Modules:AtlasCreator
Return to Slicer 3.6 Documentation
AtlasCreator
General Information
Module Type & Category
Type: Built-in Loadable Module
Category: Registration
Authors, Collaborators & Contact
- Daniel Haehn, University of Pennsylvania
- Kilian Pohl, University of Pennsylvania
- Contact: Daniel Haehn (haehn@bwh.harvard.edu)
Module Description
The Atlas Creator module aligns images paired with segmentations to generate statistical atlases for several segmented structures.
Usage
This module supports different usage types:
- Simple Atlas Creation
- The advanced graphical user interface
- The command line interface
- External invocation using the Atlas Creator MRML Node
Use Cases, Examples
Input Data Requirements
The Atlas Creator expects input data to be structured the following way:
- In general each original image is accompanied by a manual segmentation.
- The images and the segmentations have to be in two different folders but have matching filenames.
- All images and segmentations have to be in Slicer-readable format.
- For Example:
- ./originals/case1.nrrd
- ./originals/case2.nrrd
- ./originals/case3.nrrd
- ./segmentations/case1.nrrd
- ./segmentations/case2.nrrd
- ./segmentations/case3.nrrd
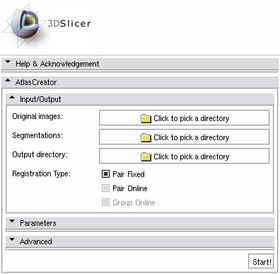
| HowTo: Simple Atlas Creation |
| The following steps perform a Pair Fixed Registration against an automatic chosen template for automatically detected structures. |
| 1. Select the directories containing the Original Images and the Segmentations in the Input/Output panel. |
| 2. Select an Output Directory in the Input/Output panel. It makes sense to create a new directory to use for the Output. |
| 3. Hit Start! |
| 4. After some wait (minutes or hours!, depending on the number of input cases), the generated atlases and the used template will be loaded into 3D Slicer. |
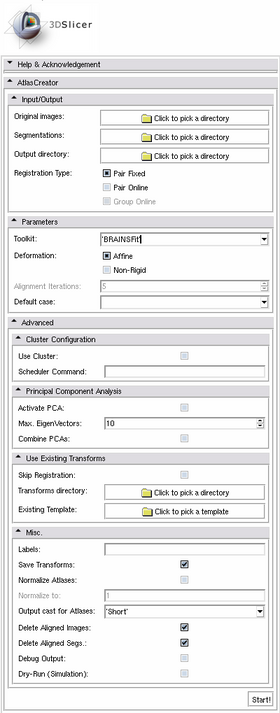
Quick Tour of Features and Use
A list panels in the interface, their features, what they mean, and how to use them. For instance:
|
The Command Line Interface
Beside using the graphical user interface in 3D Slicer, the Atlas Creator can be accessed using the commandline.
A help system is available:
$ cd Slicer3-release/lib/Slicer3/Modules/AtlasCreator/atlascreator.py
$ python atlascreator.py --help
AtlasCreator for 3D Slicer
Version v0.4
Usage:
-h, --help
Show this information.
-i, --images DIR
Directory containing original images.
-s, --segmentations DIR
Directory containing segmentations.
-o, --output DIR
Output directory.
--cmtk
Use the CMTK toolkit for registration and resampling, instead of BRAINSFit.
The CMTK4Slicer extensions have to be installed in order to use CMTK.
--skipRegistration
Skip the registration and use existing transforms.
The following arguments have to be specified if the registration is skipped:
--transforms DIR
Directory containing existing transforms.
--existingTemplate FILEPATH
Filepath to an existing template used for resampling only.
--dynamic
Use a dynamic template for registration based on means of images.
The following arguments have to be specified if dynamic registration is chosen:
-m, --meanIterations INT
Number of iterations to compute and register against a mean image.
--fixed
Use a fixed template for registration.
The following arguments have to be specified if fixed registration is chosen:
--template FILEPATH
Filepath to an image used as a template for fixed registration.
--ignoreTemplateSegmentation
If activated, the template's segmentation will not be added to the atlases.
-n, --non-rigid
Use Non-Rigid registration additionally.
-w, --writeTransforms
Write transforms to output directory.
--keepAligned
Keep the aligned images and segmentations.
-l, --labels STRING
List of labels to include for the atlases, f.e. "3 4 5 6 8 10".
DEFAULT: detect labels automatically
--normalize
Normalize Atlases to 0..1.
If activated, the output cast will be set to Double.
--normalizeTo INT
The upper value to normalize the atlases to.
DEFAULT: 1
--outputCast INT
Output cast for the atlases. Possible values:
0: Char
1: Unsigned Char
2: Double
3: Float
4: Int
5: Unsigned Int
6: Long
7: Unsigned Long
8: Short
9: Unsigned Short
DEFAULT: 8
-c, --cluster
Use the cluster mode.
The following arguments have to be specified if cluster mode is chosen:
--schedulerCommand EXECUTABLE
The executable to use as a scheduler in cluster mode, f.e. "qsub".
--pca
Perform PCA Analysis on top of Resampling.
--pcaMaxEigenVectors INT
The number of maximal Eigenvectors to use for model generation.
DEFAULT: 10
--pcaCombine
Combine the PCA output.
--slicer FILEPATH
Filepath to the 3D Slicer launcher including arguments, f.e. "/usr/bin/Slicer3 --tmp_dir /var/tmp".
DEFAULT: Find the 3D Slicer launcher automatically.
-d, --debug
Enable debug information.
--dryrun
Output executable commands instead of running the registration or resampling.
--examples
Show usage examples.
Developed by Daniel Haehn and Kilian Pohl, University of Pennsylvania. The research was funded by an ARRA supplement to NIH NCRR (P41 RR13218).
Thanks to everyone!
Examples:
$ python atlascreator.py --examples
AtlasCreator for 3D Slicer
Version v0.4alpha
Examples:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1. Run fixed registration with the testdata and normalize the atlases to 1:
python atlascreator.py -i TestData/originals/ -s TestData/segmentations/ -o /tmp/acout --fixed --template TestData/originals/case62.nrrd -w -l "3 4 5 6 7 8 9" --normalize
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2. Run fixed registration with the testdata and use CMTK instead of BRAINSFit and label auto-detection:
python atlascreator.py -i TestData/originals/ -s TestData/segmentations/ -o /tmp/acout --fixed --template TestData/originals/case62.nrrd -w --cmtk
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
3. Run dynamic registration with the testdata and normalize the atlases to 0..100:
python atlascreator.py -i TestData/originals/ -s TestData/segmentations/ -o /tmp/acout --dynamic --meanIterations 5 -w -l "3 4 5 6 7 8 9" --normalize --normalizeTo 100
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
4. Run dynamic registration with the testdata on a cluster (scheduler command "qsub -l centos5"):
python atlascreator.py -i TestData/originals/ -s TestData/segmentations/ -o /tmp/acout --dynamic --meanIterations 5 -w -l "3 4 5 6 7 8 9" --normalize --cluster --schedulerCommand "qsub -l centos5"
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
5. Use existing registrations and just re-sample
python atlascreator.py --skipRegistration --transforms /tmp/acout --existingTemplate TestData/segmentations/case62.nrrd -s TestData/segmentations/ -o /tmp/acout -l "3 4 5 6 7 8 9" --normalize --outputCast 3
Development
Notes from the Developer(s)
Dependencies
Tests
On the Dashboard, these tests verify that the module is working on various platforms:
- MyModuleTest1 MyModuleTest1.cxx
- MyModuleTest2 MyModuleTest2.cxx
Known bugs
Usability issues
Source code & documentation
Links to the module's source code:
Source code:
Doxygen documentation: