget('Red')
redLogic = red.sliceLogic()
# Print current slice offset position
print(redLogic.GetSliceOffset())
# Change slice position
redLogic.SetSliceOffset(20)
Change slice orientation
Get 'Red' slice node and rotate around X and Y axes.
sliceNode = slicer.app.layoutManager().sliceWidget('Red').mrmlSliceNode()
sliceToRas = sliceNode.GetSliceToRAS()
transform=vtk.vtkTransform()
transform.SetMatrix(SliceToRAS)
transform.RotateX(20)
transform.RotateY(15)
sliceToRas.DeepCopy(transform.GetMatrix())
sliceNode.UpdateMatrices()
Show slice views in 3D window
Equivalent to clicking 'eye' icon in the slice view controller.
layoutManager = slicer.app.layoutManager() for sliceViewName in layoutManager.sliceViewNames(): controller = layoutManager.sliceWidget(sliceViewName).sliceController() controller.setSliceVisible(True)
Reset field of view to show background volume maximized
Equivalent to click small rectangle button ("Adjust the slice viewer's field of view...") in the slice view controller.
slicer.util.resetSliceViews()
Rotate slice views to volume plane
Aligns slice views to volume axes, shows original image acquisition planes in slice views.
volumeNode = slicer.util.getNode('MRHead')
layoutManager = slicer.app.layoutManager()
for sliceViewName in layoutManager.sliceViewNames():
layoutManager.sliceWidget(sliceViewName).mrmlSliceNode().RotateToVolumePlane(volumeNode)
Iterate over current visible slice views, and set foreground and background images
slicer.util.setSliceViewerLayers(background=mrVolume, foreground=ctVolume)
Internally, this method performs something like this:
layoutManager = slicer.app.layoutManager()
for sliceViewName in layoutManager.sliceViewNames():
compositeNode = layoutManager.sliceWidget(sliceViewName).sliceLogic().GetSliceCompositeNode()
# setup background volume
compositeNode.SetBackgroundVolumeID(mrVolume.GetID())
# setup foreground volume
compositeNode.SetForegroundVolumeID(ctVolume.GetID())
# change opacity
compositeNode.SetForegroundOpacity(0.3)
Show a volume in slice views
Recommended:
volumeNode = slicer.util.getNode('YourVolumeNode')
slicer.util.setSliceViewerLayers(background=volumeNode)
or
Show volume in all visible views where volume selection propagation is enabled:
volumeNode = slicer.util.getNode('YourVolumeNode')
applicationLogic = slicer.app.applicationLogic()
selectionNode = applicationLogic.GetSelectionNode()
selectionNode.SetSecondaryVolumeID(volumeNode.GetID())
applicationLogic.PropagateForegroundVolumeSelection(0)
or
Show volume in selected views:
n = slicer.util.getNode('YourVolumeNode')
for color in ['Red', 'Yellow', 'Green']:
slicer.app.layoutManager().sliceWidget(color).sliceLogic().GetSliceCompositeNode().SetForegroundVolumeID(n.GetID())
Show comparison view of all model files a folder
# Inputs
modelDir = "c:/some/folder/containing/models"
modelFileExt = "stl"
numberOfColumns = 4
import math
import os
modelFiles = list(f for f in os.listdir(modelDir) if f.endswith('.' + modelFileExt))
# Create a custom layout
numberOfRows = int(math.ceil(len(modelFiles)/numberOfColumns))
customLayoutId=567 # we pick a random id that is not used by others
slicer.app.setRenderPaused(True)
customLayout = '<layout type="vertical">'
viewIndex = 0
for rowIndex in range(numberOfRows):
customLayout += '<item><layout type="horizontal">'
for colIndex in range(numberOfColumns):
name = os.path.basename(modelFiles[viewIndex]) if viewIndex < len(modelFiles) else "compare "+str(viewIndex)
customLayout += '<item><view class="vtkMRMLViewNode" singletontag="'+name
customLayout += '"><property name="viewlabel" action="default">'+name+'</property></view></item>'
viewIndex += 1
customLayout += '</layout></item>'
customLayout += '</layout>'
if not slicer.app.layoutManager().layoutLogic().GetLayoutNode().SetLayoutDescription(customLayoutId, customLayout):
slicer.app.layoutManager().layoutLogic().GetLayoutNode().AddLayoutDescription(customLayoutId, customLayout)
slicer.app.layoutManager().setLayout(customLayoutId)
# Load and show each model in a view
for modelIndex, modelFile in enumerate(modelFiles):
# Show only one model in each view
name = os.path.basename(modelFile)
viewNode = slicer.mrmlScene.GetSingletonNode(name, "vtkMRMLViewNode")
viewNode.LinkedControlOn()
modelNode = slicer.util.loadModel(modelDir+"/"+modelFile)
modelNode.GetDisplayNode().AddViewNodeID(viewNode.GetID())
slicer.app.setRenderPaused(False)
Change opacity of foreground volume in slice views
slicer.util.setSliceViewerLayers(foregroundOpacity=0.4)
or
Change opacity in a selected view
lm = slicer.app.layoutManager()
sliceLogic = lm.sliceWidget('Red').sliceLogic()
compositeNode = sliceLogic.GetSliceCompositeNode()
compositeNode.SetForegroundOpacity(0.4)
Fit slice plane to markup fiducials
sliceNode = slicer.mrmlScene.GetNodeByID("vtkMRMLSliceNodeRed")
markupsNode = slicer.mrmlScene.GetFirstNodeByName("F")
# Get markup point positions as numpy arrays
import numpy as np
p1 = np.zeros(3)
p2 = np.zeros(3)
p3 = np.zeros(3)
markupsNode.GetNthFiducialPosition(0, p1)
markupsNode.GetNthFiducialPosition(1, p2)
markupsNode.GetNthFiducialPosition(2, p3)
# Get plane axis directions
n = np.cross(p2-p1, p2-p3) # plane normal direction
n = n/np.linalg.norm(n)
t = np.cross([0.0, 0.0, 1], n) # plane transverse direction
t = t/np.linalg.norm(t)
# Set slice plane orientation and position
sliceNode.SetSliceToRASByNTP(n[0], n[1], n[2], t[0], t[1], t[2], p1[0], p1[1], p1[2], 0)
Save a series of images from a Slice View
You can use ScreenCapture module to capture series of images. To do it programmatically, save the following into a file such as '/tmp/record.py' and then in the slicer python console type "execfile('/tmp/record.py')"
layoutName = 'Green'
imagePathPattern = '/tmp/image-%03d.png'
steps = 10
widget = slicer.app.layoutManager().sliceWidget(layoutName)
view = widget.sliceView()
logic = widget.sliceLogic()
bounds = [0,]*6
logic.GetSliceBounds(bounds)
for step in range(steps):
offset = bounds[4] + step/(1.*steps) * (bounds[5]-bounds[4])
logic.SetSliceOffset(offset)
view.forceRender()
image = qt.QPixmap.grabWidget(view).toImage()
image.save(imagePathPattern % step)
Rasterize a model and save it to a series of image files
This example shows how to generate a stack of image files from an STL file:
inputModelFile = "/some/input/folder/SomeShape.stl"
outputDir = "/some/output/folder"
outputVolumeLabelValue = 100
outputVolumeSpacingMm = [0.5, 0.5, 0.5]
outputVolumeMarginMm = [10.0, 10.0, 10.0]
# Read model
inputModel = slicer.util.loadModel(inputModelFile)
# Determine output volume geometry and create a corresponding reference volume
import math
import numpy as np
bounds = np.zeros(6)
inputModel.GetBounds(bounds)
imageData = vtk.vtkImageData()
imageSize = [ int((bounds[axis*2+1]-bounds[axis*2]+outputVolumeMarginMm[axis]*2.0)/outputVolumeSpacingMm[axis]) for axis in range(3) ]
imageOrigin = [ bounds[axis*2]-outputVolumeMarginMm[axis] for axis in range(3) ]
imageData.SetDimensions(imageSize)
imageData.AllocateScalars(vtk.VTK_UNSIGNED_CHAR, 1)
imageData.GetPointData().GetScalars().Fill(0)
referenceVolumeNode = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass("vtkMRMLScalarVolumeNode")
referenceVolumeNode.SetOrigin(imageOrigin)
referenceVolumeNode.SetSpacing(outputVolumeSpacingMm)
referenceVolumeNode.SetAndObserveImageData(imageData)
referenceVolumeNode.CreateDefaultDisplayNodes()
# Convert model to labelmap
seg = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass('vtkMRMLSegmentationNode')
seg.SetReferenceImageGeometryParameterFromVolumeNode(referenceVolumeNode)
slicer.modules.segmentations.logic().ImportModelToSegmentationNode(inputModel, seg)
seg.CreateBinaryLabelmapRepresentation()
outputLabelmapVolumeNode = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass('vtkMRMLLabelMapVolumeNode')
slicer.modules.segmentations.logic().ExportVisibleSegmentsToLabelmapNode(seg, outputLabelmapVolumeNode, referenceVolumeNode)
outputLabelmapVolumeArray = (slicer.util.arrayFromVolume(outputLabelmapVolumeNode) * outputVolumeLabelValue).astype('int8')
# Write labelmap volume to series of TIFF files
pip_install("imageio")
import imageio
for i in range(len(outputLabelmapVolumeArray)):
imageio.imwrite(f'{outputDir}/image_{i:03}.tiff', outputLabelmapVolumeArray[i])
Save the scene into a new directory
# Create a new directory where the scene will be saved into
import time
sceneSaveDirectory = slicer.app.temporaryPath + "/saved-scene-" + time.strftime("%Y%m%d-%H%M%S")
if not os.access(sceneSaveDirectory, os.F_OK):
os.makedirs(sceneSaveDirectory)
# Save the scene
if slicer.app.applicationLogic().SaveSceneToSlicerDataBundleDirectory(sceneSaveDirectory, None):
logging.info("Scene saved to: {0}".format(sceneSaveDirectory))
else:
logging.error("Scene saving failed")
Save the scene into a single MRB file
# Generate file name
import time
sceneSaveFilename = slicer.app.temporaryPath + "/saved-scene-" + time.strftime("%Y%m%d-%H%M%S") + ".mrb"
# Save scene
if slicer.util.saveScene(sceneSaveFilename):
logging.info("Scene saved to: {0}".format(sceneSaveFilename))
else:
logging.error("Scene saving failed")
Save a node to file
Save a transform node to file (should work with any other node type, if file extension is set to a supported one):
myNode = getNode("LinearTransform_3")
myStorageNode = myNode.CreateDefaultStorageNode()
myStorageNode.SetFileName("c:/tmp/something.tfm")
myStorageNode.WriteData(myNode)
Override default scene save dialog
Place this class in the scripted module file to override
class MyModuleFileDialog ():
"""This specially named class is detected by the scripted loadable
module and is the target for optional drag and drop operations.
See: Base/QTGUI/qSlicerScriptedFileDialog.h.
This class is used for overriding default scene save dialog
with simple saving the scene without asking anything.
"""
def __init__(self,qSlicerFileDialog ):
self.qSlicerFileDialog = qSlicerFileDialog
qSlicerFileDialog.fileType = 'NoFile'
qSlicerFileDialog.description = 'Save scene'
qSlicerFileDialog.action = slicer.qSlicerFileDialog.Write
def execDialog(self):
# Implement custom scene save operation here.
# Return True if saving completed successfully,
# return False if saving was cancelled.
...
return saved
Override application close behavior
When application close is requested then by default confirmation popup is displayed. To customize this behavior (for example, allow application closing without displaying default confirmation popup) an event filter can be installed for the close event on the main window:
class CloseApplicationEventFilter(qt.QWidget):
def eventFilter(self, object, event):
if event.type() == qt.QEvent.Close:
event.accept()
return True
return False
filter = CloseApplicationEventFilter()
slicer.util.mainWindow().installEventFilter(filter)
Center the 3D View on the Scene
layoutManager = slicer.app.layoutManager() threeDWidget = layoutManager.threeDWidget(0) threeDView = threeDWidget.threeDView() threeDView.resetFocalPoint()
Rotate the 3D View
layoutManager = slicer.app.layoutManager() threeDWidget = layoutManager.threeDWidget(0) threeDView = threeDWidget.threeDView() threeDView.yaw()
Display text in a 3D view or slice view
The easiest way to show information overlaid on a viewer is to use corner annotations.
view=slicer.app.layoutManager().threeDWidget(0).threeDView() # Set text to "Something" view.cornerAnnotation().SetText(vtk.vtkCornerAnnotation.UpperRight,"Something") # Set color to red view.cornerAnnotation().GetTextProperty().SetColor(1,0,0) # Update the view view.forceRender()
To display text in slice views, replace the first line by this line (and consider hiding slice view annotations, to prevent them from overwriting the text you place there):
view=slicer.app.layoutManager().sliceWidget("Red").sliceView()
Hide slice view annotations (DataProbe)
# Disable slice annotations immediately
sliceAnnotations = slicer.modules.DataProbeInstance.infoWidget.sliceAnnotations
sliceAnnotations.sliceViewAnnotationsEnabled=False
sliceAnnotations.updateSliceViewFromGUI()
# Disable slice annotations persistently (after Slicer restarts)
settings = qt.QSettings()
settings.setValue('DataProbe/sliceViewAnnotations.enabled', 0)
Show scalar bar (DataProbe)
Display color bar for background volume in slice views:
sliceAnnotations = slicer.modules.DataProbeInstance.infoWidget.sliceAnnotations sliceAnnotations.sliceViewAnnotationsEnabled = True sliceAnnotations.scalarBarEnabled = 1 sliceAnnotations.scalarBarSelectedLayer = 'background' # alternative is 'foreground' sliceAnnotations.rangeLabelFormat = 'test %G' sliceAnnotations.updateSliceViewFromGUI()
Turning off interpolation
You can turn off interpolation for newly loaded volumes with this script from Steve Pieper.
def NoInterpolate(caller,event):
for node in slicer.util.getNodes('*').values():
if node.IsA('vtkMRMLScalarVolumeDisplayNode'):
node.SetInterpolate(0)
slicer.mrmlScene.AddObserver(slicer.mrmlScene.NodeAddedEvent, NoInterpolate)
The below link explains how to put this in your startup script.
http://www.na-mic.org/Wiki/index.php/AHM2012-Slicer-Python#Refining_the_code_and_UI_with_slicerrc
Customize viewer layout
Show a custom layout of a 3D view on top of the red slice view:
customLayout = """
<layout type="vertical" split="true">
<item>
<view class="vtkMRMLViewNode" singletontag="1">
<property name="viewlabel" action="default">1</property>
</view>
</item>
<item>
<view class="vtkMRMLSliceNode" singletontag="Red">
<property name="orientation" action="default">Axial</property>
<property name="viewlabel" action="default">R</property>
<property name="viewcolor" action="default">#F34A33</property>
</view>
</item>
</layout>
"""
# Built-in layout IDs are all below 100, so you can choose any large random number
# for your custom layout ID.
customLayoutId=501
layoutManager = slicer.app.layoutManager()
layoutManager.layoutLogic().GetLayoutNode().AddLayoutDescription(customLayoutId, customLayout)
# Switch to the new custom layout
layoutManager.setLayout(customLayoutId)
See description of standard layouts (that can be used as examples) here: https://github.com/Slicer/Slicer/blob/master/Libs/MRML/Logic/vtkMRMLLayoutLogic.cxx
You can use this code snippet to add a button to the layout selector toolbar:
# Add button to layout selector toolbar for this custom layout
viewToolBar = mainWindow().findChild('QToolBar', 'ViewToolBar')
layoutMenu = viewToolBar.widgetForAction(viewToolBar.actions()[0]).menu()
layoutSwitchActionParent = layoutMenu # use `layoutMenu` to add inside layout list, use `viewToolBar` to add next the standard layout list
layoutSwitchAction = layoutSwitchActionParent.addAction("My view") # add inside layout list
layoutSwitchAction.setData(layoutId)
layoutSwitchAction.setIcon(qt.QIcon(':Icons/Go.png'))
layoutSwitchAction.setToolTip('3D and slice view')
Customize keyboard shortcuts
Keyboard shortcuts can be specified for activating any Slicer feature by adding a couple of lines to your .slicerrc file.
For example, this script registers Ctrl+b, Ctrl+n, Ctrl+m, Ctrl+, keyboard shortcuts to switch between red, yellow, green, and 4-up view layouts.
shortcuts = [
('Ctrl+b', lambda: slicer.app.layoutManager().setLayout(slicer.vtkMRMLLayoutNode.SlicerLayoutOneUpRedSliceView)),
('Ctrl+n', lambda: slicer.app.layoutManager().setLayout(slicer.vtkMRMLLayoutNode.SlicerLayoutOneUpYellowSliceView)),
('Ctrl+m', lambda: slicer.app.layoutManager().setLayout(slicer.vtkMRMLLayoutNode.SlicerLayoutOneUpGreenSliceView)),
('Ctrl+,', lambda: slicer.app.layoutManager().setLayout(slicer.vtkMRMLLayoutNode.SlicerLayoutFourUpView))
]
for (shortcutKey, callback) in shortcuts:
shortcut = qt.QShortcut(slicer.util.mainWindow())
shortcut.setKey(qt.QKeySequence(shortcutKey))
shortcut.connect( 'activated()', callback)
Here's an example for cycling through Segment Editor effects (requested on the forum for the SlicerMorph project).
def cycleEffect(delta=1):
try:
orderedNames = list(slicer.modules.SegmentEditorWidget.editor.effectNameOrder())
allNames = slicer.modules.SegmentEditorWidget.editor.availableEffectNames()
for name in allNames:
try:
orderedNames.index(name)
except ValueError:
orderedNames.append(name)
orderedNames.insert(0, None)
activeEffect = slicer.modules.SegmentEditorWidget.editor.activeEffect()
if activeEffect:
activeName = slicer.modules.SegmentEditorWidget.editor.activeEffect().name
else:
activeName = None
newIndex = (orderedNames.index(activeName) + delta) % len(orderedNames)
slicer.modules.SegmentEditorWidget.editor.setActiveEffectByName(orderedNames[newIndex])
except AttributeError:
# module not active
pass
shortcuts = [
('`', lambda: cycleEffect(-1)),
('~', lambda: cycleEffect(1)),
]
for (shortcutKey, callback) in shortcuts:
shortcut = qt.QShortcut(slicer.util.mainWindow())
shortcut.setKey(qt.QKeySequence(shortcutKey))
shortcut.connect( 'activated()', callback)
Customize keyboard/mouse gestures in viewers
Example for making the 3D view rotate using right-click-and-drag:
threeDViewWidget = slicer.app.layoutManager().threeDWidget(0)
cameraDisplayableManager = threeDViewWidget.threeDView().displayableManagerByClassName('vtkMRMLCameraDisplayableManager')
cameraWidget = cameraDisplayableManager.GetCameraWidget()
# Remove old mapping from right-click-and-drag
cameraWidget.SetEventTranslationClickAndDrag(cameraWidget.WidgetStateIdle, vtk.vtkCommand.RightButtonPressEvent, vtk.vtkEvent.NoModifier,
cameraWidget.WidgetStateRotate, vtk.vtkWidgetEvent.NoEvent, vtk.vtkWidgetEvent.NoEvent)
# Make right-click-and-drag rotate the view
cameraWidget.SetEventTranslationClickAndDrag(cameraWidget.WidgetStateIdle, vtk.vtkCommand.RightButtonPressEvent, vtk.vtkEvent.NoModifier,
cameraWidget.WidgetStateRotate, cameraWidget.WidgetEventRotateStart, cameraWidget.WidgetEventRotateEnd)
Disable certain user interactions in slice views
For example, disable slice browsing using mouse wheel and keyboard shortcuts in the red slice viewer:
interactorStyle = slicer.app.layoutManager().sliceWidget('Red').sliceView().sliceViewInteractorStyle()
interactorStyle.SetActionEnabled(interactorStyle.BrowseSlice, False)
Hide all slice view controllers:
lm = slicer.app.layoutManager() for sliceViewName in lm.sliceViewNames(): lm.sliceWidget(sliceViewName).sliceController().setVisible(False)
Hide all 3D view controllers:
lm = slicer.app.layoutManager() for viewIndex in range(slicer.app.layoutManager().threeDViewCount): lm.threeDWidget(0).threeDController().setVisible(False)
Change default slice view orientation
You can left-right "flip" slice view orientation presets (show patient left side on left/right side of the screen) by copy-pasting the script below to your .slicerrc.py file.
# Axial slice axes:
# 1 0 0
# 0 1 0
# 0 0 1
axialSliceToRas=vtk.vtkMatrix3x3()
# Coronal slice axes:
# 1 0 0
# 0 0 -1
# 0 1 0
coronalSliceToRas=vtk.vtkMatrix3x3()
coronalSliceToRas.SetElement(1,1, 0)
coronalSliceToRas.SetElement(1,2, -1)
coronalSliceToRas.SetElement(2,1, 1)
coronalSliceToRas.SetElement(2,2, 0)
# Replace orientation presets in all existing slice nodes and in the default slice node
sliceNodes = slicer.util.getNodesByClass('vtkMRMLSliceNode')
sliceNodes.append(slicer.mrmlScene.GetDefaultNodeByClass('vtkMRMLSliceNode'))
for sliceNode in sliceNodes:
orientationPresetName = sliceNode.GetOrientation()
sliceNode.RemoveSliceOrientationPreset("Axial")
sliceNode.AddSliceOrientationPreset("Axial", axialSliceToRas)
sliceNode.RemoveSliceOrientationPreset("Coronal")
sliceNode.AddSliceOrientationPreset("Coronal", coronalSliceToRas)
sliceNode.SetOrientation(orientationPresetName)
Set all slice views linked by default
You can make slice views linked by default (when application starts or the scene is cleared) by copy-pasting the script below to your .slicerrc.py file.
# Set linked slice views in all existing slice composite nodes and in the default node
sliceCompositeNodes = slicer.util.getNodesByClass('vtkMRMLSliceCompositeNode')
defaultSliceCompositeNode = slicer.mrmlScene.GetDefaultNodeByClass('vtkMRMLSliceCompositeNode')
if not defaultSliceCompositeNode:
defaultSliceCompositeNode = slicer.mrmlScene.CreateNodeByClass('vtkMRMLSliceCompositeNode')
defaultSliceCompositeNode.UnRegister(None) # CreateNodeByClass is factory method, need to unregister the result to prevent memory leaks
slicer.mrmlScene.AddDefaultNode(defaultSliceCompositeNode)
sliceCompositeNodes.append(defaultSliceCompositeNode)
for sliceCompositeNode in sliceCompositeNodes:
sliceCompositeNode.SetLinkedControl(True)
Set crosshair jump mode to centered by default
You can change default slice jump mode (when application starts or the scene is cleared) by copy-pasting the script below to your .slicerrc.py file.
crosshair=slicer.mrmlScene.GetFirstNodeByClass("vtkMRMLCrosshairNode")
crosshair.SetCrosshairBehavior(crosshair.CenteredJumpSlice)
Add keyboard shortcut to jump to center or world coordinate system
You can copy-paste this into the Python console to jump slice views to (0,0,0) position on (Ctrl+e):
shortcut = qt.QShortcut(qt.QKeySequence('Ctrl+e'), slicer.util.mainWindow())
shortcut.connect('activated()',
lambda: slicer.modules.markups.logic().JumpSlicesToLocation(0,0,0, True))
Display mouse pointer coordinates in alternative coordinate system
The Data probe only shows coordinate values in the world coordinate system. You can make the world coordinate system mean anything you want (e.g., MNI) by applying a transform to the volume that transforms it into that space. See more details in here.
def onMouseMoved(observer,eventid):
mniToWorldTransformNode = getNode('LinearTransform_3') # replace this by the name of your actual MNI to world transform
worldToMniTransform = vtk.vtkGeneralTransform()
mniToWorldTransformNode.GetTransformToWorld(worldToMniTransform)
ras=[0,0,0]
mni=[0,0,0]
crosshairNode.GetCursorPositionRAS(ras)
worldToMniTransform.TransformPoint(ras, mni)
_ras = "; ".join([str(k) for k in ras])
_mni = "; ".join([str(k) for k in mni])
slicer.util.showStatusMessage(f"RAS={_ras} MNI={_mni}")
crosshairNode=slicer.util.getNode('Crosshair')
observationId = crosshairNode.AddObserver(slicer.vtkMRMLCrosshairNode.CursorPositionModifiedEvent, onMouseMoved)
# Run this to stop displaying values:
# crosshairNode.RemoveObserver(observationId)
Set up custom units in slice view ruler
For microscopy or micro-CT images you may want to switch unit to micrometer instead of the default mm. To do that, 1. change the unit in Application settings / Units and 2. update ruler display settings using the script below (it can be copied to your Application startup script):
lm = slicer.app.layoutManager()
for sliceViewName in lm.sliceViewNames():
sliceView = lm.sliceWidget(sliceViewName).sliceView()
displayableManager = sliceView.displayableManagerByClassName("vtkMRMLRulerDisplayableManager")
displayableManager.RemoveAllRulerScalePresets()
displayableManager.AddRulerScalePreset( 0.001, 5, 2, "nm", 1000.0)
displayableManager.AddRulerScalePreset( 0.010, 5, 2, "nm", 1000.0)
displayableManager.AddRulerScalePreset( 0.100, 5, 2, "nm", 1000.0)
displayableManager.AddRulerScalePreset( 0.500, 5, 1, "nm", 1000.0)
displayableManager.AddRulerScalePreset( 1.0, 5, 2, "um", 1.0)
displayableManager.AddRulerScalePreset( 5.0, 5, 1, "um", 1.0)
displayableManager.AddRulerScalePreset( 10.0, 5, 2, "um", 1.0)
displayableManager.AddRulerScalePreset( 50.0, 5, 1, "um", 1.0)
displayableManager.AddRulerScalePreset( 100.0, 5, 2, "um", 1.0)
displayableManager.AddRulerScalePreset( 500.0, 5, 1, "um", 1.0)
displayableManager.AddRulerScalePreset(1000.0, 5, 2, "mm", 0.001)
Show orientation marker in all views
viewNodes = slicer.util.getNodesByClass('vtkMRMLAbstractViewNode')
for viewNode in viewNodes:
viewNode.SetOrientationMarkerType(slicer.vtkMRMLAbstractViewNode.OrientationMarkerTypeAxes)
Show a slice view outside the view layout
# layout name is used to create and identify the underlying slice node and should be set to a value that is not used in any of the layouts owned by the layout manager
layoutName = "TestSlice1"
layoutLabel = "TS1"
layoutColor = [1.0, 1.0, 0.0]
# ownerNode manages this view instead of the layout manager (it can be any node in the scene)
viewOwnerNode = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass("vtkMRMLScriptedModuleNode")
# Create MRML nodes
viewLogic = slicer.vtkMRMLSliceLogic()
viewLogic.SetMRMLScene(slicer.mrmlScene)
viewNode = viewLogic.AddSliceNode(layoutName)
viewNode.SetLayoutLabel(layoutLabel)
viewNode.SetLayoutColor(layoutColor)
viewNode.SetAndObserveParentLayoutNodeID(viewOwnerNode.GetID())
# Create widget
viewWidget = slicer.qMRMLSliceWidget()
viewWidget.setMRMLScene(slicer.mrmlScene)
viewWidget.setMRMLSliceNode(viewNode)
sliceLogics = slicer.app.applicationLogic().GetSliceLogics()
viewWidget.setSliceLogics(sliceLogics)
sliceLogics.AddItem(viewWidget.sliceLogic())
viewWidget.show()
Show a 3D view outside the view layout
# layout name is used to create and identify the underlying view node and should be set to a value that is not used in any of the layouts owned by the layout manager
layoutName = "Test3DView"
layoutLabel = "T3"
layoutColor = [1.0, 1.0, 0.0]
# ownerNode manages this view instead of the layout manager (it can be any node in the scene)
viewOwnerNode = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass("vtkMRMLScriptedModuleNode")
# Create MRML node
viewLogic = slicer.vtkMRMLViewLogic()
viewLogic.SetMRMLScene(slicer.mrmlScene)
viewNode = viewLogic.AddViewNode(layoutName)
viewNode.SetLayoutLabel(layoutLabel)
viewNode.SetLayoutColor(layoutColor)
viewNode.SetAndObserveParentLayoutNodeID(viewOwnerNode.GetID())
# Create widget
viewWidget = slicer.qMRMLThreeDWidget()
viewWidget.setMRMLScene(slicer.mrmlScene)
viewWidget.setMRMLViewNode(viewNode)
viewWidget.show()
Get displayable manager of a certain type for a certain view
threeDViewWidget = slicer.app.layoutManager().threeDWidget(0)
modelDisplayableManager = threeDViewWidget.threeDView().displayableManagerByClassName('vtkMRMLModelDisplayableManager')
if modelDisplayableManager is None:
logging.error('Failed to find the model displayable manager')
Running an ITK filter in Python using SimpleITK
Open the "Sample Data" module and download "MR Head", then paste the following snippet in Python interactor:
import SampleData
import SimpleITK as sitk
import sitkUtils
# Get input volume node
inputVolumeNode = SampleData.SampleDataLogic().downloadMRHead()
# Create new volume node for output
outputVolumeNode = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass('vtkMRMLScalarVolumeNode', 'MRHeadFiltered')
# Run processing
inputImage = sitkUtils.PullVolumeFromSlicer(inputVolumeNode)
filter = sitk.SignedMaurerDistanceMapImageFilter()
outputImage = filter.Execute(inputImage)
sitkUtils.PushVolumeToSlicer(outputImage, outputVolumeNode)
# Show processing result
slicer.util.setSliceViewerLayers(background=outputVolumeNode)
More information:
- See the SimpleITK documentation for SimpleITK examples: http://www.itk.org/SimpleITKDoxygen/html/examples.html
- sitkUtils in Slicer is used for pushing and pulling images from Slicer to SimpleITK: https://github.com/Slicer/Slicer/blob/master/Base/Python/sitkUtils.py
Get current mouse coordinates in a slice view
You can get 3D (RAS) coordinates of the current mouse cursor from the crosshair singleton node as shown in the example below:
def onMouseMoved(observer,eventid):
ras=[0,0,0]
crosshairNode.GetCursorPositionRAS(ras)
print(ras)
crosshairNode=slicer.util.getNode('Crosshair')
crosshairNode.AddObserver(slicer.vtkMRMLCrosshairNode.CursorPositionModifiedEvent, onMouseMoved)
Get DataProbe text
You can get the mouse location in pixel coordinates along with the pixel value at the mouse by hitting the '.' (period) key in a slice view after pasting in the following code.
def printDataProbe():
infoWidget = slicer.modules.DataProbeInstance.infoWidget
for layer in ('B', 'F', 'L'):
print(infoWidget.layerNames[layer].text, infoWidget.layerIJKs[layer].text, infoWidget.layerValues[layer].text)
s = qt.QShortcut(qt.QKeySequence('.'), mainWindow())
s.connect('activated()', printDataProbe)
Get axial slice as numpy array
An axis-aligned (axial/sagittal/coronal/) slices of a volume can be extracted using simple numpy array indexing. For example:
import SampleData volumeNode = SampleData.SampleDataLogic().downloadMRHead() sliceIndex = 12 voxels = slicer.util.arrayFromVolume(volumeNode) # Get volume as numpy array slice = voxels[sliceIndex:,:] # Get one slice of the volume as numpy array
Get reformatted image from a slice viewer as numpy array
Set up 'red' slice viewer to show thick slab reconstructed from 3 slices:
sliceNodeID = 'vtkMRMLSliceNodeRed'
# Get image data from slice view
sliceNode = slicer.mrmlScene.GetNodeByID(sliceNodeID)
appLogic = slicer.app.applicationLogic()
sliceLogic = appLogic.GetSliceLogic(sliceNode)
sliceLayerLogic = sliceLogic.GetBackgroundLayer()
reslice = sliceLayerLogic.GetReslice()
reslicedImage = vtk.vtkImageData()
reslicedImage.DeepCopy(reslice.GetOutput())
# Create new volume node using resliced image
volumeNode = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass("vtkMRMLScalarVolumeNode")
volumeNode.SetIJKToRASMatrix(sliceNode.GetXYToRAS())
volumeNode.SetAndObserveImageData(reslicedImage)
volumeNode.CreateDefaultDisplayNodes()
volumeNode.CreateDefaultStorageNode()
# Get voxels as a numpy array
voxels = slicer.util.arrayFromVolume(volumeNode)
print(voxels.shape)
Combine multiple volumes into one
This example combines two volumes into a new one by subtracting one from the other.
import SampleData [input1Volume, input2Volume] = SampleData.SampleDataLogic().downloadDentalSurgery() import slicer.util a = slicer.util.arrayFromVolume(input1Volume) b = slicer.util.arrayFromVolume(input2Volume) # 'a' and 'b' are numpy arrays, # they can be combined using any numpy array operations # to produce the result array 'c' c = b-a volumeNode = slicer.modules.volumes.logic().CloneVolume(input1Volume, "Difference") slicer.util.updateVolumeFromArray(volumeNode, c) setSliceViewerLayers(background=volumeNode)
Add noise to image
This example shows how to add simulated noise to a volume.
import SampleData import numpy as np # Get a sample input volume node volumeNode = SampleData.SampleDataLogic().downloadMRHead() # Get volume as numpy array and add noise voxels = slicer.util.arrayFromVolume(volumeNode) voxels[:] = voxels + np.random.normal(0.0, 20.0, size=voxels.shape) slicer.util.arrayFromVolumeModified(volumeNode)
Mask volume using segmentation
This example shows how to blank out voxels of a volume outside all segments.
# Input nodes
volumeNode = getNode('MRHead')
segmentationNode = getNode('Segmentation')
# Write segmentation to labelmap volume node with a geometry that matches the volume node
labelmapVolumeNode = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass('vtkMRMLLabelMapVolumeNode')
slicer.modules.segmentations.logic().ExportVisibleSegmentsToLabelmapNode(segmentationNode, labelmapVolumeNode, volumeNode)
# Masking
import numpy as np
voxels = slicer.util.arrayFromVolume(volumeNode)
mask = slicer.util.arrayFromVolume(labelmapVolumeNode)
maskedVoxels = np.copy(voxels) # we don't want to modify the original volume
maskedVoxels[mask==0] = 0
# Write masked volume to volume node and show it
maskedVolumeNode = slicer.modules.volumes.logic().CloneVolume(volumeNode, "Masked")
slicer.util.updateVolumeFromArray(maskedVolumeNode, maskedVoxels)
slicer.util.setSliceViewerLayers(maskedVolumeNode)
Apply random deformations to image
This example shows how to apply random translation, rotation, and deformations to a volume to simulate variation in patient positioning, soft tissue motion, and random anatomical variations. Control points are placed on a regularly spaced grid and then each control point is displaced by a random amount. Thin-plate spline transform is computed from the original and transformed point list.
https://gist.github.com/lassoan/428af5285da75dc033d32ebff65ba940
Thick slab reconstruction and maximum/minimum intensity volume projections
Set up 'red' slice viewer to show thick slab reconstructed from 3 slices:
sliceNode = slicer.mrmlScene.GetNodeByID('vtkMRMLSliceNodeRed')
appLogic = slicer.app.applicationLogic()
sliceLogic = appLogic.GetSliceLogic(sliceNode)
sliceLayerLogic = sliceLogic.GetBackgroundLayer()
reslice = sliceLayerLogic.GetReslice()
reslice.SetSlabModeToMean()
reslice.SetSlabNumberOfSlices(10) # mean of 10 slices will computed
reslice.SetSlabSliceSpacingFraction(0.3) # spacing between each slice is 0.3 pixel (total 10 * 0.3 = 3 pixel neighborhood)
sliceNode.Modified()
Set up 'red' slice viewer to show maximum intensity projection (MIP):
sliceNode = slicer.mrmlScene.GetNodeByID('vtkMRMLSliceNodeRed')
appLogic = slicer.app.applicationLogic()
sliceLogic = appLogic.GetSliceLogic(sliceNode)
sliceLayerLogic = sliceLogic.GetBackgroundLayer()
reslice = sliceLayerLogic.GetReslice()
reslice.SetSlabModeToMax()
reslice.SetSlabNumberOfSlices(600) # use a large number of slices (600) to cover the entire volume
reslice.SetSlabSliceSpacingFraction(0.5) # spacing between slices are 0.5 pixel (supersampling is useful to reduce interpolation artifacts)
sliceNode.Modified()
The projected image is available in a vtkImageData object by calling reslice.GetOutput().
Change default file type for nodes (that have never been saved yet)
Default node can be specified that will be used as a basis of all new storage nodes. This can be used for setting default file extension. For example, change file format to STL for model nodes:
defaultModelStorageNode = slicer.vtkMRMLModelStorageNode()
defaultModelStorageNode.SetDefaultWriteFileExtension('stl')
slicer.mrmlScene.AddDefaultNode(defaultModelStorageNode)
To permanently change default file extension on your computer, copy-paste the code above into your application startup script (you can find its location in menu: Edit / Application settings / General / Application startup script).
Change file type for saving for all volumes (with already existing storage nodes)
If it is not necessary to preserve file paths then the simplest is to configure default storage node (as shown in the example above), then delete all existing storage nodes. When save dialog is opened, default storage nodes will be recreated.
# Delete existing model storage nodes so that they will be recreated with default settings
existingModelStorageNodes = slicer.util.getNodesByClass('vtkMRMLModelStorageNode')
for modelStorageNode in existingModelStorageNodes:
slicer.mrmlScene.RemoveNode(modelStorageNode)
To update existing storage nodes to use new file extension (but keep all other parameters unchanged) you can use this approach (example is for volume storage):
requiredFileExtension = '.nia'
originalFileExtension = '.nrrd'
volumeNodes = slicer.util.getNodesByClass('vtkMRMLScalarVolumeNode')
for volumeNode in volumeNodes:
volumeStorageNode = volumeNode.GetStorageNode()
if not volumeStorageNode:
volumeNode.AddDefaultStorageNode()
volumeStorageNode = volumeNode.GetStorageNode()
volumeStorageNode.SetFileName(volumeNode.GetName()+requiredFileExtension)
else:
volumeStorageNode.SetFileName(volumeStorageNode.GetFileName().replace(originalFileExtension, requiredFileExtension))
To set all volume nodes to save uncompressed by default (add this to .slicerrc.py so it takes effect for the whole session):
#set the default volume storage to not compress by default
defaultVolumeStorageNode = slicer.vtkMRMLVolumeArchetypeStorageNode()
defaultVolumeStorageNode.SetUseCompression(0)
slicer.mrmlScene.AddDefaultNode(defaultVolumeStorageNode)
logging.info("Volume nodes will be stored uncompressed by default")
Same thing as above, but applied to all segmentations instead of volumes:
#set the default volume storage to not compress by default
defaultVolumeStorageNode = slicer.vtkMRMLSegmentationStorageNode()
defaultVolumeStorageNode.SetUseCompression(0)
slicer.mrmlScene.AddDefaultNode(defaultVolumeStorageNode)
logging.info("Segmentation nodes will be stored uncompressed
Sequences
Access voxels of a 4D volume as numpy array
# Get sequence node
import SampleData
sequenceNode = SampleData.SampleDataLogic().downloadSample('CTPCardioSeq')
# Alternatively, get the first sequence node in the scene:
# sequenceNode = slicer.util.getNodesByClass('vtkMRMLSequenceNode')[0]
# Get voxels of itemIndex'th volume as numpy array
itemIndex = 5
voxelArray = slicer.util.arrayFromVolume(sequenceNode.GetNthDataNode(itemIndex))
Get index value
print("Index value of {0}th item: {1} = {2} {3}".format(
itemIndex,
sequenceNode.GetIndexName(),
sequenceNode.GetNthIndexValue(itemIndex),
sequenceNode.GetIndexUnit()))
Browse a sequence and access currently displayed nodes
# Get a sequence node
import SampleData
sequenceNode = SampleData.SampleDataLogic().downloadSample('CTPCardioSeq')
# Find corresponding sequence browser node
browserNode = slicer.modules.sequences.logic().GetFirstBrowserNodeForSequenceNode(sequenceNode)
# Print sequence information
print("Number of items in the sequence: {0}".format(browserNode.GetNumberOfItems()))
print("Index name: {0}".format(browserNode.GetMasterSequenceNode().GetIndexName()))
# Jump to a selected sequence item
browserNode.SetSelectedItemNumber(5)
# Get currently displayed volume node voxels as numpy array
volumeNode = browserNode.GetProxyNode(sequenceNode)
voxelArray = slicer.util.arrayFromVolume(volumeNode)
```
===Concatenate all sequences in the scene into a new sequence===
<pre>
# Get all sequence nodes in the scene
sequenceNodes = slicer.util.getNodesByClass('vtkMRMLSequenceNode')
mergedSequenceNode = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass('vtkMRMLSequenceNode', 'Merged sequence')
# Merge all sequence nodes into a new sequence node
mergedIndexValue = 0
for sequenceNode in sequenceNodes:
for itemIndex in range(sequenceNode.GetNumberOfDataNodes()):
dataNode = sequenceNode.GetNthDataNode(itemIndex)
mergedSequenceNode.SetDataNodeAtValue(dataNode, str(mergedIndexValue))
mergedIndexValue += 1
# Delete the sequence node we copied the data from, to prevent sharing of the same
# node by multiple sequences
slicer.mrmlScene.RemoveNode(sequenceNode)
# Create a sequence browser node for the new merged sequence
mergedSequenceBrowserNode = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass('vtkMRMLSequenceBrowserNode', 'Merged')
mergedSequenceBrowserNode.AddSynchronizedSequenceNode(mergedSequenceNode)
slicer.modules.sequencebrowser.setToolBarActiveBrowserNode(mergedSequenceBrowserNode)
# Show proxy node in slice viewers
mergedProxyNode = mergedSequenceBrowserNode.GetProxyNode(mergedSequenceNode)
slicer.util.setSliceViewerLayers(background=mergedProxyNode)
Segmentations
Create a segmentation from a labelmap volume and display in 3D
labelmapVolumeNode = getNode('label')
seg = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass('vtkMRMLSegmentationNode')
slicer.modules.segmentations.logic().ImportLabelmapToSegmentationNode(labelmapVolumeNode, seg)
seg.CreateClosedSurfaceRepresentation()
slicer.mrmlScene.RemoveNode(labelmapVolumeNode)
The last line is optional. It removes the original labelmap volume so that the same information is not shown twice.
Export labelmap node from segmentation node
Export labelmap matching reference geometry of the segmentation:
segmentationNode = getNode('Segmentation')
labelmapVolumeNode = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass('vtkMRMLLabelMapVolumeNode')
slicer.modules.segmentations.logic().ExportAllSegmentsToLabelmapNode(segmentationNode, labelmapVolumeNode, slicer.vtkSegmentation.EXTENT_REFERENCE_GEOMETRY)
Export smallest possible labelmap:
segmentationNode = getNode('Segmentation')
labelmapVolumeNode = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass('vtkMRMLLabelMapVolumeNode')
slicer.modules.segmentations.logic().ExportAllSegmentsToLabelmapNode(segmentationNode, labelmapVolumeNode)
Export labelmap that matches geometry of a chosen reference volume:
segmentationNode = getNode('Segmentation')
labelmapVolumeNode = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass('vtkMRMLLabelMapVolumeNode')
slicer.modules.segmentations.logic().ExportVisibleSegmentsToLabelmapNode(segmentationNode, labelmapVolumeNode, referenceVolumeNode)
Export a selection of segments (identified by their names):
segmentNames = ["Prostate", "Urethra"]
segmentIds = vtk.vtkStringArray()
for segmentName in segmentNames:
segmentId = segmentationNode.GetSegmentation().GetSegmentIdBySegmentName(segmentName)
segmentIds.InsertNextValue(segmentId)
slicer.vtkSlicerSegmentationsModuleLogic.ExportSegmentsToLabelmapNode(segmentationNode, segmentIds, labelmapVolumeNode, referenceVolumeNode)
Export to file by pressing Ctrl+Shift+S key:
outputPath = "c:/tmp"
def exportLabelmap():
segmentationNode = slicer.mrmlScene.GetFirstNodeByClass("vtkMRMLSegmentationNode")
referenceVolumeNode = slicer.mrmlScene.GetFirstNodeByClass("vtkMRMLScalarVolumeNode")
labelmapVolumeNode = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass('vtkMRMLLabelMapVolumeNode')
slicer.modules.segmentations.logic().ExportVisibleSegmentsToLabelmapNode(segmentationNode, labelmapVolumeNode, referenceVolumeNode)
filepath = outputPath + "/" + referenceVolumeNode.GetName()+"-label.nrrd"
slicer.util.saveNode(labelmapVolumeNode, filepath)
slicer.mrmlScene.RemoveNode(labelmapVolumeNode.GetDisplayNode().GetColorNode())
slicer.mrmlScene.RemoveNode(labelmapVolumeNode)
slicer.util.delayDisplay("Segmentation saved to "+filepath)
shortcut = qt.QShortcut(slicer.util.mainWindow())
shortcut.setKey(qt.QKeySequence('Ctrl+Shift+s'))
shortcut.connect( 'activated()', exportLabelmap)
Export model nodes from segmentation node
segmentationNode = getNode("Segmentation")
shNode = slicer.mrmlScene.GetSubjectHierarchyNode()
exportFolderItemId = shNode.CreateFolderItem(shNode.GetSceneItemID(), "Segments")
slicer.modules.segmentations.logic().ExportAllSegmentsToModels(segmentationNode, exportFolderItemId)
Create a hollow model from boundary of solid segment
In most cases, the most robust and flexible tool for creating empty shell models (e.g., vessel wall model from contrast agent segmentation) is the "Hollow" effect in Segment Editor module. However, for very thin shells, extrusion of the exported surface mesh representation may be just as robust and require less memory and computation time. In this case it may be a better approach to to export the segment to a mesh and extrude it along surface normal direction:
Example using Dynamic Modeler module (allows real-time update of parameters, using GUI in Dynamic Modeler module):
segmentationNode = getNode("Segmentation")
# Export segments to models
shNode = slicer.mrmlScene.GetSubjectHierarchyNode()
exportFolderItemId = shNode.CreateFolderItem(shNode.GetSceneItemID(), "Segments")
slicer.modules.segmentations.logic().ExportAllSegmentsToModels(segmentationNode, exportFolderItemId)
segmentModels = vtk.vtkCollection()
shNode.GetDataNodesInBranch(exportFolderItemId, segmentModels)
# Get exported model of first segment
modelNode = segmentModels.GetItemAsObject(0)
# Set up Hollow tool
hollowModeler = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass("vtkMRMLDynamicModelerNode")
hollowModeler.SetToolName("Hollow")
hollowModeler.SetNodeReferenceID("Hollow.InputModel", modelNode.GetID())
hollowedModelNode = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass("vtkMRMLModelNode") # this node will store the hollow model
hollowModeler.SetNodeReferenceID("Hollow.OutputModel", hollowedModelNode.GetID())
hollowModeler.SetAttribute("ShellThickness", "2.5") # grow outside
hollowModeler.SetContinuousUpdate(True) # auto-update output model if input parameters are changed
# Hide inputs, show output
segmentation.GetDisplayNode().SetVisibility(False)
modelNode.GetDisplayNode().SetVisibility(False)
hollowedModelNode.GetDisplayNode().SetOpacity(0.5)
Example using VTK filters:
# Get closed surface representation of the segment
shellThickness = 3.0 # mm
segmentationNode = getNode('Segmentation')
segmentationNode.CreateClosedSurfaceRepresentation()
polyData = segmentationNode.GetClosedSurfaceInternalRepresentation('Segment_1')
# Create shell
extrude = vtk.vtkLinearExtrusionFilter()
extrude.SetInputData(polyData)
extrude.SetExtrusionTypeToNormalExtrusion()
extrude.SetScaleFactor(shellThickness)
# Compute consistent surface normals
triangle_filter = vtk.vtkTriangleFilter()
triangle_filter.SetInputConnection(extrude.GetOutputPort())
normals = vtk.vtkPolyDataNormals()
normals.SetInputConnection(triangle_filter.GetOutputPort())
normals.FlipNormalsOn()
# Save result into new model node
slicer.modules.models.logic().AddModel(normals.GetOutputPort())
Show a segmentation in 3D
Segmentation can only be shown in 3D if closed surface representation (or other 3D-displayable representation) is available. To create closed surface representation:
segmentation.CreateClosedSurfaceRepresentation()
Get a representation of a segment
Access binary labelmap stored in a segmentation node (without exporting it to a volume node) - if it does not exist, it will return None:
image = slicer.vtkOrientedImageData() segmentationNode.GetBinaryLabelmapRepresentation(segmentID, image)
Get closed surface, if it does not exist, it will return None:
outputPolyData = vtk.vtkPolyData() segmentationNode.GetClosedSurfaceRepresentation(segmentID, outputPolyData)
Get binary labelmap representation. If it does not exist then it will be created for that single segment. Applies parent transforms by default (if not desired, another argument needs to be added to the end: false):
import vtkSegmentationCorePython as vtkSegmentationCore outputOrientedImageData = vtkSegmentationCore.vtkOrientedImageData() slicer.vtkSlicerSegmentationsModuleLogic.GetSegmentBinaryLabelmapRepresentation(segmentationNode, segmentID, outputOrientedImageData)
Same as above, for closed surface representation:
outputPolyData = vtk.vtkPolyData() slicer.vtkSlicerSegmentationsModuleLogic.GetSegmentClosedSurfaceRepresentation(segmentationNode, segmentID, outputPolyData)
Convert all segments using default path and conversion parameters
segmentationNode.CreateBinaryLabelmapRepresentation()
Convert all segments using custom path or conversion parameters
Change reference image geometry parameter based on an existing referenceImageData image:
referenceGeometry = slicer.vtkSegmentationConverter.SerializeImageGeometry(referenceImageData) segmentation.SetConversionParameter(slicer.vtkSegmentationConverter.GetReferenceImageGeometryParameterName(), referenceGeometry)
Re-convert using a modified conversion parameter
Changing smoothing factor for closed surface generation:
import vtkSegmentationCorePython as vtkSegmentationCore
segmentation = getNode('Segmentation').GetSegmentation()
# Turn of surface smoothing
segmentation.SetConversionParameter('Smoothing factor','0.0')
# Recreate representation using modified parameters (and default conversion path)
segmentation.RemoveRepresentation(vtkSegmentationCore.vtkSegmentationConverter.GetSegmentationClosedSurfaceRepresentationName())
segmentation.CreateRepresentation(vtkSegmentationCore.vtkSegmentationConverter.GetSegmentationClosedSurfaceRepresentationName())
Create keyboard shortcut for toggling sphere brush for paint and erase effects
def toggleSphereBrush():
segmentEditorWidget = slicer.modules.segmenteditor.widgetRepresentation().self().editor
paintEffect = segmentEditorWidget.effectByName("Paint")
isSphere = paintEffect.integerParameter('BrushSphere')
# BrushSphere is "common" parameter (shared between paint and erase)
paintEffect.setCommonParameter("BrushSphere", 0 if isSphere else 1)
shortcut = qt.QShortcut(slicer.util.mainWindow())
shortcut.setKey(qt.QKeySequence("s"))
shortcut.connect('activated()', toggleSphereBrush)
Customize list of displayed Segment editor effects
Only show Paint and Erase effects:
segmentEditorWidget = slicer.modules.segmenteditor.widgetRepresentation().self().editor segmentEditorWidget.setEffectNameOrder(['Paint', 'Erase']) segmentEditorWidget.unorderedEffectsVisible = False
Show list of all available effect names:
segmentEditorWidget = slicer.modules.segmenteditor.widgetRepresentation().self().editor print(segmentEditorWidget.availableEffectNames())
Get centroid of a segment in world (RAS) coordinates
This example shows how to get centroid of a segment in world coordinates and show that position in all slice views.
segmentationNode = getNode('Segmentation')
segmentId = 'Segment_1'
# Get array voxel coordinates
import numpy as np
seg=arrayFromSegment(segmentation_node, segmentId)
# numpy array has voxel coordinates in reverse order (KJI instead of IJK)
# and the array is cropped to minimum size in the segmentation
mean_KjiCropped = [coords.mean() for coords in np.nonzero(seg)]
# Get segmentation voxel coordinates
segImage = segmentationNode.GetBinaryLabelmapRepresentation(segmentId)
segImageExtent = segImage.GetExtent()
# origin of the array in voxel coordinates is determined by the start extent
mean_Ijk = [mean_KjiCropped[2], mean_KjiCropped[1], mean_KjiCropped[0]] + np.array([segImageExtent[0], segImageExtent[2], segImageExtent[4]])
# Get segmentation physical coordinates
ijkToWorld = vtk.vtkMatrix4x4()
segImage.GetImageToWorldMatrix(ijkToWorld)
mean_World = [0, 0, 0, 1]
ijkToRas.MultiplyPoint(np.append(mean_Ijk,1.0), mean_World)
mean_World = mean_World[0:3]
# If segmentation node is transformed, apply that transform to get RAS coordinates
transformWorldToRas = vtk.vtkGeneralTransform()
slicer.vtkMRMLTransformNode.GetTransformBetweenNodes(segmentationNode.GetParentTransformNode(), None, transformWorldToRas)
mean_Ras = transformWorldToRas.TransformPoint(mean_World)
# Show mean position value and jump to it in all slice viewers
print(mean_Ras)
slicer.modules.markups.logic().JumpSlicesToLocation(mean_Ras[0], mean_Ras[1], mean_Ras[2], True)
Get histogram of a segmented region
# Generate input data
################################################
# Load master volume
import SampleData
sampleDataLogic = SampleData.SampleDataLogic()
masterVolumeNode = sampleDataLogic.downloadMRBrainTumor1()
# Create segmentation
segmentationNode = slicer.vtkMRMLSegmentationNode()
slicer.mrmlScene.AddNode(segmentationNode)
segmentationNode.CreateDefaultDisplayNodes() # only needed for display
segmentationNode.SetReferenceImageGeometryParameterFromVolumeNode(masterVolumeNode)
# Create segment
tumorSeed = vtk.vtkSphereSource()
tumorSeed.SetCenter(-6, 30, 28)
tumorSeed.SetRadius(25)
tumorSeed.Update()
segmentationNode.AddSegmentFromClosedSurfaceRepresentation(tumorSeed.GetOutput(), "Segment A", [1.0,0.0,0.0])
# Compute histogram
################################################
labelValue = 1 # label value of first segment
# Get segmentation as labelmap volume node
labelmapVolumeNode = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass('vtkMRMLLabelMapVolumeNode')
slicer.modules.segmentations.logic().ExportVisibleSegmentsToLabelmapNode(segmentationNode, labelmapVolumeNode, masterVolumeNode)
# Extract all voxels of the segment as numpy array
volumeArray = slicer.util.arrayFromVolume(masterVolumeNode)
labelArray = slicer.util.arrayFromVolume(labelmapVolumeNode)
segmentVoxels = volumeArray[labelArray==labelValue]
# Compute histogram
import numpy as np
histogram = np.histogram(segmentVoxels, bins=50)
# Plot histogram
################################################
slicer.util.plot(histogram, xColumnIndex = 1)
Get segments visible at a selected position
Show in the console names of segments visible at a markups fiducial position:
segmentationNode = slicer.mrmlScene.GetFirstNodeByClass("vtkMRMLSegmentationNode")
markupsFiducialNode = slicer.mrmlScene.GetFirstNodeByClass("vtkMRMLMarkupsFiducialNode")
sliceViewLabel = "Red" # any slice view where segmentation node is visible works
def printSegmentNames(unused1=None, unused2=None):
sliceViewWidget = slicer.app.layoutManager().sliceWidget(sliceViewLabel)
segmentationsDisplayableManager = sliceViewWidget.sliceView().displayableManagerByClassName('vtkMRMLSegmentationsDisplayableManager2D')
ras = [0,0,0]
markupsFiducialNode.GetNthControlPointPositionWorld(0, ras)
segmentIds = vtk.vtkStringArray()
segmentationsDisplayableManager.GetVisibleSegmentsForPosition(ras, segmentationNode.GetDisplayNode(), segmentIds)
for idIndex in range(segmentIds.GetNumberOfValues()):
segment = segmentationNode.GetSegmentation().GetSegment(segmentIds.GetValue(idIndex))
print('Segment found at position {0}: {1}'.format(ras, segment.GetName()))
# Observe markup node changes
markupsFiducialNode.AddObserver(slicer.vtkMRMLMarkupsPlaneNode.PointModifiedEvent, printSegmentNames)
printSegmentNames()
Set default segmentation options
Allow segments to overlap each other by default:
defaultSegmentEditorNode = slicer.vtkMRMLSegmentEditorNode() defaultSegmentEditorNode.SetOverwriteMode(slicer.vtkMRMLSegmentEditorNode.OverwriteNone) slicer.mrmlScene.AddDefaultNode(defaultSegmentEditorNode)
To always make this the default, add the lines above to your .slicerrc file.
How to run segment editor effects from a script
Editor effects are complex because they need to handle changing master volumes, undo/redo, masking operations, etc. Therefore, it is recommended to use the effect by instantiating a qMRMLSegmentEditorWidget or use/extract processing logic of the effect and use that from a script.
Use Segment editor effects from script (qMRMLSegmentEditorWidget)
Examples:
- brain tumor segmentation using grow from seeds effect
- AI-assisted brain tumor segmentation
- skin surface extraction using thresholding and smoothing
- mask a volume with segments and compute histogram for each region
- create fat/muscle/bone segment by thresholding and report volume of each segment
- segment cranial cavity automatically in dry bone skull CT
- remove patient table from CT image
Description of effect parameters are available here.
Use logic of effect from a script
This example shows how to perform operations on segmentations using VTK filters extracted from an effect:
Process segment using a VTK filter
This example shows how to apply a VTK filter to a segment that dilates the image by a specified margin.
segmentationNode = getNode('Segmentation')
segmentId = "Segment_1"
kernelSize = [3,1,5]
# Export segment as vtkImageData (via temporary labelmap volume node)
segmentIds = vtk.vtkStringArray()
segmentIds.InsertNextValue(segmentId)
labelmapVolumeNode = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass('vtkMRMLLabelMapVolumeNode')
slicer.modules.segmentations.logic().ExportSegmentsToLabelmapNode(segmentationNode, segmentIds, labelmapVolumeNode)
# Process segmentation
segmentImageData = labelmapVolumeNode.GetImageData()
erodeDilate = vtk.vtkImageDilateErode3D()
erodeDilate.SetInputData(segmentImageData)
erodeDilate.SetDilateValue(1)
erodeDilate.SetErodeValue(0)
erodeDilate.SetKernelSize(*kernelSize)
erodeDilate.Update()
segmentImageData.DeepCopy(erodeDilate.GetOutput())
# Import segment from vtkImageData
slicer.modules.segmentations.logic().ImportLabelmapToSegmentationNode(labelmapVolumeNode, segmentationNode, segmentIds)
# Cleanup temporary nodes
slicer.mrmlScene.RemoveNode(labelmapVolumeNode.GetDisplayNode().GetColorNode())
slicer.mrmlScene.RemoveNode(labelmapVolumeNode)
Get information from segmentation nrrd file header
You can use this code snippet to get information from segmentation (.seg.nrrd), for example when creating numpy arrays for generating training data for deep learning networks. This script can be used in any Python environment, not just inside Slicer.
# pip_install('pynrrd')
def read_segmentation_info(filename):
import nrrd
header = nrrd.read_header(filename)
segmentation_info = {}
segments = []
segment_index = 0
while True:
prefix = "Segment{0}_".format(segment_index)
if not prefix + "ID" in header.keys():
break
segment = {}
segment["index"] = segment_index
segment["color"] = [float(i) for i in header[prefix + "Color"].split(" ")] # Segment0_Color:=0.501961 0.682353 0.501961
segment["colorAutoGenerated"] = int(header[prefix + "ColorAutoGenerated"]) != 0 # Segment0_ColorAutoGenerated:=1
segment["extent"] = [int(i) for i in header[prefix + "Extent"].split(" ")] # Segment0_Extent:=68 203 53 211 24 118
segment["id"] = header[prefix + "ID"] # Segment0_ID:=Segment_1
segment["labelValue"] = int(header[prefix + "LabelValue"]) # Segment0_LabelValue:=1
segment["layer"] = int(header[prefix + "Layer"]) # Segment0_Layer:=0
segment["name"] = header[prefix + "Name"] # Segment0_Name:=Segment_1
segment["nameAutoGenerated"] = int(header[prefix + "NameAutoGenerated"]) != 0 # Segment0_NameAutoGenerated:=1
# Segment0_Tags:=Segmentation.Status:inprogress|TerminologyEntry:Segmentation category and type - 3D Slicer General Anatomy list
# ~SCT^85756007^Tissue~SCT^85756007^Tissue~^^~Anatomic codes - DICOM master list~^^~^^|
tags = {}
tags_str = header[prefix + "Tags"].split("|")
for tag_str in tags_str:
tag_str = tag_str.strip()
if not tag_str:
continue
key, value = tag_str.split(":", maxsplit=1)
tags[key] = value
segment["tags"] = tags
segments.append(segment)
segment_index += 1
segmentation_info["segments"] = segments
return segmentation_info
def segment_from_name(segmentation_info, segment_name):
for segment in segmentation_info["segments"]:
if segment_name == segment["name"]:
return segment
raise KeyError('segment not found by name ' + segment_name)
def segment_names(segmentation_info):
names = []
for segment in segmentation_info["segments"]:
names.append(segment["name"])
return names
def extract_segments(voxels, header, segmentation_info, segment_names_to_label_values):
import numpy as np
# Create empty array from last 3 dimensions (output will be flattened to a 3D array)
output_voxels = np.zeros(voxels.shape[-3:])
# Copy non-segmentation fields to the extracted header
output_header = {}
for key in header.keys():
if not re.match("^Segment[0-9]+_.+", key):
output_header[key] = header[key]
# Copy extracted segments
dims = len(voxels.shape)
for output_segment_index, segment_name_to_label_value in enumerate(segment_names_to_label_values):
# Copy relabeled voxel data
segment = segment_from_name(segmentation_info, segment_name_to_label_value[0])
input_label_value = segment["labelValue"]
output_label_value = segment_name_to_label_value[1]
if dims == 3:
output_voxels[voxels == input_label_value] = output_label_value
elif dims == 4:
inputLayer = segment["layer"]
output_voxels[voxels[inputLayer,:,:,:] == input_label_value] = output_label_value
else:
raise ValueError("Voxel array dimension is invalid")
# Copy all segment fields corresponding to this segment
for key in header.keys():
prefix = "Segment{0}_".format(segment["index"])
matched = re.match("^"+prefix+"(.+)", key)
if matched:
field_name = matched.groups()[0]
if field_name == "LabelValue":
value = output_label_value
elif field_name == "Layer":
# output is a single layer (3D volume)
value = 0
else:
value = header[key]
output_header["Segment{0}_".format(output_segment_index) + field_name] = value
# Remove unnecessary 4th dimension (volume is collapsed into 3D)
if dims == 4:
# Remove "none" from "none (0,1,0) (0,0,-1) (-1.2999954223632812,0,0)"
output_header["space directions"] = output_header["space directions"][-3:,:]
# Remove "list" from "list domain domain domain"
output_header["kinds"] = output_header["kinds"][-3:]
return output_voxels, output_header
# Read segmentation and show some information about segments
filename = "c:/Users/andra/OneDrive/Projects/SegmentationPynrrd/SegmentationOverlapping.seg.nrrd"
segmentation_info = read_segmentation_info(filename)
number_of_segments = len(segmentation_info["segments"])
names = segment_names(segmentation_info)
label0 = segment_from_name(segmentation_info, names[0])["labelValue"]
print("Number of segments: " + str())
print("Segment names: " + str(names))
print("Label value of {0}: {1}".format(names[0], label0))
# Extract selected segments with chosen label values
extracted_filename = "c:/Users/andra/OneDrive/Projects/SegmentationPynrrd/SegmentationExtracted.seg.nrrd"
voxels, header = nrrd.read(filename)
segment_list = [("Segment_1", 10), ("Segment_3", 12), ("Segment_4", 6)]
extracted_voxels, extracted_header = extract_segments(voxels, header, segmentation_info, segment_list)
nrrd.write(extracted_filename, extracted_voxels, extracted_header)
Quantifying segments
Get centroid of each segment
Place a markups fiducial point at the centroid of each segment.
segmentationNode = getNode('Segmentation')
# Compute centroids
import SegmentStatistics
segStatLogic = SegmentStatistics.SegmentStatisticsLogic()
segStatLogic.getParameterNode().SetParameter("Segmentation", segmentationNode.GetID())
segStatLogic.getParameterNode().SetParameter("LabelmapSegmentStatisticsPlugin.centroid_ras.enabled", str(True))
segStatLogic.computeStatistics()
stats = segStatLogic.getStatistics()
# Place a markup point in each centroid
markupsNode = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass("vtkMRMLMarkupsFiducialNode")
markupsNode.CreateDefaultDisplayNodes()
for segmentId in stats['SegmentIDs']:
centroid_ras = stats[segmentId,"LabelmapSegmentStatisticsPlugin.centroid_ras"]
segmentName = segmentationNode.GetSegmentation().GetSegment(segmentId).GetName()
markupsNode.AddFiducialFromArray(centroid_ras, segmentName)
Get size, position, and orientation of each segment
This example computes oriented bounding box for each segment and displays them using annotation ROI.
segmentationNode = getNode('Segmentation')
# Compute bounding boxes
import SegmentStatistics
segStatLogic = SegmentStatistics.SegmentStatisticsLogic()
segStatLogic.getParameterNode().SetParameter("Segmentation", segmentationNode.GetID())
segStatLogic.getParameterNode().SetParameter("LabelmapSegmentStatisticsPlugin.obb_origin_ras.enabled",str(True))
segStatLogic.getParameterNode().SetParameter("LabelmapSegmentStatisticsPlugin.obb_diameter_mm.enabled",str(True))
segStatLogic.getParameterNode().SetParameter("LabelmapSegmentStatisticsPlugin.obb_direction_ras_x.enabled",str(True))
segStatLogic.getParameterNode().SetParameter("LabelmapSegmentStatisticsPlugin.obb_direction_ras_y.enabled",str(True))
segStatLogic.getParameterNode().SetParameter("LabelmapSegmentStatisticsPlugin.obb_direction_ras_z.enabled",str(True))
segStatLogic.computeStatistics()
stats = segStatLogic.getStatistics()
# Draw ROI for each oriented bounding box
import numpy as np
for segmentId in stats['SegmentIDs']:
# Get bounding box
obb_origin_ras = np.array(stats[segmentId,"LabelmapSegmentStatisticsPlugin.obb_origin_ras"])
obb_diameter_mm = np.array(stats[segmentId,"LabelmapSegmentStatisticsPlugin.obb_diameter_mm"])
obb_direction_ras_x = np.array(stats[segmentId,"LabelmapSegmentStatisticsPlugin.obb_direction_ras_x"])
obb_direction_ras_y = np.array(stats[segmentId,"LabelmapSegmentStatisticsPlugin.obb_direction_ras_y"])
obb_direction_ras_z = np.array(stats[segmentId,"LabelmapSegmentStatisticsPlugin.obb_direction_ras_z"])
# Create ROI
segment = segmentationNode.GetSegmentation().GetSegment(segmentId)
roi=slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass("vtkMRMLAnnotationROINode")
roi.SetName(segment.GetName()+' bounding box')
roi.SetXYZ(0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
roi.SetRadiusXYZ(*(0.5*obb_diameter_mm))
# Position and orient ROI using a transform
obb_center_ras = obb_origin_ras+0.5*(obb_diameter_mm[0] * obb_direction_ras_x + obb_diameter_mm[1] * obb_direction_ras_y + obb_diameter_mm[2] * obb_direction_ras_z)
boundingBoxToRasTransform = np.row_stack((np.column_stack((obb_direction_ras_x, obb_direction_ras_y, obb_direction_ras_z, obb_center_ras)), (0, 0, 0, 1)))
boundingBoxToRasTransformMatrix = slicer.util.vtkMatrixFromArray(boundingBoxToRasTransform)
transformNode = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass('vtkMRMLTransformNode')
transformNode.SetAndObserveMatrixTransformToParent(boundingBoxToRasTransformMatrix)
roi.SetAndObserveTransformNodeID(transformNode.GetID())
Complete list of available parameters can be obtained by running segStatLogic.getParameterNode().GetParameterNames().
Markups
Load markups fiducial list from file
Markups fiducials can be loaded from file:
slicer.util.loadMarkupsFiducialList('/path/to/list/F.fcsv')
Adding Fiducials Programatically
Markups fiducials can be added to the currently active list from the python console by using the following module logic command:
slicer.modules.markups.logic().AddFiducial()
The command with no arguments will place a new fiducial at the origin. You can also pass it an initial location:
slicer.modules.markups.logic().AddFiducial(1.0, -2.0, 3.3)
How to draw a curve using control points stored in a numpy array
# Create random numpy array to use as input
import numpy as np
pointPositions = np.random.uniform(-50,50,size=[15,3])
# Create curve from numpy array
curveNode = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass("vtkMRMLMarkupsCurveNode")
slicer.util.updateMarkupsControlPointsFromArray(curveNode, pointPositions)
Add a button to module GUI to activate fiducial placement
This code snippet creates a toggle button, which activates fiducial placement when pressed (and deactivates when released).
The qSlicerMarkupsPlaceWidget widget can automatically activate placement of multiple points and can show buttons for deleting points, changing colors, lock, and hide points.
w=slicer.qSlicerMarkupsPlaceWidget() w.setMRMLScene(slicer.mrmlScene) markupsNodeID = slicer.modules.markups.logic().AddNewFiducialNode() w.setCurrentNode(slicer.mrmlScene.GetNodeByID(markupsNodeID)) # Hide all buttons and only show place button w.buttonsVisible=False w.placeButton().show() w.show()
Adding Fiducials via Mouse Clicks
You can also set the mouse mode into Markups fiducial placement by calling:
placeModePersistence = 1 slicer.modules.markups.logic().StartPlaceMode(placeModePersistence)
A lower level way to do this is via the selection and interaction nodes:
selectionNode = slicer.mrmlScene.GetNodeByID("vtkMRMLSelectionNodeSingleton")
selectionNode.SetReferenceActivePlaceNodeClassName("vtkMRMLMarkupsFiducialNode")
interactionNode = slicer.mrmlScene.GetNodeByID("vtkMRMLInteractionNodeSingleton")
placeModePersistence = 1
interactionNode.SetPlaceModePersistence(placeModePersistence)
# mode 1 is Place, can also be accessed via slicer.vtkMRMLInteractionNode().Place
interactionNode.SetCurrentInteractionMode(1)
To switch back to view transform once you're done placing fiducials:
interactionNode = slicer.mrmlScene.GetNodeByID("vtkMRMLInteractionNodeSingleton")
interactionNode.SwitchToViewTransformMode()
# also turn off place mode persistence if required
interactionNode.SetPlaceModePersistence(0)
Access to Fiducial Properties
Each vtkMRMLMarkupsFiducialNode has a vector of points in it which can be accessed from python:
fidNode = getNode("vtkMRMLMarkupsFiducialNode1")
n = fidNode.AddFiducial(4.0, 5.5, -6.0)
fidNode.SetNthFiducialLabel(n, "new label")
# each markup is given a unique id which can be accessed from the superclass level
id1 = fidNode.GetNthMarkupID(n)
# manually set the position
fidNode.SetNthFiducialPosition(n, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0)
# set the label
fidNode.SetNthFiducialLabel(n, "New label")
# set the selected flag, only selected = 1 fiducials will be passed to CLIs
fidNode.SetNthFiducialSelected(n, 1)
# set the visibility flag
fidNode.SetNthFiducialVisibility(n, 0)
You can loop over the fiducials in a list and get the coordinates:
fidList = slicer.util.getNode('F')
numFids = fidList.GetNumberOfFiducials()
for i in range(numFids):
ras = [0,0,0]
fidList.GetNthFiducialPosition(i,ras)
# the world position is the RAS position with any transform matrices applied
world = [0,0,0,0]
fidList.GetNthFiducialWorldCoordinates(0,world)
print(i,": RAS =",ras,", world =",world)
You can also look at the sample code in the Endoscopy module to see how python is used to access fiducials from a scripted module.
Accessing views, renderers, and cameras
Iterate through all 3D views in current layout:
layoutManager = slicer.app.layoutManager()
for threeDViewIndex in range(layoutManager.threeDViewCount) :
view = layoutManager.threeDWidget(threeDViewIndex).threeDView()
threeDViewNode = view.mrmlViewNode()
cameraNode = slicer.modules.cameras.logic().GetViewActiveCameraNode(threeDViewNode)
print('View node for 3D widget ' + str(threeDViewIndex))
print(' Name: ' + threeDViewNode .GetName())
print(' ID: ' + threeDViewNode .GetID())
print(' Camera ID: ' + cameraNode.GetID())
Iterate through all slice views in current layout:
layoutManager = slicer.app.layoutManager()
for sliceViewName in layoutManager.sliceViewNames():
view = layoutManager.sliceWidget(sliceViewName).sliceView()
sliceNode = view.mrmlSliceNode()
sliceLogic = slicer.app.applicationLogic().GetSliceLogic(sliceNode)
compositeNode = sliceLogic.GetSliceCompositeNode()
print('Slice view ' + str(sliceViewName))
print(' Name: ' + sliceNode.GetName())
print(' ID: ' + sliceNode.GetID())
print(' Background volume: {0}'.format(compositeNode.GetBackgroundVolumeID()))
print(' Foreground volume: {0} (opacity: {1})'.format(compositeNode.GetForegroundVolumeID(), compositeNode.GetForegroundOpacity()))
print(' Label volume: {0} (opacity: {1})'.format(compositeNode.GetLabelVolumeID(), compositeNode.GetLabelOpacity()))
For low-level manipulation of views, it is possible to access VTK render windows, renderers and cameras of views in the current layout.
renderWindow = view.renderWindow() renderers = renderWindow.GetRenderers() renderer = renderers.GetItemAsObject(0) camera = cameraNode.GetCamera()
Access VTK actor properties
This example shows how to access and modify VTK actor properties to experiment with physically-based rendering.
modelNode = slicer.util.getNode('MyModel')
threeDViewWidget = slicer.app.layoutManager().threeDWidget(0)
modelDisplayableManager = threeDViewWidget.threeDView().displayableManagerByClassName('vtkMRMLModelDisplayableManager')
actor=modelDisplayableManager.GetActorByID(modelNode.GetDisplayNode().GetID())
property=actor.GetProperty()
property.SetInterpolationToPBR()
property.SetMetallic(0.5)
property.SetRoughness(0.5)
property.SetColor(0.5,0.5,0.9)
slicer.util.forceRenderAllViews()
See more information on physically based rendering in VTK here: https://blog.kitware.com/vtk-pbr/
Hide view controller bars
slicer.app.layoutManager().threeDWidget(0).threeDController().setVisible(False)
slicer.app.layoutManager().sliceWidget('Red').sliceController().setVisible(False)
slicer.app.layoutManager().plotWidget(0).plotController().setVisible(False)
slicer.app.layoutManager().tableWidget(0).tableController().setVisible(False)
Customize widgets in view controller bars
sliceController = slicer.app.layoutManager().sliceWidget("Red").sliceController()
# hide what is not needed
sliceController.pinButton().hide()
#sliceController.viewLabel().hide()
sliceController.fitToWindowToolButton().hide()
sliceController.sliceOffsetSlider().hide()
# add custom widgets
myButton = qt.QPushButton("My custom button")
sliceController.barLayout().addWidget(myButton)
Change 3D view background color
viewNode = slicer.app.layoutManager().threeDWidget(0).mrmlViewNode() viewNode.SetBackgroundColor(1,0,0) viewNode.SetBackgroundColor2(1,0,0)
Change view axis labels
labels = ['x', 'X', 'y', 'Y', 'z', 'Z']
viewNode = slicer.app.layoutManager().threeDWidget(0).mrmlViewNode()
# for slice view:
# viewNode = slicer.app.layoutManager().sliceWidget('Red').mrmlSliceNode()
for index, label in enumerate(labels):
viewNode.SetAxisLabel(index, label)
Hide Slicer logo from main window (to increase space)
slicer.util.findChild(slicer.util.mainWindow(), 'LogoLabel').visible = False
Subject hierarchy
Get the pseudo-singleton subject hierarchy node
It manages the whole hierarchy and provides functions to access and manipulate
shNode = slicer.mrmlScene.GetSubjectHierarchyNode()
Create subject hierarchy item
# If it is for a data node, it is automatically created, but the create function can be used to set parent: shNode.CreateItem(parentItemID, dataNode) # If it is a hierarchy item without a data node, then the create function must be used: shNode.CreateSubjectItem(parentItemID, name) shNode.CreateFolderItem(parentItemID, name) shNode.CreateHierarchyItem(parentItemID, name, level) # Advanced method to set level attribute manually (usually subject, study, or folder, but it can be a virtual branch for example)
Get subject hierarchy item
Items in subject hierarchy are uniquely identified by integer IDs
# Get scene item ID first because it is the root item: sceneItemID = shNode.GetSceneItemID() # Get direct child by name subjectItemID = shNode.GetItemChildWithName(sceneItemID, 'Subject_1') # Get item for data node itemID = shNode.GetItemByDataNode(dataNode) # Get item by UID (such as DICOM) itemID = shNode.GetItemByUID(slicer.vtkMRMLSubjectHierarchyConstants.GetDICOMUIDName(), seriesInstanceUid) itemID = shNode.GetItemByUIDList(slicer.vtkMRMLSubjectHierarchyConstants.GetDICOMInstanceUIDName(), instanceUID) # Invalid item ID for checking validity of a given ID (most functions return the invalid ID when item is not found) invalidItemID = slicer.vtkMRMLSubjectHierarchyNode.GetInvalidItemID()
Traverse children of a subject hierarchy item
children = vtk.vtkIdList() shNode.GetItemChildren(parent, children) # Add a third argument with value True for recursive query for i in range(children.GetNumberOfIds()): child = children.GetId(i) ...
Manipulate subject hierarchy item
Instead of node operations on the individual subject hierarchy nodes, item operations are performed on the one subject hierarchy node.
# Set item name
shNode.SetItemName(itemID, 'NewName')
# Set item parent (reparent)
shNode.SetItemParent(itemID, newParentItemID)
# Set visibility of data node associated to an item
shNode.SetItemDisplayVisibility(itemID, 1)
# Set visibility of whole branch
# Note: Folder-type items (fodler, subject, study, etc.) create their own display nodes when show/hiding from UI.
# The displayable managers use SH information to determine visibility of an item, so no need to show/hide individual leaf nodes any more.
# Once the folder display node is created, it can be shown hidden simply using shNode.SetItemDisplayVisibility
# From python, this is how to trigger creating a folder display node
pluginHandler = slicer.qSlicerSubjectHierarchyPluginHandler().instance()
folderPlugin = pluginHandler.pluginByName('Folder')
folderPlugin.setDisplayVisibility(folderItemID, 1)
Filter items in TreeView or ComboBox
Displayed items can be filtered using setAttributeFilter method. An example of the usage can be found in the unit test. Modified version here:
print(shTreeView.displayedItemCount()) # 5
shTreeView.setAttributeFilter('DICOM.Modality') # Nodes must have this attribute
print(shTreeView.displayedItemCount()) # 3
shTreeView.setAttributeFilter('DICOM.Modality','CT') # Have attribute and equal 'CT'
print(shTreeView.displayedItemCount()) # 1
shTreeView.removeAttributeFilter()
print(shTreeView.displayedItemCount()) # 5
Listen to subject hierarchy item events
The subject hierarchy node sends the node item id as calldata. Item IDs are vtkIdType, which are NOT vtkObjects. You need to use vtk.calldata_type(vtk.VTK_LONG) (otherwise the application crashes).
class MyListenerClass(VTKObservationMixin):
def __init__(self):
VTKObservationMixin.__init__(self)
shNode = slicer.vtkMRMLSubjectHierarchyNode.GetSubjectHierarchyNode(slicer.mrmlScene)
self.addObserver(shNode, shNode.SubjectHierarchyItemModifiedEvent, self.shItemModifiedEvent)
@vtk.calldata_type(vtk.VTK_LONG)
def shItemModifiedEvent(self, caller, eventId, callData):
print("SH Node modified")
print("SH item ID: {0}".format(callData))
If an object that supports view context menus (e.g. markups) is right-clicked in a slice or 3D view, it can offer custom actions. Due to internal limitations these plugins must be set up differently, as explained here. This example makes it easier to create such a plugin.
import vtk, qt, ctk, slicer
from slicer.ScriptedLoadableModule import *
from slicer.util import VTKObservationMixin
from SubjectHierarchyPlugins import AbstractScriptedSubjectHierarchyPlugin
class ViewContextMenu(ScriptedLoadableModule):
"""Uses ScriptedLoadableModule base class, available at:
https://github.com/Slicer/Slicer/blob/master/Base/Python/slicer/ScriptedLoadableModule.py
"""
def __init__(self, parent):
ScriptedLoadableModule.__init__(self, parent)
self.parent.title = "Markup Editor"
self.parent.categories = ["SlicerMorph", "Labs"]
self.parent.dependencies = []
self.parent.contributors = ["Steve Pieper (Isomics, Inc.)"]
self.parent.helpText = """
A tool to manipulate Markups using the Segment Editor as a geometry backend
"""
self.parent.helpText += self.getDefaultModuleDocumentationLink()
self.parent.acknowledgementText = """
This module was developed by Steve Pieper, Sara Rolfe and Murat Maga,
through a NSF ABI Development grant, "An Integrated Platform for Retrieval,
Visualization and Analysis of 3D Morphology From Digital Biological Collections"
(Award Numbers: 1759883 (Murat Maga), 1759637 (Adam Summers), 1759839 (Douglas Boyer)).
This file was originally developed by Jean-Christophe Fillion-Robin, Kitware Inc.,
Andras Lasso, PerkLab, and Steve Pieper, Isomics, Inc.
and was partially funded by NIH grant 3P41RR013218-12S1.
"""
#
# register subject hierarchy plugin once app is initialized
#
def onStartupCompleted():
import SubjectHierarchyPlugins
from ViewContextMenu import ViewContextMenuSubjectHierarchyPlugin
scriptedPlugin = slicer.qSlicerSubjectHierarchyScriptedPlugin(None)
scriptedPlugin.setPythonSource(ViewContextMenuSubjectHierarchyPlugin.filePath)
pluginHandler = slicer.qSlicerSubjectHierarchyPluginHandler.instance()
pluginHandler.registerPlugin(scriptedPlugin)
print('ViewContextMenuSubjectHierarchyPlugin loaded')
slicer.app.connect("startupCompleted()", onStartupCompleted)
class ViewContextMenuSubjectHierarchyPlugin(AbstractScriptedSubjectHierarchyPlugin):
# Necessary static member to be able to set python source to scripted subject hierarchy plugin
filePath = __file__
def __init__(self, scriptedPlugin):
self.viewAction = qt.QAction(f"CUSTOM VIEW ...", scriptedPlugin)
self.viewAction.objectName = 'CustomViewAction'
self.viewAction.connect("triggered()", self.onViewAction)
def onViewAction(self):
print(f"VIEW ACTION")
def viewContextMenuActions(self):
return [self.viewAction]
def showViewContextMenuActionsForItem(self, itemID, eventData=None):
pluginHandler = slicer.qSlicerSubjectHierarchyPluginHandler.instance()
pluginLogic = pluginHandler.pluginLogic()
menuActions = list(pluginLogic.availableViewMenuActionNames())
menuActions.append('CustomViewAction')
pluginLogic.setDisplayedViewMenuActionNames(menuActions)
self.viewAction.visible = True
When right-clicking certain types of nodes in the 2D/3D views, a subject hierarchy menu pops up. If menu actions need to be removed, a whitelist can be used to specify the ones that should show up.
pluginHandler = slicer.qSlicerSubjectHierarchyPluginHandler.instance()
pluginLogic = pluginHandler.pluginLogic()
menuActions = pluginLogic.availableViewMenuActionNames()
# Returns ('RenamePointAction', 'DeletePointAction', 'ToggleSelectPointAction', 'EditPropertiesAction')
newActions = ['RenamePointAction']
pluginLogic.setDisplayedViewMenuActionNames(newActions)
Plotting
Slicer plots displayed in view layout
Create histogram plot of a volume and show it embedded in the view layout. More information: https://www.slicer.org/wiki/Documentation/Nightly/Developers/Plots
Using slicer.util.plot utility function
# Get a volume from SampleData and compute its histogram import SampleData import numpy as np volumeNode = SampleData.SampleDataLogic().downloadMRHead() histogram = np.histogram(arrayFromVolume(volumeNode), bins=50) chartNode = slicer.util.plot(histogram, xColumnIndex = 1) chartNode.SetYAxisRangeAuto(False) chartNode.SetYAxisRange(0, 4e5)
Using MRML classes only
# Get a volume from SampleData
import SampleData
volumeNode = SampleData.SampleDataLogic().downloadMRHead()
# Compute histogram values
import numpy as np
histogram = np.histogram(arrayFromVolume(volumeNode), bins=50)
# Save results to a new table node
tableNode=slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass("vtkMRMLTableNode")
updateTableFromArray(tableNode, histogram)
tableNode.GetTable().GetColumn(0).SetName("Count")
tableNode.GetTable().GetColumn(1).SetName("Intensity")
# Create plot
plotSeriesNode = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass("vtkMRMLPlotSeriesNode", volumeNode.GetName() + ' histogram')
plotSeriesNode.SetAndObserveTableNodeID(tableNode.GetID())
plotSeriesNode.SetXColumnName("Intensity")
plotSeriesNode.SetYColumnName("Count")
plotSeriesNode.SetPlotType(plotSeriesNode.PlotTypeScatterBar)
plotSeriesNode.SetColor(0, 0.6, 1.0)
# Create chart and add plot
plotChartNode = slicer.mrmlScene.AddNewNodeByClass("vtkMRMLPlotChartNode")
plotChartNode.AddAndObservePlotSeriesNodeID(plotSeriesNode.GetID())
plotChartNode.YAxisRangeAutoOff()
plotChartNode.SetYAxisRange(0, 500000)
# Show plot in layout
slicer.modules.plots.logic().ShowChartInLayout(plotChartNode)
Using matplotlib
Matplotlib may be used from within Slicer, but the default Tk backend locks up and crashes Slicer. However, Matplotlib may still be used through other backends. More details can be found on the MatPlotLib pages.
Non-interactive plot
try:
import matplotlib
except ModuleNotFoundError:
pip_install('matplotlib')
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('Agg')
from pylab import *
t1 = arange(0.0, 5.0, 0.1)
t2 = arange(0.0, 5.0, 0.02)
t3 = arange(0.0, 2.0, 0.01)
subplot(211)
plot(t1, cos(2*pi*t1)*exp(-t1), 'bo', t2, cos(2*pi*t2)*exp(-t2), 'k')
grid(True)
title('A tale of 2 subplots')
ylabel('Damped')
subplot(212)
plot(t3, cos(2*pi*t3), 'r--')
grid(True)
xlabel('time (s)')
ylabel('Undamped')
savefig('MatplotlibExample.png')
# Static image view
pm = qt.QPixmap("MatplotlibExample.png")
imageWidget = qt.QLabel()
imageWidget.setPixmap(pm)
imageWidget.setScaledContents(True)
imageWidget.show()
Plot in Slicer Jupyter notebook
import JupyterNotebooksLib as slicernb
try:
import matplotlib
except ModuleNotFoundError:
pip_install('matplotlib')
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('Agg')
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def f(t):
s1 = np.cos(2*np.pi*t)
e1 = np.exp(-t)
return s1 * e1
t1 = np.arange(0.0, 5.0, 0.1)
t2 = np.arange(0.0, 5.0, 0.02)
t3 = np.arange(0.0, 2.0, 0.01)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 1, constrained_layout=True)
axs[0].plot(t1, f(t1), 'o', t2, f(t2), '-')
axs[0].set_title('subplot 1')
axs[0].set_xlabel('distance (m)')
axs[0].set_ylabel('Damped oscillation')
fig.suptitle('This is a somewhat long figure title', fontsize=16)
axs[1].plot(t3, np.cos(2*np.pi*t3), '--')
axs[1].set_xlabel('time (s)')
axs[1].set_title('subplot 2')
axs[1].set_ylabel('Undamped')
slicernb.MatplotlibDisplay(matplotlib.pyplot)
Interactive plot using wxWidgets GUI toolkit
try:
import matplotlib
import wx
except ModuleNotFoundError:
pip_install('matplotlib wxPython')
import matplotlib
# Get a volume from SampleData and compute its histogram
import SampleData
import numpy as np
volumeNode = SampleData.SampleDataLogic().downloadMRHead()
histogram = np.histogram(arrayFromVolume(volumeNode), bins=50)
# Set matplotlib to use WXAgg backend
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('WXAgg')
# Show an interactive plot
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(histogram[1][1:], histogram[0].astype(float))
ax.grid(True)
ax.set_ylim((0, 4e5))
plt.show(block=False)
Execute external applications
How to run external applications from Slicer.
Run process in default environment
When a process is launched from Slicer then by default Slicer's ITK, VTK, Qt, etc. libraries are used. If an external application has its own version of these libraries, then the application is expected to crash. To prevent crashing, the application must be run in the environment where Slicer started up (without all Slicer-specific library paths). This startup environment can be retrieved using slicer.util.startupEnvironment().
Example: run Python3 script from Slicer:
command_to_execute = ["/usr/bin/python3", "-c", "print('hola')"]
from subprocess import check_output
check_output(
command_to_execute,
env=slicer.util.startupEnvironment()
)
will output:
'hola\n'
On some systems, shell=True must be specified as well.
Manage extensions
Download and install extension
extensionName = 'SlicerIGT'
em = slicer.app.extensionsManagerModel()
if not em.isExtensionInstalled(extensionName):
extensionMetaData = em.retrieveExtensionMetadataByName(extensionName)
url = em.serverUrl().toString()+'/download/item/'+extensionMetaData['item_id']
extensionPackageFilename = slicer.app.temporaryPath+'/'+extensionMetaData['md5']
slicer.util.downloadFile(url, extensionPackageFilename)
em.installExtension(extensionPackageFilename)
slicer.util.restart()
Install a module directly from a git repository
This can be useful for sharing code in development without requiring a restart of Slicer.
https://gist.github.com/pieper/a9c0ba57de3833c9f5aea68247bda597